


Dravyaguna – Ayurveda medical science
Ayurveda is the branch of science that deals with the Guna and Karma of dravyas, which are Ayushya and Anayushya.
Dravyaguna has been defined by Acharya P.V. Sharma as the branch of science, which deals with Namarupa, Gunakarma and Prayoga of Dravyas.
Lakshana of Saptapadartha:
Example: Vamana, Virechana, Langhana, Brahmana etc.
Introduction:
All dravyas (Kaarya dravyas) mentioned in Dravyaguna Adhikara are Paanchbhoutik in nature. The Dravyas contain Prithivi etc Mahabhutas in different proportions.
Nirukti:
Dravya is defined as that which possesses Guna (Rasa-Guna-Virya-Vipaka-Prabhva) and Karma (Samyoga-Vibhaga etc ) in Samavaya sambandha (Inherent relation).
Other author’s have given similar definition of Dravya as:
Panchbhoutikatva of Dravya:
The combination of Prithvi, Ap, Tejas, Vayu and Akasha mahabhuta is responsible for the formation of Dravya.
Even though each Mahabhuta has different Guna, they combine to form a dravya. Just like vatadi doshas (each having different guna) combine to give rise to vyadhi, Shukra-Shonita combine to form Garbha (Shukra is Soumya and Shonita is Agneya). In the same way, the Panchamahabhutas having different gunas combine to form Dravya.
All Karya dravyas are made of Panchamahabhutas.
The role played by each of the Mahabhuta is explained as follows;
a. Pruthvi is the Adhisthaan
Prithvi is the Adhisthaan or the Upadana karana, just like Mrut (Mud) is for the formation of Ghata (Pot).
b. Ambu Yoni:
The word Yoni is derived from:
c. Agni-Pavana-Nabhasa-Samavayata:
By the Samavaya sambandha (Inherent relation) of Agni – Pavan- Akasha, further Nirvrutti and Vishesha occurs.
Agni-Pavana-Akasha is responsible for the Nirvrutti (the proper swaroopa utpatti of the dravya) and Vishesha (differentiation as Parthiva, Aapya, and so on based on predominance of the mahabhutas).
Specific Roles of Each:
i. Agni is responsible for Kathinya (Hardness), Paaka (Proper formation) and Roopa utpatti (Appearance).
ii. Vaayu helps in developing Kathinya (Hardness), Urdhva-Adha-Tiryak vistara ( giving di mensions) and Kriya utpatti ( movement).
iii. Akasha helps in providing Avakasha ( Space) among the components of the dravya.
Thus, the Nishpatti/Utpatti of all Ahara and Oushadha dravyas occurs from the Panchamahabhutas.
(Medicinal properties of Dravya)
The human body is made from Panchamahabhutas. All dravyas are also Panchbhoutik in nature. Therefore, Dravya can be used to control the Sthana, Vridhi and Kshaya of Doshas.
Further explaining how the dravyas acts on the Tridoshas, Sushruta says;
Thek Rasa, Guna, Virya, Vipaka of the dravya are responsible for the Kshaya, Vrudhi or Samyata of Dosha, Dhatu and Mala.
All dravyas present around us are having medicinal properties and it depends on the yukti of the physician using it. As Acharya Charaka states that, even a poison can be an effective medicine when purified and used in the right dose. Similarly an effective Medicine May become a posion when not used appropriately.
Drug being medicinal/non- medicinal depends on Yukti i.e Upaya (Samskara etc) and Artha/ Prayojana ( Mode of administration).
Upaaya:
By proper Samskara and its use in appropriate Desha-Kaala etc, even poisonous drugs can act as medicine.
Visha is Apathyakari, but even it can act as pathya with proper upaya as told in udara chikitsa.
Prayojana:
Truna, Pamsu etc dravyas are non-medicinal and cannot be Bheshaja, but they can be used for the purpose of Svedana etc external procedures.
Therefore, it is proved that no dravya is anoushadhibhuta. They can be used either internally or externally with proper samskara, samyoga etc by considering the matra, kala, vaya, anupana and so on.
Dravya Pradhanyata:
Dravya is Pradhana among the Rasa Panchaka as Dravya is the Ashraya for the others.
It is observed that Vipaka is dependent on Virya, Virya cannot exist without Rasa and Rasa cannot exist without dravya. Thus, each avayava (component) is interdependent and therefore it is claimed that Dravya is superior to all other avayavas.
In this context, Chakrapani further clarifies that a Sheeta virya drug, which is composed of Jala and Pruthvi, will give rise to Madhura/Guru vipaka. Similarly, an Ushna virya dravya is made up of Agni and Akasha will undergo Katu/Laghu vipaka. Thus dravya is acting as a medium for the existence of virya, vipaka etc.
Hence, dravya is pradhana.
The genesis of rasa, guna etc occurs simultaneously with dravya but not separately. This relation is compared with Deha (Body) and Dehina (Atma / Soul). Even the eight types of virya are dependent upon the dravyas. Rasa is one of the sartha guna, and gunas are devoid of any activity independently.
Vipaka also depends upon dravya but not on rasas alone, hence dravya is explained with importance.
Sushruta and Nagarjuna have given the following explanations and examples for the Dravya Pradhanyata.
(i) Vyavasthitatva:
The Dravya is vyavasthita ( Stable ) in nature, but not rasadi. For example, taste of unripe mango will keep on changing till it ripens, but the fruit is known as mango fruit till the end and not something else.
Example: The fruit of Mango is Kashaya in rasa when it is unripe, and when it is halfripe it turns Amla and the fully ripened mango is Madhura. Therefore, there is a transformation in the rasa of mango from the unripe stage to the fully ripe stage. Though the rasa changes in different stage, the fruit will remain “Mango” itself and will not transform into something else like Amrataka or Koshamra.
Nagarjuna has used the word “Vyavasthaanat” for the same:
Dravya is vyavasthita unlike gunas. Example: The green colour of Black Jamoon (Jambava) fruit when it is very tender will turn into brinjal colour after sometime and finally become black like Anjana when it is fully ripe. Thus, the colour etc factors changes but the fruit remains the same.
(ii) Nityatva:
Dravya is Nitya, whereas the Rasadi gunas are Anitya
When the Dravya is made into Kalka, Svarasa, Kwatha and so on, the Rasa, Gandha etc of the Dravya may be altered, but the Dravya remains the same, i.e. it will be still called as Kalka or Svarasa of the given material. The rasa, gunas that change are Anitya, whereas Dravya is Nitya. Therefore, Dravya is pradhana.
(iii) Svajati Avasthanatva:
A dravya belonging to one jati (Category) will not change into another i.e. a Parthiva dravya even after Parinama (Transformation) remains Parthiva, Aapya remains Aapya and so on.
Example:
Due to parinama, the rasa of milk changes from madhura to amla and the form changes from Ksheera to dadhi, but the jati i.e. the Aapyatva remains the same. Therefore, even though the rasa, guna change the dravya maintains its jati and hence dravya is pradhana.
(iv) Panchendriya Grahanat:
Dravya can be perceived by all the indriyas unlike the rasadi.
The Shabda, Sparsha, Roopa, Rasa and Gandha gyana of a dravya is possible. Each dravya has specific sound. Parthiva dravya makes solid sound like kata-kat, Apya dravya make Khalkhala shabda, Taijasa dravy makes tat-tat shabda, Akasha and Vayu are amurtha hence they are understood by Anumana.
Thus, Dravya can be perceived by all the indriyas.
Haranachandra explains this by Deergha shashkuli nyaya:
Taking example of Shashkuli, Shashkuli can be seen with the eyes, it can be touched to know its texture, the smell of it can be perceived through nose, its taste can be appreciated by eating and the sound can be heard while eating. Thus, it can be accessed through all the indriyas.
* Badanta Nagarjuna has described it as “Sarvendriyopalabdhi”.
Dravya is sarva indriya grahya, whereas rasadi are ekendriya grahya. Rasa is percieved through rasanendriya, Vipaka, Virya through adhivasa and karma is seen through Chakshurindriya.
The commentator explains how Shabda, Sparsha, Rupa, rasa and Gandha gyana of a dravya is obtained with the example of Yasthimadhu as dravya.
(v) Aashrayatva:
Only dravya can act as Ashraya for rasadi which are present in the dravya in samavayi sambandha.
The Ashrita rasa, guna etc are paratantra and apradhana. Dravya being the ashraya is pradhana.
(vi) Arambhasamarthya:
Initiation of a specific pharmacological action is possible only by using the dravya. One cannot pick rasadi gunas and start the treatment.
Example: Vidarigandhadi dravyas can be made into various kalpanas like churna and so on and used in treatment, but it is not possible to do so with individual rasa, guna etc. Therefore, dravya is pradhana.
(vii) Shastra Pramanyat:
All Shastras have considered dravya as pradhana. Different vargas, ganas are made based on the dravya and not rasadi. Even though we have the madhura skandha and so on, they are nothing but the classification of dravya based on rasa.
Shastras have said that whatever gunas/qualities are present in dravya, the same is present in the Shareera and hence dravyas of required qualities can be used to manage the increase or decrease of any qualities in the shareera. Therefore dravya is very important.
(viii) Kramapekshitatva:
The properties depend upon the state of the dravya.
The dravya and rasadi are interdependent, as Sushruta says the genesis of dravya and rasa occurs simultaneously. So, the rasadi gunas also continuously change with the change in the state of the dravya.
Example:
When the drug is tender then the properties will remain incomplete, and when the drug matures all the properties will be present in it.
(ix) Ekadesha Sadyatva:
Dravya can be used in treatment by taking a part of it, but rasadi cannot be used because of Niravayavatvat.
Example: The latex of Snuhi can be used in many diseases but its taste cannot be used seperately. Therefore dravya is pradhana.
The extra points described by Rasa vaisheshika are as follows:
(x) Vikalpasamarthya:
Dravya may be converted into different forms like Churna, Kalka, Kashaya etc, but rasadi cannot be utilised for the same purpose.
(xi) Pratighatasamarthya:
Pratighata means avarana i.e to occupy some space. Dravya being a murtha bhava occupies a specified space, which cannot be replaced by anything else, where rasa, guna etc are amurta and hence they are not capable of causing pratighata/avarana.
(xii) Taratamayoganupalabdhi
Tara-Tama grading is seen in rasa, guna, karma like
In dravya such Tara-tama grading is not possible.
Therefore, Dravya is pradhana because of tara-tama abhava.
Need for Classification of Dravyas:
Classification in Vedic era:
Based on Karya-Karana:
Based on Karya-Karana, they can be classified as:
a. Karana dravya: Panchamahabhuta, Atma, Manas, Kaala and Disha.
b. Kaarya dravya: Infinite. Example: Ghata, Pata, Masha,Mudga, Guduchi etc.
Based on Existence/non-existence of Chetana they are Classified as:
(i) Chetana: which are having chetana (Aatma).eg: organisms, trees etc.
Characteristics of chetana dravyas:
Classification of Chetana dravyas:-
● Antaschetana: those in which the feelings of pleasure or pain are not explicit.
Trees, shrubs, creepers etc are predominant in tamo guna, and hence the characters of Chetana dravya cannot be explicitly seen in them; however, they have sense of pleasure or pain and have all the characteristics of Chetana dravya and presence of special sense can be demonstrated in them as follows:
● Bahirantashchetana: those who can express their feelings explicitly. eg: birds, animals, human beings.
(ii) Achetana/Nirendriya/Anashana: Inanimate substances. Example: Suvarna etc. Dhatus.
Utpatti/Nishpatti Bheda:
(i) Parthiva Dravya:
| Indriyartha | Rasa | Guna | Karma | Vipaka |
| Gandha | Madhura Slightly Kashaya | Guru, Khara, Kathina, Manda, Sthira, Vishada, Sandra, Sthoola. | Upachaya, Sanghata, Gourava, Sthairya, Bala, Adhogamana. | Guru |
(ii) Aapya Dravya:
| Indriyartha | Rasa | Guna | Karma | Vipaka |
| Rasa | Madhura Slightly Kashaya Lavana | Drava, Snigdha, Sheeta, Manda, Mrudu, Sandra, Pichila, Stimita, Sara | Upachaya, Sanghata, Gourava, Sthairya, Bala, Adhogamana. | Guru |
(iii) Taljasa Dravya:
| Indriyartha | Rasa | Guna | Karma | Vipaka |
| Roopa | Katu and slightly Amla lavana | Ushna, Tikshna, Sukshma, Laghu, ruksha, vishada, khara. | Dahana, Pachana ,Prabha, Varna, Prakashana, Daruna, Taapana, Urdwagamana. | Laghu |
(iv) Vayavya Dravya:
| Indriyartha | Rasa | Guna | Karma | Vipaka |
| Sparsha | Kashaya Slightly tikta | Laghu, Sheeta, Ruksha, Khara, Vishada, Vikasi, Vyavayi | Virukshana, Vicharana, Glapana, Vaishadyakara, Laghavakara, Karshana, Ashukari | Laghu |
(v) Akashiya Dravya:
| Indriyartha | Rasa | Guna | Karma | Vipaka |
| Shabda | Avyakta | Mrudu, Laghu, Shlakshna, Sukshma, Vyavayi, Vishada, Vivikta | Mardava, Soushirya, Laghava, Vivarana | Laghu |
Yoni Bheda:
(i) Jaangama:
That which is derived from Animal source is Jangama. Eg: Kasturi, Gorochana
Jangama dravyas can be again classified as:
(a) Jarayuja:
Animals which have placental birth like man, tiger, lion, cow etc. are Jarayuja.
(b) Andaja:
Birds, reptiles etc, which have their birth through eggs. Ex: Crow, Snakes, Lizards, Fish etc.
(c) Svedaja:
Creatures, which have their birth in sveda (dirty water etc), are svedaja. Example: Flies, mosquitos, lice, ants and worms found in faeces.
(d) Udbhija:
Smaller creatures and animals, which are born in the mud or clay. Ex: Frogs etc.
●Dalhana has quoted some exceptions:
(ii) Oudbhida:
Those, which grow by piercing through the soil, are known as Oudbhida dravyas.
Oudbhida dravyas are classified as:
a. Vanaspati:
Those plants, which bear fruits without flowers, are vanaspati. Ex: Vata, Udumbara.
b. Veerudha:
Those plants, which twine, crawl or climb, are known as veerudha.
Veerudha is sub-divided into:
c. Vanaspatya:
Those plants, which possess both the flowers and fruits, are known as Vanaspatya or Vruksha or Sapushpa. Example: Aamra, Jambu etc.
d. Oushadhi:
Those plants, that die after yielding fruits or after harvest. Example: Paddy, Pulses, wheat, maize etc.
iii. Parthiva/Bhouma:
Those substances that are available beneath the surface of earth are known as Parthiva. Example: Mineral ores, Metals, Salts, Alkalies etc.
Prayoga Bheda:
Based on the utility, dravya are classified as:
i. Oushadha Dravya:
Example: Haritaki, Amalaki, Chitraka which are used for their therapeutic effects based on their potency.
ii. Aahara Dravya:
Example: Shaali, Mudga, Taila are used as diet based upon their primary metabolites viz carbohydrates, proteins and fats.
Rasa Bheda:
Virya Bheda: Based on Virya, Dravya is of two Types
Dosha Karma Bheda: Based on Dosha Karma, they are Divided into three i.e. Shamana, Kopana and Svasthahita.
i. Shamana:
ii. Kopana:
iii. Svasthahita: Raktashaali, Mudga, Antariksha Jala etc.
Samsthanika Karma Bheda: They can be Classified as
1. Samshaman: Example:- Guduchi
ii. Samshodhana: they can be classified as
Vipaka Bheda:
Classification in Samhitas and Nighantus
I. Classification of Aahara dravyas:
A. Charaka has classified the aahara dravyas in 12 vargas;
The Ahita and Hita ahara dravyas mentioned by Charaka are as follows (Ch.su 25/39)
| S.N. | Varga | Hita Tama | Ahita Tama |
| 1. | Shukadhanya | Raktashaali | Yavaka |
| 2. | Shamidhanya | Mudga | Masha |
| 3. | Udaka | Antariksha | Varshanadeya |
| 4. | Lavana | Saindhava | Oushara |
| 5. | Shaaka | Jivanti | Sarshapa |
| 6. | Mrugamamsa | Eneya | Gomamsa |
| 7. | Pakshi | Lava | Kaanakapota |
| 8. | Bileshaya | Godha | Manduka |
| 9. | Matsya | Rohita | Chilichima |
| 10. | Ghruta | Goghruta | Avika ghruta |
| 11. | Dugdha | Godugdha | Avi kshira |
| 12. | Sthavara sneha | Tila taila | Kusumbha taila |
| 13. | Anupa mruga vasa | Varaha vasa | Mahisha vasa |
| 14. | Matsya vasa | Chuluki vasa | Kumbhira vasa |
| 15. | Jalachara vihanga vasa | Pakahamsa vasa | Kaakamadguvasa |
| 16. | Vishkira shakuni vasa | Kukkuta vasa | Chataka vasa |
| 17. | Shaakhada meda | Ajameda | Hastimeda |
| 18. | Kanda | Shrungavera | Aaluka |
| 19. | Phala | Mrudveeka | Likucha |
| 20. | Ikshu vikara | Sharkara | Phanita |
B. Sushruta has Classified Aahara Dravyas into Drava Dravya and Anna Dravya.
1. Drava Dravya are Classified as follows:
| 1. Jala Varga | 2. Kshira varga |
| 3. Dadhi varga | 4. Takra varga |
| 5. Ghruta varga | 6. Taila varga |
| 7. Madhu varga | 8. Ikshu varga |
| 9. Madya varga | 10. Mutra varga |
2. Anna Dravya is Classified as follows:
| 1. Shaali varga | 2. Kudhanya |
| 3. Vaidala | 4. Mamsa (8 upavargas) |
| 5.Phala | 6. Shaaka |
| 7. Pushpa | 8. Kanda |
| 9. Lavana | 10. Kshara |
| 11. Dhatu | 12. Ratna |
| 13. Krutanna |
II. Classification of Oushadha Vargas:
Charaka has classified 500 medicinal plants under 50 vargas each having 10 drugs in it. (Ch. Su 4). The detailed description of these vargas are done in a separate chapter.
Apart from the mahakashayas, Charaka has classified the Samshodhana dravyas as follows:
Sushruta has classified the medicinal plants in 37 vargas. (Su.su 38/3). The vargas are classified based on karma but they are named based on the first drug in the group.
| S.N. | Varga | Drugs | Karma | Vipaka |
| 1. | Vidarigandhadi | Shalaparni, Vidari, Nagabala, Atibala, Gokshura, Prishniparni, Shatavari, Sariva, Krishnasariva, Jivaka, Rushabhaka, Mashaparni, Mudgaparni, Bruhati dvaya, Punarnava, Eranda, Hamsapadi, Vruschikali, Kapikachu. | Pittavatahara, Bruhmana, Angamarda-prashamana, Shvasahara, Kasahara. | Shosha, Gulma, Angamarda, Urdhvashvasa, Kasa, Prameha, Kustha, Jvara, Chardi, Kandu, Vrana, Visha. |
| 2. | Aragwadhadi | Aragwadha, Madanaphala, Gopaghonta, Kutaja, Patha, Vikankata, Patala, Murva, Indrayava, Saptaparna, Nimba, Pita & Nila saireyaka, Guduchi, Chitraka, Sharangestha, Karanja, Putika, Patola, Kiratatikta. | Kaphaghna, Vishaghna,Kusthaghna, Jvaraghna, Kandughna, Chardinigrahana, Vranashodhana. | Prameha, Kustha, Jvara,Chardi, Kandu, Vrana, Visha. |
| 3. | Saalasaaradi | Salasara, Sarja, Khadira, Swetakhadira, Tindukabheda, Kramuka, Bhurja, Meshashringa, Tinisha, Chandana, Raktachandana, Shimshipa, Shirisha, Asana, Dhava, Arjuna, Tala, Shaka, Naktamala, Putikaranja, Ashvakarna, Agaru, Pitachandana. | Kaphaghna, Medohara, Kusthaghna | Kustha,Prameha,pandu, Medoroga |
| 4. | Varunadi | Varuna, Artgaka, Shobhanjana, Madhushigru, Tarkari, Meshashrungi, Pootika, Naktamala, Morata, Agnimantha, Nila & Pita Saireyaka, Bimbi, Vasuka, Apamarga, Chitraka, Shatavari, Bilva, Ajashringi, Darbha, Bruhati dvaya. | Kaphaghna, Medohara | Shirashula, Gulma,Abhyantara vidradhi |
| 5. | Viratarvadi | Virataru, Pita & Nila Saireyaka, Darbha, Bandaka, Gundra, Nala, Kusha, Kasha, Pashanabheda, Agnimantha, Morata, Vasuka, Apamarga, Shyonaka, Shitivara, Shitivarabheda, Suvarchala, Gokshura. | Vatahara, Mutrajanana, Ashmari bhedana | Vatavyadhi, Ashmarisharkara,Mutrakruchra, Mutraghata. |
| 6. | Rodhradi | Rodhra, Savara lodhra, Palasha, Shyonaka, Ashoka, Phanji, Katphala, Elvaluka, Shallaki, Jingini, Kadamba, Shala, Kadali. | Kaphaghna, Medohara,Varnya,Vishaghna,Stambhana. | Yonivikara, Visha, Medoroga. |
| 7. | Arkadi | Arka, Alarka, Karanja, Putika, Nagadanti, Apamarga, Bharngi, Rasna, Kalihari, Shveta, Mahashveta, Vruschikali, Jyotishmati, Ingudi. | Kaphaghna,Medohara,Vishaghna, Vranashodhana,Kushaghna,krimighna | Krimi, Kusha, Vrana, Medoroga, Visha |
| 8. | Surasadi | Krishna & Sweta tulsi, Phanignyaka, Arjaka, Bhustruna, Gandhatruna, Rajika, Varvari, Kasamarda, Chikkika, Khara-pushpa, Vidanga, Katphala, Surasi, Nirgundi, Mundi, Mushakarni, Phanji, Kakajangha,Kakamachi, Vishamushti. | Kaphaghna, Krimighna, Shwasahara, Kasahara, Vranashodhana | Krimi, Pratishyaya, Aruchi, Swasa, Kasa, Vrana. |
| 9. | Mushkakadi | Mushkaka, Palasha, Dhava, Chitraka, Madana, Kutaja, Shimshipa, Snuhi, Triphala. | Medohara,Shukrashodhana,Ashmaribhedana | Medoroga, Shukravikara, Ashmari, Prameha, Arsha, Pandu. |
| 10. | Pippalyadi | Pippali, Pippalimoola, Chavya, Chitraka, Shunthi, Maricha, Gajapippali, Harenuka, Ela, Ajamoda, Indrayava, Patha, Jeeraka, Sarshapa, Mahanimbaphala, Hingu, Bharangi, Madhurasa, Ativisha, Vacha, Vidanga, Katuki. | Kaphaghna, Vatahara,Deepana, Shoolaprashamana, Aamapachana. | Pratishyaya, Aruchi, Gulma, Shoola, Amadosha, Vatakapharoga. |
| 11. | Eladi | Ela, Tagara, Kustha, Mamsi, Rohisha, Tvakpatra, Nagapushpa, Priyangu, Harenuka, Vyaghranakha, Shukti chanda, Sthouneyaka, Shriveshtaka, Tvak, Choraka, Elvaluka, Guggulu, Sarjarasa, Shilarasa, Kunduru, Agaru, Sprukka, Usheera, Deavadru, Kesar, Punnagakesar. | Vatashleshmahara, Vishaghna, Varnya, Kandughna. | Kandu, Pidaka, Kotha, Visha. |
| 12. | Vachadi | Vacha, Musta, Ativisha, Haritaki, Devadaru, Nagakesara. | Stanyashodhana Doshapachana | Stanyavikara Aamatisara |
| 13. | Haridradi | Haridra, Daruharidra, Prushniparni, Indrayava, Yasthimadhu. | ||
| 14. | Shyamadi | Shyama, Mahashyamna, Trivrut, Danti, Shankhini, Tilvaka, Kampillaka, Mahanimba, Kramuka, Dravanti, Indrayana, Aragwadha, Karanja, Putikaranja, Guduchi, Saptala, Vrudhadarukabheda, Snuhi, Svarnakshiri. | Bhedana, Anulomana,Vishaghna | Gulma, Aanaha, Udara, Udavarta, Visha. |
| 15. | Bruhatyadi | Bruhati, Kantakari, Indrayava, Patha, Madhuka. | Tridoshahara, Pachana, Mutrajanana | Aruchi, Hrullasa, Mutrakrichra. |
| 16. | Patoladi | Patola, Chandan, Raktachandana, Murva, Guduchi, Patha, Katuki. | Kaphapitta shaman, Jvarahara, Vranya. | Aruchi, Jvara, Vrana, Chardi, Kandu, Visha |
| 17. | Kakolyadi | Kakoli, Kshirakakoli, Jeevaka, Rishabhaka, Mudgaparni, Mashaparni, Meda, Mahameda, Guduchi, Karkatashringi, Vamshalochana, Padmaka, Prapoundarika, Ridhi, Vridhi, Mrudvika, Jivanti, Madhuka. | Vatapittahara, Raktashamaka, Jeevaniya, Bruhmana, Vrushya, Stanyajanana, Kaphakaraka. | Dourbalya, Karshya, Stanyavikara, Raktapitta |
| 18. | Ushakadi | Ushaka (Kshara vishesha), Saindhava, Shilajatu, Kasisa dvaya, Hingu, Tutha. | Kaphamedohara, Mutrajanana | Medoroga, Ashmari, Mutrakrichra, Gulma |
| 19. | Sarivadi | Sariva, Madhuka, Chandana, Raktachandana, Padmaka, Gambhariphala, Madhookapushpa, Usheera. | Raktapittasha mana Trushnahara Dahashamana Jvaraghna | Raktapitta Trushna Daha Pittajvara |
| 20. | Anjanadi | Souveeranjana, Rasanjana, Nagakesara, Priyangu, Nilotpala, Mamsi, Padmakesara, Madhuka. | Raktapittahara Vishaghna Dahaprashamana | Raktapitta Visha Daaha |
| 21. | Parushakadi | Parushaka, Draksha, Katphala, Dadima, Rajadana, Nirmaliphala, Shakaphala, Triphala. | Vatahara, Hrudya Trushnahara, Rochana, Mutrajanana | Mutrakrichra Hrudroga Trushna Aruchi |
| 22. | Priyangvadi | Priyangu, Lajjalu, Dhataki, Punnaga, Nagakesara, Chandana, Raktachandan, Mocharasa, Rasanjana, Kumbhika, Srotanjana, Padmakesara, Manjistha, Dhanvayasa. | Pittahara, Sthambhana, Sandhaniya, Vranaropana. | Pakvatisara Vrana Raktapitta |
| 23. | Ambasthadi | Ambastha, Dhatakipushpa, Lajjalu, Aralu, Madhuka, Bilva, Savara lodhra, Palasha, Nandivruksha, Padmakesara. | ||
| 24. | Nyagrodhadi | Nyagrodha, Udumbara, Ashwatha, Plaksha, Madhooka, Amrataka, Arjuna, Amra,Koshamra, Chorakapatra, Jambudvaya, Priyala, Madhuka, Katphala, Vetasa, Kadamba, Badari, Tinduka, Shallaki, Rodhra, Savara lodhra, Bhallataka, Palasha, Nandivruksha. | Sangrahi, Sandhaniya, Vranya ,Raktapittaprash amana, Daahap rashamana, Medohara. | Vrana, Asthibhagna. Raktapitta, Daaha, Prameha, Yonivikara. |
| 25. | Guduchyadi | Guduchi, Nimba, Dhanyaka, Chandana, Padmaka. | Jvarahara, Deepana, Trushnahara, Dahashamana | Hrullasa, Aruchi, Chardi, Trishna, Daha. |
| 26. | Utpaladi | Nilotpala, Raktotpala, Swetotpala, Sougandhika, Kuvalaya, Pundarika and Madhuka. | Dahaprashamana, Raktapittahara, Trushnahara, Vishaghna, Hrudya. | Daaha, Raktapitta, Trushna, Visha, Chardi, Hrudroga, Murcha. |
| 27. | Mustadi | Musta, Haridra, Daruharidra, Haritaki, Amalaki, Vibhitaki, Kustha, Sweta Vacha, Vacha, Patha, Katuki, Sharangestha, Ativisha, Ela, Bhallataka, Chitraka. | Kaphahara, Stanyashodhana, Pachana. | Yonivikara Stanyadosha Aamadosha |
| 28. | Triphala | Haritaki, Amalaki, Vibhitaki. | Kaphapittahara Kusthaghna, Deepana, Chakshushya, Vishamajvarahara | Prameha, Kustha, Netraroga, Agnimandya, Vishmajvara |
| 29. | Trikatu | Pippali, Maricha, Shunthi. | Kaphahara, Medohara, Kusthaghna, Deepana | Prameha, Kustha, Tvakroga, Gulma, Peenasa, Mandagni. |
| 30. | Amalakyadi | Amalaki, Haritaki, Pippali, Chitraka. | Kaphaghna, Rochana, Jvarahara, Deepana, Vrushya, Chakshushya. | Jvara, Netraroga, Aruchi, Udaravikara. |
| 31. | Trapvadi | Vanga, Naga, Tamra, Rajata, Suvarna, Loha, Mandura. | Krimighna, Vishaghna, Hrudya. | Garadosha, Krimi, Trushna, Visha, Hrudroga, Pandu, Prameha. |
| 32. | Lakshadi | Laksha, Aragwadha, Kutaja, Karavira, Katphala, Haridra, Daruharidra, Nimba, Saptaparna, Jati, Trayamana. | Kashaya- TiktaMadhura, Kapha-Pittahara, Kusthaghna, Krimighna, Vranashodhana. | Kustha, Krimi, Dusthavrana. |
| 33. | Laghu panchamoola | Gokshura, Bruhati, Kantakari, Prishniparni, Shalaparni. | Kashaya-Tikta Madhura, VatoPittahara, Bruhmana, Balya | Shvasa, Tridoshahara, Aamadosha, Jvara. |
| 34. | Bruhat panchamoola | Bilva, Agnimantha, Shyonaka, Patala, Gambhari. | Tikta-Madhura, Katu, Kaphavatahara, Deepana. | |
| 35. | Valli panchamoola | Vidari, Sariva, Manjistha, Guduchi, Meshashrungi. | Kaphaghna, Raktapittashamana, Shukradosha Shothahara, | Raktapitta, Shotha, Prameha, Shukashodhana |
| 36. | Kantaka panchamoola | Karamarda, Gokshura, Saireyaka, Shatavari, Himsra. | ||
| 37. | Truna panchamoola | Kusha, Kasa, Nala, Darbha, Kandekshu. | Raktapittashamana, , Mutrajanana. | Raktapitta Mutrakrichra. |
Charaka and Sushruta have classified the medicinal plants based on karma, while Charaka has named them based on karma, Sushruta has named the ganas based on the first drug in it.
The details of the Vargas of Charaka which can be compared with that of Sushrutas gana is presented in the following table;
| S.N. | Charakokta Varga | Sushruta Gana |
| 1. | Jeevaniya | Kakolyadi |
| 2. | Bruhmaniya | Vidarigandhadi |
| 3. | Lekhaniya | Mustadi |
| 4. | Bhedaniya | Shyamadi |
| 5. | Sandhaniya | Ambasthadi, Priyangvadi |
| 6. | Deepaniya | Pippalyadi |
| 7. | Balya | Laghupanchamoola |
| 8. | Varnya | Eladi |
| 9. | Hrudya | Parushakadi |
| 10. | Truptighna | Patoladi |
| 11. | Arshoghna | Mushkakadi |
| 12. | Kusthaghna | Aragwadhadi, Salasaradi, Arkadi, Lakshadi. |
| 13. | Kandughna | Eladi, Aragwadhadi |
| 14. | Krimighna | Surasadi, Lakshadi |
| 15. | Vishaghna | Rodhradi, Aragwadadi, Arkadi, Anjanadi. |
| 16. | Stanyajanana | Kakolyadi |
| 17. | Stanyashodhana | Mustadi, Vachadi, Haridradi. |
| 18. | Virechanopaga | Parushakadi |
| 19. | Chardinigrahana | Nyagrodhadi |
| 20. | Trushnanigrahana | Guduchyadi, Utpaladi, Sarivadi, Parushakadi. |
| 21. | Hikkanigrahana | Bruhatyadi, Vidarigandhadi |
| 22. | Pureeshasangrahaniya | Rodhradi, Priyangvadi, Ambasthadi . |
| 23. | Mutrasangrahaniya | Nyagrodhadi, Salasaradi. |
| 24. | Mutravirechaniya | Trunapanchamoola, Viratarvadi |
| 25. | Mutravirajaniya | Utpaladi |
| 26. | Kasahara | Vidarigandhadi |
| 27. | Shwasahara | Pippalyadi, Surasadi |
| 28. | Shothahara | Dashamoola |
| 29. | Jvarahara | Sarivadi, Patoladi, Amalakyadi. |
| 30. | Shramahara | Parushakadi |
| 31. | Dahaprashamana | Sarivadi, Anjanadi, Utpaladi. |
| 32. | Sheetaprashamana | Pippalyadi, Surasadi |
| 33. | Udardaprashamana | Salasaradi |
| 34. | Angamardaprashamana | Vidarigandhadi |
| 35. | Shoolaprashamana | Pippalyadi |
| 36. | Shonitasthapana | Priyangvadi, Anjanadi. |
| 37. | Vedanasthapana | Rodhradi |
| 38. | Sangyasthapana | Priyangvadi |
| 39. | Prajasthapana | Vidarigandhadi, Kakolyadi |
| 40. | Vayasthapana | Kakolyadi, Vidarigandhadi |
| 41. | Vamana | Urdwabhagahara |
| 42. | Virechana | Adhobhagahara |
| 43. | Shodhana | Ubhayatobhagahara |
Vagbhata has classified 33 vargas. (A. H. Su. 15). In these, the first four are related to Samshodhana i.e Vamana, Virechana, Niruhana and Shirovirechana. The next three are Shamana vargas, i.e Vatasamshamana, Pittasamshana and Kaphasamshana. The eight varga is Jeevaniya which is same as that of Charaka. The next 25 starting from Vidaryadi are the same as that of Sushruta.
| S.N. | Name of the Varga | Drugs | Karma and Prayoga |
| 1. | Vamana | Madana, Madhuka, Katutumbi, Nimba, Bimbi, Vishala, Vamana Trapusa, Kutaja, Murva, Devadali, Krimighna, Vidula, Chitraka, Chitra, Koshataki, Rajakoshataki, Karanja, Pippali, Lavana, Vacha, Ela and Sarshapa. | Vamana |
| 2. | Virechana | Danti, Trivrut, Triphala, Indrayana, Snuhi, Shankhini, Nilini, Tilvaka, Aragwadha, Kampillaka, Swarnakshiri, Dugdha and Mutra. | Virechana |
| 3. | Niruhana | Madana, Kutaja, Kustha, Devadali, Madhuka, Vacha, Dashamoola, Devadaru, Rasna, Yava, Shatapushpa, Koshataki, Kulatha, Madhu, Lavana and Trivrut. | Vatashodhana |
| 4. | Shirovirechana | Vidanga, Apamarga, Trikatu, Daruharidra, Sarjarasa, Shirisha, Bruhati,Shigru bija, Madhookasara, saindhava, Rasanjana, Ela, Bruhat ela and Pruthvika. | Shirashodhana |
| 5. | Vatasamshana | Devadaru, Tagara, Kustha, Dashamoola, Bala, Viratarvyadi gana, Vidaryadi gana. | Vata Shamana |
| 6. | Pittasamshana | Durva, Ananta, Nimba, Vasa, Kapikachu, Gundra,Shatavari, Shitapaki, Priyangu, Shalaparni,Prishniparní, Kamala, Vanya, Nyagrodhadi gana, Padmakadi gana, Sarivadi gana | Pitta Shamana |
| 7. | Kaphasam-shana | Aaragwadhadi, Arkadigana, Mushkakadi gana, Surasadi gana, Mustadi gana, Asanadi gana, Vatsakadi gana. | Kapha Shamana |
| 8. | Jeevaniya | Jeevanti, Kakoli, Ksheerakakoli, Meda, Mahameda, Mudgaparní, Mashaparni, Rushabhaka, Jeevaka, Madhuka. | Jeevaniya |
| 9. | Vidaryadi | Vidari, Eranda, Vruschikali, Punarnava, Sahadeva, Vishvadeva, Mudgaparni, Mashaparni, Kapikachu, Jeevanapanchamoola, Hrusvapanchamoola, Sariva, Hamsapadi. | Vatapitta shamanHrudya, Bruhmana, Shosha, Gulma, Angamarda, Svasa kasahara. |
| 10. | Sarivadi | Sariva, Ushira, Gambhari, Madhuka, Shishiradvaya (Sveta chandana and rakta chandana), Madhuyasthi, Parushaka. | Dahaprashamana, Raktapitta, Trushna, Jvarahara. |
| 11. | Padmakadi | Padmaka, Pundraka, Vruddhi, Tugakshiri, Riddhi, Karkatshringi, Guduchi, Jeevaniya varga. | Vatapittashamaka, Stanyajanana, Prinana, Jeevana, Bruhmana, Vrushya. |
| 12. | Parushakadi | Parushaka, Triphala, Draksha, Katphala, Katakaphala, Rajahva, Dadima, Shaaka. | Vatashamaka, Trushna, Mutravikara nashaka. |
| 13. | Anjanadi | Anjana, Priyangu, Jatamamsi, Padma, Utpala, Rasanjana, Ela, Madhuka and Nagakesara. | Pittashamaka, Vishaghna, Antardhahahara |
| 14. | Patoladi | Patola, Katuka, Chandana, Madhusrava, Guduchi, Patha. | Kaphapittahara, Kustha, Jvara, Visha, Vamana, Aruchi, Kamalanashaka. |
| 15. | 15. Guduchyadi | Guduchi, Padmaka, Nimba, Dhanyaka and Raktachandana. | Kaphapittahara, jvaraghna, Chardi, Daha, Trushna nashaka, Agnivardhaka. |
| 16. | Aragwadhadi | Aragwadha, Indrayava, Patala, Kakatikta, Nimba, Guduchi, Madhurasa, Vikankata, Patha, Bhunimba, Saireyaka, Patola, Karanja yugma (Karanja, Chirabilva), Saptaparna, Chitraka, Sushavi, Phala (Madanaphala), Bana (Nila saireyaka), Ghonta (Badarabheda). | Kaphashamaka, Chardi, Kustha,Visha,Jvara,Kandu,Prameha,nashaka,Dustha vrana shodhana |
| 17. | Asanadi | Asana, Tinisha, Bhurja, Arjuna, Chirabilva, Khadira, Kadara, Bhandi, Shimshipa, Meshashrungi, Trihima (Sveta chandana, Raktachandana, Kaliyaka), Tala, Palasha, Agaru, Shaaka, Shaala, Kramuka, Dhava, Kalinga, Chagakarna, Ashvakarna. | Kaphashamaka, Svitra, Kustha, Krimi, Panduroga, Prameha, Medodosha nashaka. |
| 18. | Varunadi | Varuna, Saireyaka yugma (Saireyaka, Nila saireyaka), Shatavari, Chitraka, Morata, Bilva, Ajashringi, Bruhati dvaya (Bruhati, Kantakari), Karanja dwaya (Karanja, Chirabilva), Jayadvaya (Agnimantha, Tarkari), Bahalapallava (Shigru), Darbha, Rujakara (Artagala). | Kaphashamaka, Medodosha, Mandagni,Aadhyavata, Shirashula, Gulma, Antah vidradhi nashaka. |
| 19. | Ushakadi | Ushaka (Kshara vishesha), Tutthaka, Hingu, Kasisa dvaya, Saindhava, Shilajatu. | Kaphashamaka, Mutrakrichra, Ashmari, Gulma, Medodoshahara. |
| 20. | Viratarvadi | Vellantara, Agnimantha, Booka (Ishvaram allika), Vrusha, Pashanabheda, Gokshura, Itkata, Saireyaka, Bana, Kasha, Vandaka, Nala, Kusha dvaya (Kusha, Darbha), Guntha, Gundra, Shyonaka, Morata, Kuranta, Karambha, Partha (Suvarchala). | Vaatajanya roganashaka, Ashmari, Sharkara, Mutrakrichra, Mutraghata. |
| 21. | Rodhradi | Rodhra, Shabararodhra, Palasha, Jinghini, Sarala, Katphala, Yukta (Rasna), Kadamba, Kadali, Asoka, Elvaluka, Paripelava, Mocha (Shallaki). | Kaphashamaka, Medodosha, Visha, Krimi, Kusthahara and specially vranashodhana. |
| 22. | Arkadi | Arka, Alarka, Nagadanti, Vishalya (Kalihari), Bharangi, Rasna, Vruschikali, Prakirya (Chirabilva), Apamarga, Pitataila (Jyotishmati), Udakirya (Karanja), Shveta, Mahashweta, Ingudi. | Kaphashamaka, Medodosha, Krimi, Pratishyaya, Aruchi, Swasa, Kasahara, and Vranashodhana. |
| 23. | Surasadi | Krishna and sweta tulsi, Phanignyaka, Kalamala, Vidanga, Kharbusa, Mushakarni, Katphala,Kasamarda, Kshavaka, Sarasi, Bharangi, Karmuka, Kakamachi, Kulahala (Mundi), Vishamushti, Bhustrana, Bhutakeshi. | Kaphashamaka, Medodosha, Krimi, Pratishyaya, Aruchi, Swasa, Kasahara, and Vranashodhana. |
| 24. | Mushkakadi | Mushkaka, Snuhi, Triphala, Chitraka, Palasha, Dhava, Shimshipa. | Kaphashamaka,Gulma, Prameha, Ashmari, Panduroga, Medodosha, Arsha, Shukra dosha nashaka. |
| 25. | Vatsakadi | Kutaja, Murva, Bharngi, Katuka, Maricha, Ativisha, Gandira, Ela, Patha, Ajaji, Katvangaphala, Ajamoda, Sarshapa, Vacha, Jeraka, Hingu, Vidanga, Ajagandha, Panchakola. | Vatakaphashamaka, Medodosha, Pinasa, Gulma, Jvara, Shoola, Arsha nashaka. |
| 26. | Vachadi Aamatisara, | Vacha, Mustaka, Devadaru, Shunthi, Ativisha, Haritaki. | Kaphashamaka, Medodosha, Aadhyavata, Stanyadoshahara |
| 27. | Haridradi | Haridra, Daruharidra, Madhuyasthi, Prushniparni, Indrayava. | |
| 28. | Priyangvadi | Priyangupushpa, Rasanjana, Srotanjana, Padma, Padmakesara, Manjistha, Ananta, Manadruma, Mocharasa, Samanga (Lajjalu), Punnaga, Chandana and, Dhataki. | Pakvatisaarahara, Sandhaniya, Pittashamaka Vranaropana. |
| 29. | Ambasthadi | Ambastha, Madhuka, Lajjalu, Nandivruksha, Palasha, Kachura, Rodhra, Dhataki, Bilvamajja, Katvanga, Kamalakesara. | |
| 30. | Mustadi | Musta, Vacha, Chitraka, Haridra, Daruharidra, Katuka, Kakatikta, Bhallataka, Patha, Triphala, Ativisha, Kustha, Ela, Haimavati (Sweta vacha) | Yoniroga and Stanyaroga hara, Malapachana. |
| 31. | Nyagrodhadi | Nyagrodha, Aswatha, Sadaphala (Udumbara), Rodhra, Savara lodhra, Jambu dvaya (Jambu, Kakajambu), Arjuna, Kapitana, Somavalka, Plaksha, Amra, Vetasa, Priyala, Palasha, Nandi vruksha, Badari, Kadamba, Virala (Tinduki), Madhuyasthi, Madhooka. | Vranya, Sangrahi, Bhagnasandhanakara, Medoroga, RaktapittaTrusha, Daaha, Yoniroga nashaka. |
| 32. | Eladi | Ela yugma (Sukshma ela, sthula ela), Turushka, Kustha, Phalini, Jatamamsi, Jala (Sugandhabala), Dhyamaka (Rohisha), Sprukka, Choraka, Chocha, Patra, Tagara, Sthouneyaka, Jatirasa, Shukti (Nakha), Vyaghranakha, Devadaru, Agaru, Shrivasaka, Kesara, Chanda, Guggulu, Sarjarasa, Khapura (Kunduru),Punnagakesara, Nagakesara. | Vatakaphashamaka, Varnaprasadana, Visha, Kandu, Pitika,Kotha nashaka. |
| 33. | Shyamadi | Shyama, Danti, Dravanti, Kramuka, Kutarana (Sweta trivrut), Shankhini, Saptala, Swarnakshiri, Gavakshi, Shikhari, Rajanaka (Kampillaka), Guduchi, Karanja, Bastantri, Aragwadha, Bahala (Shigru), Bahurasa, Tikshnavruksha (Pilu) phala. | Kaphashamaka Gulma, Visha Aruchi,Hrudroga, Mutrakruchra nashaka. |
Classification in Nighantus:
| S.N. | Nighantu | No. of Vargas | Name of Vargas |
| 1. | Dhanwantari | 7 | Guduchyadi, Shatapushpadi, Chandanadi, Karaveeradi, Amradi, Swarnadi, Mishrakadi. |
| 2. | Shodhala | 27 | Guduchyadi, Shatapushpadi, Chandanadi, Karaveeradi, Amradi, Swarnadi; Lakshmanadi, Paniyadi, Paniya, Ksheera, Dadhi, Takra, Navaneeta, Ghrita, Taila, Madhu, Ikshu. |
| 3. | Dravyaguna Sangraha | 15 | Dhanya, Mamsa, Shaka, Lavanadi, Phala, Paniya, Kshoudra, Taila, Ikshvadi, Madyadi, Kritanna, Bhakshya, Ahara vidhi, Anupana vidhi, Mishraka varga. |
| 4. | Madanapala Nighantu | 23 | Abhayadi, Shunthyadi, Karpuradi, Suvarna, Vatadi, Phala, Shaka, Paanadi, Ikshukadi, Dhanyaguna, Dhanya kritannadi, Mamsa, Mishraka. |
| 5. | Raja Nighantu | 23 | Anupadi, Bhumyadi, Guduchyadi, Shatahvadi, Parpatadi, Pippalyadi, Mulakadi, Salmalyadi, Prabhadradi, Karaveeradi, Amradi, Chandanadi, Suvarnadi, Paniyadi, Ksheeradi, Shalyadi, Mamsa, Manushyadi, Simhadi, Rogadi, Mishrakadi, Ekarthadi |
| 6. | Kaiyadeva Nighantu | 9 | Oushadhi, Dhatu, Dhanya, Drava, Pakwanna, Mamsa, sihara, Mishraka, Nanartha. |
Taxonomical Classification:
Taxonomical classification classifies drugs into-Kingdom, Order, Family, Generacies, , Species, Sub-species etc. This method of classification is based on the natural relationship or phylogeny among plants or animals. A large number of plant families have certain distin guishing characters that allows all plants coming under them to be studied at once.
Example of the Taxonomical classification:
Kingdom: Spermatophyta
Division: Angiospermae
Class: Dicotyledons
Subclass: Sympetale
Order: Tubiflorae
Family: Solanaceae
Genus: Atropa, Hyoscymus, Dattura
Species: Hyoscymus niger, Datura stramonium, Atropa belladonna
The purpose of latin name is to provide some information that distinguishes it from other plants.
The specific epithet applied to the plant is often helpful in describing the plant, it tells the colour of flowers, height of plant, leaves are long or thin or flat, where the plant comes from, condition in which it grows naturally, whether climber/creeper etc.
Example:
Morphological classification:
I. Based on the nature of the stem, they are classified as-Herbs, Shrubs, Trees and Climbers.
1.Herbs: They are small plants with soft stems. According to the duration of life they are classified as-Annuals, Biennials and Perennials. 1.
a. Annuals: They live for few months or at most for one year producing flowers, fruits and seeds within this period. Example: Sunflower, Mustard, Rice, Pea, Bean etc.
b. Biennials: Plants that live for two years. They attain their full vegetative growth in the 1st year and produce flowers and seeds in the 2nd year, after which they die. Example: Cabbage, Raddish, Beet, Carrot, Turnip etc.
c. Perennials: Plants that persist for a number of years. The aerial parts may die after flowering season, but in the next year new shoots develop again from the underground stem after few showers. Ex: Canna, Ginger etc.
2. Shrubs:
These are medium sized plants with hard and woody stems which branch profusely from near the ground so that the plants become bushy in habit without a clear trunk. Shrubs are larger than herbs and smaller than trees. Example: China rose, night jasmine, Duranta etc.
3. Trees: These are large plants with a single stout trunk and hard and woody branches formed profusely (except most palms). Example: Mango, Jack, Teak.
4. Climbers: These have thin and long stems with diffuse branches. They climb by means of some special organs of attachment or by their twining stem. as:
They are classified
i. Rootlet climbers: they climb with the help of small adventitious roots. Example: Piper longum, Piper chaba etc.
ii. Hook climber: They climb by means of a curved hook.
Example: Climbing rose, Bougainvilla.
iii. Tendril climber: slender leafless spirally coiled structures called tendrils help in climbing. Example: Cardispermum, Naravelia.
iv. Leaf climbers: The petioles coil around any neighboring object that helps the plant climb. Example: Gloriosa.
v. Stem climbers: The long and slender stems twine bodily around trees, shrubs and hedges. Example: Country bean, Clitoria etc.
vi.Lianes: Very thick and woody perennial climbers, commonly found in forests. Example: Bauhinia vahli.
Based on the mode of nourishment, plants are classified as;
I. Autophytes: Green plants that normally prepare their own food.
II. Heterophytes: Plants that depend on other sources for food.
These Heterophytes are of various kinds;
i. Parasites: These plants grow on other living plants and absorb organic food from the host by their sucking roots called Haustoria. Different types of parasites are;
ii. Epiphytes (Epi-Upon, Phyta-plants): These plants grow on other plants only for support and do no draw food from them. Example: Vanda, Orchid etc.
iii. Saprophytes (Sapros-rotten, Phyta-plants): These are plants that grow in place rich in decaying organic substances of vegetable and animal origin and derive their nutrition from them. Example: Birds nest orchid, Chain orchid etc.
iv. Symbionts: (Syn-together, bios-life): When two organisms live together, like they are parts of the same plant, and are of mutual help to each other, they are called symbionts. Example: Lichens.
v. Carnivorous plants: These are plants that capture insects and small animals and feed upon them absorbing only the nitrogenous compounds from their bodies. Example: Pitcher plant.
Guna Nirukti:
The word “Guna” is formed by adding
The factor, which is inherently present in dravya, and is responsible for attracting people towards the dravya, is guna.
Guna Lakshana:
Nyaya and Vaisheshika darshanas were among the first to define Guna,
Guna resides in the Dravya. It itself is nirguna, and also it is inactive or it maintains a non-inherent relation with karma like samyoga vibhaga etc.
According to Badantha Nagarjuna, Guna has innumerable lakshanas.
Dravya -Rasa-Virya-Vipaka and Karma have a definite single lakshana, which will help to differentiate it from others. E.g., Dravya is the ashraya of shabdadi; Rasa is that percieved through the Rasanendriya; Karma is the lakshana of Virya, and Parinama is the lakshana of Vipaka.
Therefore, each of these have a specific lakshana unlike that of guna.
Gunas cannot be differentiated by a specific single lakshana, which will exclude all the other attributes from being called as guna.
Ex: Sheeta, Ushna are Sparshnendriya grahya whereas Snigdha, Ruksha are both Sparshendriya and Chakshurindriya grahya.
Therefore, Guna is considered as Vishva lakshana.
Boudha darshana:
Guna means a group of Characteristics or qualities.
Jaina darshana:
Guna is synonymous with dravyas since dravya is known through certain properties only.
Charaka Samhita:
Guna is present in the dravya in samavayi sambandha.
Guna by itself cannout produce an action
The difference between Dravya and Guna is that while dravya is capable of existing independently by itself, gunas cannot do so. It resides in the Dravya.
Guna Sankhya / Classification of Guna:
Charaka has mentioned 41 gunas, i.e.
| Artha gunas: | Shabda, Sparsha, Rupa, Rasa, gandha (5) |
| Gurvadi gunas: | Guru, Laghu etc 20 gunas |
| Budhi prayatnanta: | Icha dvesha etc. 6 gunas. |
| Paradi gunas: | Para, apara etc. 10 gunas |
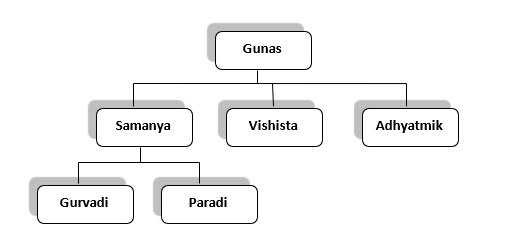
Chakrapani has classified these 41 gunas as :
| 1. | Samanya gunas: | Gurvadi (20) and Paradi (10) |
| 2. | Vishishta gunas: | Shabda, Sparsha, Rupa, Rasa gandha (5) |
| 3. | Adhyatmika gunas: | Icha, Dvesha, Sukha, Dukha, Prayatna and Budhi (6) |
Number:
Yogendranath sen considers seven adhyatmika gunas by adding mano artha, and he accepts total forty-two gunas.
The vaisheshika gunas are called so because they are pradhana gunas of each of the panchamahabhutas, the gunas of one mahabhuta being present in other is due to bhutantara anupravesha.
Gurvadi gunas are considered as samanya gunas because they are normally present in the panchamahabhutas whereas Kaviraj Gangadhara has considered gurvadi gunas as shaarira gunas.
Karmanya Gunas as per Nagarjuna
| S.N. | Charaka | Sushruta | Bhavaprakasha | Rasa Vaisheshika |
| 1. | Manda-tikshna | Mrudu-tikshna | Tikshna-shlakshna | Mrudu-tikshna |
| 2. | Sthira-sara | Manda-khara | Sthira-sara | |
| 3. | Shlakshna-khara | Shlakshana-Karkasha | Mrudu-tikshna | |
| 4. | Sandra-drava | Drava-sandra | Shushka-drava | |
| 5. | Sugandha-Durgandha | Manda-aashu | ||
| 6. | Sukshma-ashukari | |||
| 7. | Vyavayi-vikashi |
Since the guna Sankhya is considered as twenty, niyatasankhyavadi say that the extra gunas should be included under these twenty.
They say that gunas are innumerable in number and only the important ones are put under the gurvadi and it cannot be said that gunas are only 20.
Guna Swaroopa:
Some scholars opine that guna is physical property whereas some others consider it as pharmacological actions.
However, we know that karma, which is assessed by anumana through the dravyashrita guna, is the pharamacological action of the drug.
Therefore, guna can be considered as both physical and pharmacological action.
However while some drugs have both bhoutika (Physical property) and karmuka guna (pharmacological properties): eg; ushnodaka -it can be assessed both by pratyaksha and anumana, other drugs can be assessed only by anumana.
Example: Aaragwadha and Eranda taila,
The bhoutika guna and karmuka guna of eranda is “sara” and sara guna can be determined both by pratyaksha and anumana, whereas aaragwadha does not have sara guna in its swarupa and sara guna can be assessed only through its karma by help of anumana pramana.
Guna can be of two types:
1) The first type is that in which the guna always exists in the dravya, like ushnata in agni, chalatva in vayu and snehatva in taila.
2 ) The second type of gunas are called avasthika gunas:
Ex: The guruta of puranadhanya is less compared to navina dhanya. Therefore, it is said that yaavad dravyabhaavi gunas cannot be changed but the avasthika gunas undergo change, which is called as gunantaradhana. The gunas are lost either by dravyanasha or by gunantaradhana of dravya, so the yaavad dravyabhavi gunas are lost only by dravyanasha, whereas the avasthika gunas are lost by gunantaradhana.
Finally, concluding chakrapani has said that, when the dravyantara is possible by sanskara in such cases gunantara is also possible. Ex: conversion of vrihi to laja brings about changes in its guna.
Guna Karmukata:
The karma of dravyas can be accessed through the guna by anumana pramana.
Dalhana’s opinion about the difference between guna and virya is as follows:
Amalaki and Haritaki have same gunas but different virya. Haritaki is ushna and Amalaki is sheeta. The difference in action is due to the virya, hence Karma helps to differntiate between guna and Virya.
Gurvadi Gunas:
1) Guru:
The word guru in general means heavyness.
Definitions (Paribhasha):
(i) Gurutva with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties:
The property responsible for the adhogamana (Downward movement) or Patana (fall) in Jala and Bhumi is “Guru”. Therefore, in general anything which falls on the ground, or which sinks to the bottom when put in water is termed as “Guru” or Heavy.
Guru Guna is attributed to the predominance of Prithvi and Jala mahabhutas.
(ii) Guru guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Guru Guna is that which produces Shareera bruhmana. In addition, any dravya which takes a longer time to get digested (Chirapaki) is called as “Guru”.
*virechana dravyas being guru in guna helps in adhogamana of vriddha doshas.
Ex: Draksha, Kharjura, Aragwadha, Yasthimadhu, Kapikachu, Manjistha, Gokshura, Narikela, Shatavari, Masha, Mushali.
2) Laghu:
(i) Laghu with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties:
Laghu is the opposite of guru guna and hence anything which has upward movement and which floats on the surface water is laghu.
Laghu guna results due to excess of Akasha, Vayu, and Agni mahabhuta.
(ii) Laghu guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Laghu is the opposite of guru; it does lekhana of shareera and ropana of vrana.
Laghu is considered best pathya, kaphahara and shigrapaki (Quick to get digested)
Example: Guduchi, Amalaki, Aswagandha, Chitraka, Khadira, Mudga, Laaja etc.
3) Sheeta (Cold):
(i) Sheeta with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties:
Sheeta guna pradhana dravyas have ap mahabhuta pradhanata.
(ii) Sheeta guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Sheeta guna is sparshana grahya.
4) Ushna (Hot):
(i) Ushna guna with respect to its Physico- Chemical properties:
Ushna guna has agni mahabhuta pradhanata.
Ushna guna is sparshana grahya.
(ii) Ushna guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Ushna is the opposite of sheeta guna. Due to agni guna pradhanata, ushna is helpful in pachana. Sheeta does sthambhana and ushna does its opposite, it causes svedana.
Ushna is Vata-Kapahahara and Pittakara.
Examples: Maricha, Chitraka, Hingu etc.
5) (Unctous):
(i) Snigdha guna with respect to its Physico- Chemical properties:
Sneha guna is ap mahabhuta pradhana.
(ii) Snigdha guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
That which causes kleda vridhi is called as snigdha. Snigdha guna causes mruduta, and it is balya, varnya and vrushya.
Snigdha is Vatahara and Kaphakara.
Examples: Vatada, tila, priyala, eranda, shigru, karanja, ghruta, dadhi etc.
6) (Non-unctousness):
(i) Ruksha guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties:
Ruksha guna is predominant of Pritvi and Vayu mahabhuta.
Snigdha and ruksha gunas are acessed by chakshu indriya.
(ii) Ruksha guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions
7)(Mild):
(i) Manda guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties:
Anything, which takes a long time to act or is less intense or mild, is called as manda.
(ii) Manda guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Manda guna is that which dulls the activities of the body. Shamana dravyas are said to be having manda guna, as they only pacify the vitiated dosha and are not capable of putting them out of the body. Manda guna leads to shitilata and alpata in all activities. It is kapha vardhaka and pitta shamaka.
Example: Ahiphena, Vatsanabha, Ativisha.
8) (Sharp):
i) Tikshna guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties:
Tikshna represents shigrakaritva, that which acts fast.
● Tikshna guna is Tejo mahabhuta pradhana.
Tikshna rasana and sparshanendriya grahya.
(ii) Tikshna guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Tikshna guna being agni mahabhuta pradhana causes daha, paka, sravana, lekhana. Tikshna guna is Pittakara, and Kapha-Vatahara. The ability of the dravya to produces shodhana is by its tikshna guna.
Examples: Maricha, Pippali, Jayapala, Aaragwadha, Trivrut etc.
9) (Stable):
(i) Sthira guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties:
That which is devoid of chalatva (Ability to move) is sthira.
“ Sthira guna is prithvi mahabhuta pradhana.
(ii) Sthira guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Sthira guna does the sthambhana of Vata and Mala. Sthira guna is helpful in dhaarana or stabilising.
Examples: Shalaparni, Ashvagandha, Shatavari, Bala, Khadira etc.
10) (Unstable):
(i) Sara guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties:
● That which initiates the movement is Sara. Sara is opposite of sthira, and hence it has chalatva.
● Sara guna is jala mahabhuta pradhana.
(ii) Sara guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Sara guna is responsible for anulomana karma. Sara is pravartaka i.e. it initiates the movement of vata and mala.
Examples: Haritaki, Amalaki, Vibhitaki, Aaragwadha, Katuki, Trivrut, Saptala, shankhini.
11) (Soft):
(i) Mrudu guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties:
● Mrudu guna in general means soft.
Mrudu guna is akasha and ap mahabhuta pradhana
Mrudu guna is sparshanendriya grahya.
(ii) Mrudu guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
That which after entering the body causes the shithilata of mamsa is mrudu.
It is kapha vardhaka, vata pitta shamaka.
Examples: Godhuma, Vrihi, Shali, Shashtika, Dvidala, Taila, Ghruta, Vasa, Majja, Navanita.
12) (Hard):
(i) Kathina guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties:
Kathina guna is prithvi mahabhuta pradhana.
(ii) Mrudu guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
That which causes drudatha in the body is kathina.
Examples: Pravala, mukta, shankha, shukti.
13) (Non-Sticky):
Vishada means shodhana or to make shuddha.
(i) Vishada guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties
The property responsible to produce a cleansing effect is vishada.
According to Charaka: Prithvi+Agni+Vayu
According to sushruta: Aakasha.
According to rasa vaisheshika: Prithvi+Vayu
(ii) Vishada guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Hemadri commentry on sushruta is as follows:
Those drugs, which cause the dosha, dhatu and mala shodhana, and helps to expel out the hidden deep-seated mala, are considered as vishada.
Vishada guna does the kleda chedana or clears the kleda and helps in vrana ropana.
Examples: Nimba, Kshara etc.
14) (Slimy):
(i) Pichila guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties
That which is slimy and hence forms a coating (Lepa) is called as Pichila.
Pichila guna is Ap mahabhuta pradhana.
(ii) Pichila guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Pichila guna is Balya, sandhanakara, guru and jeevaniya. It causes vridhi of Kapha dosha.
Difference between picchila and snigdha:
Both are sticky in nature, but pichila has tantumatva whereas snigdha does not have it. When one touches a pichila dravya, thread like structure is formed by rubbing the fingers and drawing a part.
Examples: shleshmataka, Kokilaksha, Ksheera, Phanita, Guda, Mashaparni, Mudgaparni, Tkshu rasa etc.
Pichila and Vishada guna are acessed through chakshu indriya and sparshanendriya.
15) (Smooth ):
(i) Slakshna guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties
Shlakshna is sneha rahita, hard in structure but smooth to touch.
Shlakshna is tejo mahahuta pradhana. Acording to charaka, it is Aakasha mahabhuta pradhana.
(ii) Slakshna guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
That quality by which dravya acts as Vrana ropaka is Shlakshna. Shlakshna is similiar to picchila in being jivana, balya, sandhanakara, whereas shlakshna in addition has vrana ropana property.
Examples: Manikya, Mukta, Shankha etc.
16) (Rough):
(i) Khara guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties
Khara means that which is parusha (rough)
Karkasha guna is Vayu mahabhuta pradhana as per rasa vaisheshika.
According to Sushruta, Khara is Tejas and Vayu mahabhuta pradhana.
Khara guna is Prithvi and Vayu mahabhuta pradhana as per Charaka.
(ii) Khara guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
The property by which dravya does lekhana karma is khara. Khara guna is similar to vishada in its action, i.e. khara guna also does the scraping out of mala.
Example: Chanaka etc.
17) (Fine) :
(i) Sukshma guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties
That which has the capacity to enter minute channels and keep it open is called as sukshma.
(ii) Sukshma guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Drugs having sukshma guna are capable of entering into the minutest channels of the body easily and quickly.
Examples: Madya, Visha etc.
18) ( Gross ):
(i) Sthoola guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties
That which causes sthulata of shareera, and produces sroto avarodha is sthoola.
(ii) Sthoola guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Sthoola guna increases the sthoulya and causes sroto avarodha in the shareera.
Examples: Pishtaka, modaka etc.
19) (Solid):
(i) Sandra guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties
Any dravya which is solid i.e. which helps in accumulating or buiding up is called as Sandra.
(ii) Sandra guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
That which causes sthoulya and helps in dhatu sanghata is sandra.
Examples: Navaneeta, dadhi etc.
20) (Liquid):
(i) Drava guna with respect to its Physico-Chemical properties
Drava in general means liquid.
That which does the kledana is Drava.
(ii) Drava guna with respect to its Pharmacological actions:
Examples: Takra, Ikshu rasa etc.
According to vaisheshika, dravatva is of 2 types:
Extra Gunas:
1) Vyavaayi: the property due to which the drug spreads all over the body producing its action and then undergoes paka is vyavayi.
Examples: Bhanga, Ahiphena.
2) Vikasi: that which spread all over the body causing ojo kshinata and producing shitilata in dhatus and sandhi is vikasi.
Examples: Kramuka, Kodrava.
3 ) Sugandha: That, which gives sukha (pleasure), is sukshma, rochana and mrudu is sugandhi.
4) Durgandha : Durgandha is opposite of sugandha, and produces hrallasa and aruchi.
5) Aashukari: that which spreads quickly in the body just like taila spreads in water is called as ashukari.
6) Shushka: it is the opposite of Drava according to Bhavaprakasha.
Shushka can be included under Sandra or ruksha.
Gurvadi Guna Prayojana:
Gurvadi gunas are seen in the sharirika dhatus, they are also seen in the aahara, oushadha we consume. Therefore based on the samanya vishesha siddhanta, similar gunas will cause vridhi of the corresponding dhatus whereas viruddha (opposite) guna will cause hlasa.
The regular abhyasa of guru guna yukta ahara will cause gauravata in the shareera and laghu ahara abhyasa causes laghavata in the shareera by samanya vishesha siddhanta.
Further, the use of ahara having similar gunas to that of the dhatu will cause an increase in that dhatu and hence useful in case of dhatu kshaya. In case of dhatu vridhi, the dravyas with opposite gunas have to be used to produce hlasa or reduce the vridha dhatu.
Example: Mamsa for Mamsa vridhi, Lohita for Lohita, Medas for Medo dhatu, vasaa for vasa and so on.
If the same dravya is not available then dravyas having similar gunas should be used.
The above verse gives examples of dravyas having similar gunas that can help in dhatu or dosha vridhi in condition of kshaya.
Paradi Gunas:
Definition:
Para means pradhana or superior among dravyas of similar jaati, and apara means apradhana or inferior among a group of similar.
Para-Aparatva is applied to Desha-Kala-Vayo-Mana-Paka-Virya-Rasadi.
Yogendranath sen commentry on Charaka sutrasthana 26.
Yogendranath sen says that para-aparatva is related to sannikrushta viprakrushta as said in vaisheshika darshana. This is told in relation to two factors-desha and kala.
2) Yukti ( Rational application):
Definition:
Yukti is the proper, rational application of knowledge.
The selection of the kalpana, based on doshadi factors requires yukti.
Yukti is the proper planning of treatment, considering the factors like dosha, desha, kala and matra.
If a kalpana is selected with yukti, then it is yougika or fruitful in the disease and gives results, whereas if a kalpana is used without any yukti, then it does not give any result.
* Samyoga, parinama, sanskara etc are important factors in bhoutika kalpana and therefore they are explained seperately.
In Dravyaguna shastra, also the importance of yukti is stressed as follows:
3) Sankhya (Enumeration):
Sankhya means ganita i.e counting used as vyavahara hetu. Example: counting of different types of doshas, different types of diseases like eight types of jvara, pancha kasa and so on. Counting of different drugs in a group like triphala, fifty mahakashayas. To get the appropriate knowledge of the disease, Sankhya samprapti is mentioned among the types of samprapti.
4) Samyoga (Conjunction)
The combination of two or more substances is samyoga and this is anitya.
Types of Samyoga:
Samyoga is of three types, Dvandvakarmaja, Sarvakarmaja and Eka karmaja.
Examples: (Cha. da.)
1) The fighting of two goats is an example of dvandva karmaja samyoga.
2) Combination of lot of masha placed in a bhanda is considered as sarvakarmaja samyoga.
3) The samyoga of kaka with vruksha is considered as eka karmaja samyoga.
Types of Samyoga According to Vaisheshika Darshana:
Anyatara karmaja is same as ekakarmaja and ubhaya karmaja is same as dvandva karmaja.
The example for samyogaja samyoga is as follows.
The samyoga of hand with shakha to the samyoga of shareera with vruksha is samyogaja samyoga.
5) Vibhaga (Disjunction):
The division of a substance or combination is vibhaga, similar to samyoga vibhaga is also of three types.
1) Vibhakti: dividing a dravya into smaller parts.
Example: making guduchi into small pieces to take out the satva.
2) Viyoga: the seperation of one from another, or samyoga abhava. The three types, dvandva karmaja, sarvakarmaja, eka karmaja can be considered as types of viyoga. Ex: using only bruhati instead of bruhati dvaya.
3) Bhagasho graha: division of a dravya in specific proportion. Eg: division of 10gms of lavanabhaskara in three doses.
6) Pruthakatwa (Seperateness):
That which differentiates that “this is a ghata, and this is a pata” is called prithakatwa. It is of three types:
a) Difference in the qualities of substances in two different places or two different seasons. Eg: Chandan of meru parvata is different from that of himalayas.
b: Difference between two classes. Eg: difference between buffaloes and pigs.
c) : Difference between substances belonging to the same category. Eg: Seven types of haritaki each having unique qualities.
There is debate over the issue that anyonyabhava and pruthakatwa are same But they are different, for example, through anyonyabhava we can establish that ” ghata” is not “pata” wherein abhava is expressed however through ” pruthakatwa” we differentiate between pata and ghata which is expression of bhava. The former is non-existant while latter is existant feature.
In treatment, pruthakatwa may be used to differentiate between the qualities of two drugs.
Eg; Between guduchi swarasa and satva.
7) Parimana (Measurements):
The quality by which measurement of various things is possible is known as parimana.
Parimana is of two types:
Dairghyamana: this is nitya for nitya dravya like paramanu and anitya for anitya dravyas like dvayanuka etc.
Anityamana based on karana is of three types:
This measurement is based on anguli, hasta, aratni etc. Dairghyamana may be of another four types .
Gurutvamana: this is also of two types, i.e nitya and anitya. It is mesured by means of prastha, aadhaka etc. with the helps of vessels and balance.
In Amarakosha: we come across three type’s of measurement
8) Sanskara: (Processing):
The means (karana) through which one can bring out changes in the natural properties of the drug is called as samskara.
Samskara of a dravya is mainly aimed at :
Example: Samskara of parada, conversion of rice into different forms like odana, laja etc.
Samskara bheda according to vaisheshika:
9) Abhyasa: (Continous usage):
The regular usage of any thing over a period is known as abyasa. Sheelana and satatakriya are synonyms.
The replacement of unhealthy habits with healthy one is possible through abhyasa.
The continous usage of similar gunas cause dhatu vriddhi,
Relation of Guna with Shadupakrama:
(Badanta Nagarjuna)
1) Rasabhibhava:
Guna will supress the rasa and exhibit its effect.
Example: water is madhura in nature and should increase kapha but ushnodaka due to its guna reduces kapha. Similarly patola and bruhat panchamula are tikta in rasa, but due to their ushna guna, they subside vata.
Therefore,
That which supresses the effect of others is pradhana, just like surya over shadows, the nakshatra by its brightness. Therefore, guna is important.
2) Vipakakaranatvat:
The vipaka depends on guna i.e sheeta-snigdha-guru-pichila guna undergo guru vipaka and laghu-ruksha-vishada-teekshna undergoes laghu vipaka.
* The action of rasa is dependant on vipaka and vipaka being dependent on guna; we can consider that guna is pradhana.
just like vayu is pradhana for the action of dosha dhatu mala.
3) Sankhyabahulyaat:
Gunas are more in number than rasa, rasas are only six, whereas gunas are 10 in number.
4) Prayogabahulyaat:
Gunas are more widely used in treatment than rasas. The sheetadi gunas are usedin various forms of treatment like abhyanga, parisheka, avagaha etc whereas rasas are used only orally. Therefore, that which is used more is pradhana and hence guna is pradhana.
5) Anekakarmatva:
The gunas existing along with rasa support the activity of rasa and hence are responsible for various karma. Therefore, guna is pradhana.
6) Mahavishayatvat/Vishayabahulyaat:
The adhara bhoota dravya of guna are many in number, hence guna is pradhana. Example: Among the indriyas, mana is pradhana because of many vishayas.
7) Rasanugraha:
The gunas existing with rasas add to the quality of the rasa. Ex: ghruta is shrestha among madhura rasa dravyas because of its sheeta, snigdha, mrudu, picchila guna, mrudu, and sheeta guna and laghu paka. Saindhava is srestha among lavanas because of its natyushna, mrudu,snigdha guna. Picchila is srestha among katu dravyas because of its mrudu and guru guna.
Patola phala is srestha among tikta dravyas because of its vrushya, guru, picchila guna. Madhu is srestha among kashaya dravyas because of vrushya, and brhmana guna.
8) Upadesha:
Gunas are considered important in the classics.
Example: Guru-ushna-snigdha gunas are considered as vataghna.
9) Apadesha:
The dravyas are recognised through its gunas.
Example: This purusha is teekshna, this is geeta and mrudu.
10) Anumana:
Through kaarana i.e gunas, the effect can be inferred.
Through sheeta, ushna etc gunas, the effects like picchila, vataghna etc are assumed respectively, hence guna is important.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Guduchi – Giloy. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
The main Sanskrit names of this plant are Guduchi, Amrita, Amritavallari, Dinnodbhava, Jeevanti, Somvalli, Kundali, Chakralakshanika, Dheera, Vishalya, Rasaani, Chandrahasa, Vayastha, Mandali, Devnirmita, Soma, Chinna, Chinnaruha Vatsadni, Madhuparni and Tantrika.
Guduchi has popular names in Hindi language and in general – Giloy, Guruch, Galay, Gulbel, Gulach, Gulanch, Galo and many other names.
Its botanical name is Tinospora cordifolia (total Menispermaceae).
Guduchi is a multi-year-old, climbing, fleshy and woody vine, which grows on trees with the shelter of sources, its big vines come in the grip of climbing trees. It has very thin (paper-like) skin (cover) of gray color or yellow-white color on its stem (thick wood-like stem), on removing it, the green colored fleshy part is visible. If this scandal is cut from somewhere, then it can be seen that there are cycles in it. The root emerges from the scandal and continues to hang down. In this the letters are alternate, thick, betel-shaped (heart-shaped), pointed and smooth. There are 7-8 nerves in the leaves. The leaves are 2 to 4 inches wide and 1 to 3 inches long.
Its old leaves turn yellow and fall in the spring and new leaves emerge by the month of Jyestha. The flowers on this creeper are small, greenish yellow in color and appear in bunches in the rainy season (which usually bloom in the moonlight). In summer, flowers appear in racemes near the axon. After this, pea-like round fruits of red color come on the vine, containing small, crooked and smooth seeds which look like chili grains. The fruits are green when unripe and turn red when ripe.
The vine of Giloy or Guruch is also planted in the gardens, outside the bungalows and anywhere in the places of greenery for beauty. Its vines grow on trees, on large neem (nimb) trees, on mango trees etc.Most of them are seen spread on the rocks and on other trees. Its trunk is as thick as a finger (or sometimes thinner than that) or as thick as a thumb (or even thicker). If the vine of Giloy spreads on the ground, then coming out from place to place, its twine-like roots or fibers keep swinging downwards.
The taste of Giloy’s Kand is very bitter and there is no smell in it. Giloy is well-known for its bitterness, ‘Giloy Neem Chadhi’ is popular in its context, because Giloy is bitter like neem and the concept of considering it more beneficial is prevalent. (At some places it is also called Neem-Giloy). Giloy mounted on Neem absorbs its properties. Hence it is considered the best.
On the trunk (stem) of Giloy, there is a thin bark of ash color on gray, on peeling it, a greenish part is visible. Small knots are visible here and there. This stem shrinks on drying and the bark appears like a separate hanging (some sticky and some separate, like paper-like layers). When the pieces of Giloy’s Kand are mashed or ground in the green state, then loabi juice or feeling is felt in it. The smooth or luscious juice that comes out of the stem is very bitter in taste.
Giloy is found everywhere in India, it is generally found all over the country up to a height of about 1000 feet, especially in the hot regions (hot climate places).
The chemical composition of this plant contains berberine, guilloine, volatile oil (volatile oil, gallosterol, guillotine, fatty acid, starch, a wax-like substance. Its alkaloid called berberine and glycoside called guilloine are found. Its chemical pungent elements But by analyzing many types of active substances have been found and these chemical elements participate in the pharmacological activity of the plant.
Another species of Giloy is also found, which is called Padmaguduchi or Kanda Guduchi. Its leaves are big and are in triangle or three sections. Tumor shaped small knots are found in its trunk. This caste is less available. Some other species (Tinospora melavarica etc.) of the Tinospora genus (caste), the botanical source of this herb, are also mentioned as Guduchi, Guduchi caste or regional differences.
The juice of Guduchi (Giloy) is mainly bitter and astringent (Tiktakashaya), Anuras Katu (Charpara), Laghu (mild) in properties, Snigdha, Pichhil (greasy), Ushna Virya (hot in effect) and Vipak Madhur (on digestion). sweet). It is tridoshamak (Vata-Pitta-Kapha-destroying) with quality, this plant is Vatakaf-shamak due to heat and Kapha-pittasamak because of the presence of bitter astringent in it.
The main medicinal functions of Giloy are – Rasayana, Sangrahi, Strengthening, Agvidipak, Blood purifier, Leprosy, Pain reliever, Heart, Urine detoxification – Urination, Burning, Lactation, Satisfying, Chardi-Nigrahan, Krimighna, Jwaraghna, Medhya, Chakshushya, Poisonous, Metallic, Balya – bitter nutritive, dermatological, ulcer planting – resistant to bacterial infection and has the ability to perform many other medicinal properties.
Guduchi, better known as Giloy or Guruch, is one of the ancient herbs of Indian medical science, which is considered to be a very potent medicine like Param Rasayan and nectar, which is counted among the major herbs.This plant is used in many diseases, which has detailed scriptures and it is used medicinally in the treatment of many diseases in medical work. Guduchi (Giloy) is used for fever, chronic fever, liver disease, kamala, pandu, gout, leprosy, skin, rheumatism, debility, metallurgy, urine, anorexia, diarrhea, cough-breathing-hikka, It is used in a variety of ways in diseases such as dyspepsia, acid reflux, mouth ulcers, ulcers, eye diseases, hair loss, skin diseases, epidural diseases, gallstones, brain disorders, gonorrhea, diabetes, phlebitis, rheumatism, blood dyspepsia, inflammation, trisha and leprosy.
The main ingredient for the medicinal use of Guduchi (Giloy) is its Bael Kand (stem which is like a very thick rope), and generally Guduchi’s Kand, Swaras, Patra, Fruit and Sattva are used in medicines.
There is an important practical instruction in the scriptures regarding the medicinal use of Guduchi – ‘Pryoktavya Sadivaardra Dwiguna Naiv Karayet’. That is, Giloy should always be used in fresh (Giloy) wet condition or green condition and there is no need to double it.
Generally, in relation to the method of collection, preservation and use of medicines, there is a rule to take double the amount of green (fresh) substances, but this does not apply in the case of Guduchi, because Giloy is eaten fresh. By collecting it, it is more valuable from the point of view of medicinal use. It is practically seen that in the market (grocers or raw drugs) Sellers) Giloy’s Sushikkandi Khand (dried pieces of Giloy’s stem) are available, which are obtained in the form of Guduchi and are used only, which is not more or completely beneficial, but according to the scriptures, green Guduchi is special. It is virtuous. Which is in accordance with the scriptures. Active Ingredients in Green Guduchi. The condition of the body and the activity of Rasagun, Viryadi Karmuk component has its own importance. Giloy is widely used in medicines by making its essence, the swaras of Giloy’s Kand are used for the manufacture of many medicines and in the pharmaceutical imagination of Rasausdhis, according to the scriptures. Giloy’s letters are also taken fresh, They are also useful from the point of view of medicinal properties. If Giloy is to be collected and stored for medicinal use, then Guduchi Kand is cut into pieces and dried in the shade. Giloy essence is made and kept safe in a suitable vessel (glass vial). Guduchi’s fruits are useful if plucked fresh and used.
Guduchi has been classified into various medicinal herbs in Ayurvedic codes – Triptighna, Stanyashodhan Snehopag, Trishnigrahan, Dahayrashaman, Vayahasthapana Mahakashaya has text of Guduchi in Charak Samhita. Guduchi has been included in Vallipanchamul, Aragvadhadi, Kakolyadi, Patoladi, Shayadi and Guduchyadigana of Sushruta Samhita.
Guduchi (Giloy) is widely used in the form of medicines. Guduchi is used in various medicinal concepts and formulations used in the treatment of many diseases. And Guduchi is used in the treatment of many diseases with different proportion, quantity, method of use.
(a) The preparation method of Guduchi Sattva is simple and it can be made easily at home without much expenditure. The stem pieces (green guduchi kand khand) from the fresh vine of Giloy are crushed (crushed on a cob or any other suitable vessel or place) and soaked in vegetable liquid (guduchi kand) with four times as much water.After that, after twenty-four hours, filter the medicine by mashing it well in water; Then this liquid is filtered and the top water is taken out and a white colored substance settles down in it. After drying it, fill it in a vial (glass bottle) or a suitable vessel and keep it safe by closing it. In this way Sat Giloy (Guduchi-Sattva) can be prepared and used in the treatment of diseases; It is very beneficial.
(b) Guduchi Sattva Ras has sweet and cold semen, sweet Vipak and short qualities; It acts as a tonic, diet, lamp, fever, beneficial for the eyes (eyes) and chemical etc. This Guduchi Satva is used in many diseases with appropriate quantity and proportion. Guduchi Sattva is given alone (alone) mixed with other medicinal formulations for therapy.
(c) Use of Guduchi Sattva with castor oil in Vatarakta, with Navaneet (butter) in Arsha, with Dadim (Pomegranate) in Aruchi, with Draksha-mridhika (raisin) in Kamla, with Trikatu in Svas-Kaas, With honey in Hikka,In urinary tract, with gond, in leprosy with Jumpli Tulsi, in eye diseases with goghrit, in Pandu with ghrita and honey (asman), with cumin and sugar candy in inflammation, with whey on diseases of deep places and in palitya. There is a law to do with Bhrishrajswaras for hair blackening (to make the hair black).
This Guhuchi extract can be used as an antibiotic medicine, because it is useful in various disorders keeping in mind the quantity, proportion, stage of the disease, condition of symptoms and other things. 200 to 250 mg in all types of fever. The amount of Guduchi satva is generally used with appropriate proportion of Gadhu Sukhoshna water or Guduchi Kavath or other fever medicine’s Kavath or Swaras to ragis.
(d) 500 mg of Guduchi Sattva in all types of fever as antibiotic or anti-bacterial medicine. (in doses up to ) can be given every four hours. Apart from this, this essence is crushed before binding any type of ulcer. It immediately blocks the blood flowing from the ulcers. Oral use of powder on the ulcers inside the mouth gives immediate benefit. In case of acidity and burning sensation in the stomach or throat, a small spoon or half spoon of cold water is taken. In addition to this, in the treatment of many diseases in various ways (externally and internally), considering the strength of the defect, the strength of the disease and the strength of the patient in any type of Pitta disorders.
Sanshamani Vati is prepared from Guduchi Ghan Sattva. 250 mg of Giloy’s essence. Vati is prepared. The more simple and accessible this medicine is, the more beneficial and extremely useful it is. Its tablets 5 to 10 with water 4-5 times a day By giving it, it is of great benefit in all types of fevers. It is beneficial in chronic fever and Rajayakshma fever.
Sanshamani Vati is prepared from Guduchi Ghan Sattva. 250 mg of Giloy’s essence. Vati is prepared. The more simple and accessible this medicine is, the more beneficial and extremely useful it is. Its tablets 5 to 10 with water 4-5 times a day By giving it, it is of great benefit in all types of fevers. It is beneficial in chronic fever and Rajayakshma fever.
In such incurable fever, the causes of which cannot be detected even after many tests, which is called ‘pyrexia of unknown o-regin’), Giloy Sattva works well in such complex stage of fever and in this way antipyretic drug is widely used. Is. Similarly, the weakness that comes after a long illness is cured by the use of Vati prepared from Giloy, gradually the weakness in the body ends and the strength starts coming again, the effect of Giloy is universal and the chemical properties do all-metal work on the body.
250 mg of Guduchi’s cube is mixed with the powder of Atis. Let’s make pills. 5-10 of these tablets can be given in all types of periodic fever, which is very beneficial and it is especially beneficial in vishamajwar (fever coming in shifts).
The pieces of Guduchi Kand (fresh Giloy) are kept after washing them thoroughly with water, three inch long pieces are cut from it. After crushing them well, put them in four times water in an iron or aluminum pan and boil them. When the water remains one-fourth, it cools and filters it twice or thrice with a cloth; And then put this pot in a pan and cook it so much that it becomes a little thicker than honey.Now after removing it from the fire, let’s dry this liquid in the sun so that it becomes capable of making tablets. Now the tablets of this substance are 250 mg. Tablets should be made. They can also be used after making them simple (grinding) at the time of need. Similar to Sanshamani Vati, Guduchi Ghan Sattva has general usefulness.
Giloy Sattva 50 grams, Sitopaladi powder 100 grams and Praval Pishti 12 grams are mixed and kept; And this medicinal mixture is consumed in the amount of two spoons in the morning and evening by licking it with honey or with some panak (sorbet),Then give some milk from above. By using it for a few days (or for 2-3 months as required), the weakness caused by diseases goes away and the body becomes vigorous. This medicine increases vitality and increases immunity.
Dry Gudni Kand (pieces of Mukhi Gilaya) and Triphala (Harad, Baheda and Amla) are taken and pounded (yavkut or coarsely pounded). Take 15 grams thick powder of it and put it in 120 grams of water and put it in a vessel and put it on the fire to make a stew and let it cool down when the quarter is left. Filter this Guduchi Kwash and add two spoons of honey and 250-500 mg. Pippali Churna (small peepal powder) is mixed and it is given to drink half in the morning and half in the evening. Along with its internal use (for eating), this mixed powder (which was used for decoction) is put in water (clean water) without making a pot and filters it well with a cloth. Putting about 10 grams of powder in a glass of water and giving it in the evening, filtering it in the morning or washing the eyes with distilled water (eye wash) is beneficial as an eye medicine.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Amalki – Amla. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
This is a typical tree of India. Our familiar and effective medicine is being used since very ancient or Vedic times. And it has been given a very high place in Ayurveda. From herbal medicine to chemical medicine, there are very few cases or experiments in which it has not been treated. It is found in almost all experiments in some form or the other.
In Charak, Sushrutadi Ayurvedic texts, Rasayan etc., mangoes have been repeatedly mentioned in cases of injustice. Its special mention is found in the Virechnopan drug group and Vaya: Sthapana, Jvarahar, Kasahar and Kushtahar Dashmaniyas in Charak Samhita. In Sushruta Samhita, it has been specially used in sub-parenchyma medicines and in many types of diseases and diseases of the digestive system. At the same time, its special experiments have been prescribed to get the beneficial properties.
Charak has given a detailed description of its preparation and some chemical preparations in Muktakantha, by whose effect even old people (like Chyavan Rishi) used to become young, getting rid of diseases was an easy thing. In fact, Amla has got the best place in Ayurveda due to having more evidence of all diseases and health and healing power than other fruits. And Triphala, Amalakyadi powder, Amalaka Rasayana, Amalaka Ghrita, Amalakavaleh, Amalakayas (Brahma) Rasayana, Amalakayadhichamatkari Gutika, Dhatryanti, Ghatri Loha etc. have special plans for it.
Ayurvedic texts have mostly been followed in Greek texts regarding this. Even the Arabic name ‘Amlaj’ and the Persian name – ‘Amlah’ are just translations of Sanskrit ‘Amalak’. Unani medicine uses like Jawarish Amla, Jawarish Amla Luluvi, Anashdaru Mada, Anoshdarululbi, Rogan Amla. There is a special plan for this in Itrifal etc.
Westerners are slowly getting full knowledge. Do the experiments of its root and flowers. They are trying to manufacture decoction of its leaves and seeds, font or mandira (shraav), fixed and volatile oils, and a kind of decoction from its root or bark.
There are two types of Amla- (1) the gardeners and (2) the wild ones.
The gooseberries that are planted in the garden are of two types, Biju (those born from seed) and Kalmi (those planted by cuttings). Beeju fruits are small; Kamli has very big fruits, these are called Rai Amla, Shah Amla, Amalju-Malak. This Amla of Kashi or Banaras is famous. These Banarasi Kalmi Amlas are guava-sized, very pulpy, fiberless and with very small kernels.
Even in wild gooseberries, some fruits are small and some are big. They are fibrous, have little pulp and large kernels. In those fibrous, Ayurvedic Nighantu, these wild mangoes have been called by the names ‘Kashthadhatri, Kshudramalak, Karkat etc.’ In common parlance, these are called Anvari, Kath Amla etc.
Sanskrit- Amlanka, Dhatri, Vyastha, Trishyaphala etc. Hindi – Amla, Amla, Awra, Auda etc. Marthi – Amli, Aval Kathi. Gujarati – Amlanunjad! Bungalow-, Ambolta. English – Indian Gooseberry, Emblic. Myrobalan | Latin- Phyllanthus Emblica, Emblica Officinalis.
Generally, its yield is more in the tropical regions of India, especially in North India, Awadh, Bihar and eastern countries, in pebble and stony land. In the foothills of the Himalayas, from Jambu to the east and in the south to Ceylon in the coastal regions, both wild and rebellious mangoes are found in abundance. It is also grown in abundance in Kashmir and Bangladesh.
The seeds of Amla are of medium size and the wild ones are slightly bigger than this. Its trees are found up to 20 to 30 feet in Rajputana and 15 to 20 feet high in Kathiawar. The tree of Kalmi Amla is smaller than Beeju and has some special long branched spread.
The trunk of a tree is not simple or straight. The wood is white and strong with some tinge. There is very little substance in it. The peel on top of the wood is of ash colour, quarter inch thick. And keeps on descending every year. The leaves are like Shami leaves or tamarind leaves, but some of them are about half an inch long.
Fruits- In the spring (Chaitra Baishakh) only after autumn, very small mustard seeds of greenish yellow color appear in jam clusters on the branches. They have a mild fragrance like lemon flowers. Male flower is stalked and female flower is stalkless or very short stalked. In the month of Bhadrapada, the fruits get frozen in place of the female flowers.
Fruits- The said fruits grow somewhat in the month of Kartik and mature till the month of Falgun. These vessels are divided into 6 equal parts by a thin line like the papery lemon of green color, like cheeks, smooth, anus and thorn.
At first some astringent sourness remains in the taste, later sweet taste comes. Chewing them and drinking it gives sweetness in the power. The peel on top of the fruit is very thin. Inside there is a hard kernel with six raised clefts.
Beeju and wild gooseberries start ripening in the month of Pausha, but they do not contain as much juice as the ripe teal gooseberries from Magh to Chaitra. Therefore, teal gooseberries are only beneficial for medicinal purposes. Beeju or wild gooseberry varies in weight from 1 tola to 1½ or 2 tola. Kalmi Amla is seen more than 5 tolas. But it often comes more in the work of marmalade. In this, some deficiency of medicinal properties is found in comparison to Biju Amla. Banarasi Kalmi Amla is considered the best, but due to their less yield than consumption, they are brought from other places and sold in the name of Banarasi. These are often sold after breaking them in raw condition. Mature Banarasi Amla is rarely available. Ripe Indian gooseberry is the best remedy for marmalade or for other medicinal purposes.
Dried Amla- Dried Amla after collecting in unripe state, is like a wild berry or a little bigger than it, hexagonal, wrinkled, beige or black in color. Amla dried after collecting in ripeness is yellowish-grey in colour, and it gets divided into 6 parts under a little pressure. In each part, a part of the pulp and kernels, contains triangular colored seeds. Keep in mind, every year best ripe semi-ripe mangoes should be collected at the right time of the season and spread on a mat to dry in the sun. Market dry mangoes are often devoid of essence.
Seeds – There are three cells in the kernels inside the mango, and two triangular seeds are found in each cell. These are also used in medicine. Oil is also extracted from them.
Amla leaves are called ‘Shatpatra’, they are offered to Lord Shiva. And worship and Yagya are taken in the work. Its root and wood are used in place of sandalwood; Rubbing it with water, sandalwood is taken out and offered to Lord Shiva. Bark, leaves, flowers and fruits are also used for dyeing purposes. The best black ink is made from dry fruits.
Harit Dhatri – amla-astringent, slightly acid-bitter, sweet, cool, light, dry, tridoshnashak (it destroys acidity, bile from sweetness and coolness, and phlegm from astringency and dryness), diarrhea, hair Beneficial and distasteful, burning, diarrhea, swelling, poisoning, thirst, obesity, nausea (nausea), agitation (afra), urination, confusion, acidity, kaas, phlegm, labor (fatigue), disorders (constipation), leprosy, blood disorders, blood bile etc. It is a choleretic disease and a geriatric chemical. Brihan is semen generator and semen killer.
Dry Amla – somewhat bitter, sour, pungent in cooking, sweet, astringent, connecting broken bones, metallic, beneficial to the eyes and hair, enhancing the radiance of the body by poultice and bile, cough, thirst, sweating, obesity, It is a poison and tridoshak.
Due to irregular diet, when pitta gets agitated, pimples or red spots appear on the body, itching continues day and night – in these and various types of Tvadoshas, vicarchika, lumps, leprosy, gout, discharge, etc. containing amla. Taking any medicine, such as Chyawanprasadi or only Amla Churna, purifies the blood, calms the false heat inside the body, heals very old canker sores and ulcers quickly. It would be better if you also bathe with gooseberry water. It calms itching, burning and burning sensation. Shamragya of giving amla in diseases of chronic bile nature, blood bile, arsh pandu and decay etc. Mixing honey or sugar in gooseberry juice calms bile, hikka, nausea, vomiting, trisha, etc., due to which it is suitable for use in acute bile outbreaks.
Consuming Indian gooseberry in semen proves to be extremely beneficial. This bile destroys all the semen defects. It sort out the heat of the semen, and makes the semen strong and capable of holding semen.
In chronic diseases of many days, dried Indian gooseberry is more beneficial as a purifier and fresh Indian gooseberry juice gives immediate benefits to the new patient. There is a lot of gallic acid in dried mangoes, so it is especially useful in raktatisar, amatisar, arsh and raktpittadi chadi. Consuming it with iron ash has special benefits in Pandu, Kamla and Ajirna.
If the eyes are red, itchy etc. due to the heat in the head, then the use of Amla externally gives quick benefits. Hair becomes soft by applying ground dry gooseberry or gooseberry oil in water. There is a kind of black color in mangoes, so white hair turns black if Amla Ayukta is applied. That’s why it often falls in hijab.
By the way, except for salt, all other juices are in Amla, however, due to the predominance of acid and astringent in it, it has a digestive and astringent effect. It is a specialty that its acid does not irritate the mucous membrane in any way, due to which the velocity of Kasadi increases or by creating acidity in the intestines, it provokes bile. That’s why consumption of Amla in the beginning, middle and end of the meal is extremely beneficial.
The properties of Amla are found to be similar to Haritaki, but there is antagonism in the semen. Amla is cold-blooded and Haritaki is hot-blooded. Amla with its special effect destroys blood bile, diabetes etc. But Haritko cannot do this work. The person who regularly consumes different types of food items made from the combination of Amla and Moong, he does not suffer from diarrhea, urinary retention and phlegm and also leprosy. Amla is the only useless medicine to get rid of gonorrhea.
Eating green fresh fruit of gooseberry makes the mouth delicious. Drinking water after eating fresh fruit in summer makes the water taste sweet, quenches thirst and cures confusion. Dried gooseberry holders are useful and best in all types of bleeding, abdominal disease, blood diarrhea and acidity. Green gooseberries are not available in twelve months, so it is customary to keep them dry. In the absence of green gooseberries, dry gooseberries are treated.
Raw, roasted, boiled or jammed (as per your choice) Amla should be eaten in the beginning, middle and end of the meal. Mixing amla in curd and eating it removes Abhishyandi defect of curd. And cures heat, bile and blood defects. You can eat curd along with gooseberry in the night as well, there is no problem. But keep in mind that the use of gooseberry is not beneficial in major diseases and obstetric disorders.
Due to the effect of amla and cold semen, it removes the heat and pungency of the blood and with its purification properties, it purifies the blood by removing the poison, sewage etc. inside the blood and also benefits the color of the blood metal. Corresponding to the blood, when it enters the flesh metal, it ignites the fleshly fire and destroys the feces of the flesh and purifies the muscle cells. After entering inside the bones, it makes the Shukra metal pure by reaching the marrow and semen and also strengthens the vatanadis. That’s why Amla has been considered as the best chemical and age or stage maker. It is the most important among all the remedies in the world and Haritaki is the most important among all the medicines that cure diseases.
With the consumption of Amla, as mentioned above, the dirty or dead atoms come out of the seven metals of the body and new strong atoms enter in their place. That is why both health and youth are attained. Diarrhea, urinary obstruction and blood disorders do not occur. The work of gooseberry is also done in the eye organs, urinary system and reproductive system. That is why it is used in various eye diseases, gonorrhea and leucorrhoea.
Chemistry of modern Europe, America etc. countries – 1-According to scientists, blood is the life of every living being. As long as this blood remains in a pure condition capable of nourishing, till then no disease can arise in the human body, nor can old age enter. But due to the opposite diet, when alkali, acid and worms etc. foreign substances get accumulated in the blood in less and more quantity, then the blood cannot operate the nutrition of the body equally, due to which many diseases arise in the body and old age due to loss of strength. starts.
If a man is able to remove the foreign elements gathered in the blood by some means, then he can attain youth by conquering all diseases and old age. To remove these foreign elements, chemists have invented three things after years of research. He has revealed that this quality only Safranjan, Olive these 2 things are not produced in India. (Safarjan is known as Safarchand, it is a Kashmiri small pear. It is abundant in India). In such a situation, the announcement of these qualities in Amla by our Charkadi sages was completely scientific. Due to these invaluable qualities, the ancient Nighantukars have addressed it with holy names like Shiva, which means welfare, Vayastha, which means maintaining condition, and Dhatri, which protects like a mother, etc. and has given it the highest place among chemical medicines.
Juice – Fresh juice is soft, mild, diuretic, ophthalmic. By drinking cow’s ghee mixed in amla juice (if there is leprosy, mix Nishodh powder in it) in Visarp disease; Consuming Cath juice, peepal powder and honey mixed with juice in Hicca disease; Honey mixed with this in urine, whiteness, polyuria; Drinking it after sprinkling it with aloe in fever; By drinking cooked in old cow’s ghee, in the blood; Drinking mixed in fresh Goughrit causes fainting disease and semen loss; In cholecystitis and vaginismus by drinking sugar and Egyptian; Consuming old jaggery mixed in gallstones; Mixing sugarcane juice in it, proved aloe in gall gulm; Drinking it mixed with sugarcane juice, dyspepsia, burning sensation in stomach, acidity. Mixing turmeric powder and honey in it and drinking it in all the premeha; Mixing white sandalwood and honey with it and drinking it in vomiting; By licking it mixed with ripe banana, honey and sugar candy, in women’s disease; Mixing honey and peepal powder in hiccup and breathing; Mixing honey, ghee and milk in blood dyspepsia; Drinking turmeric powder mixed with bile in urine; And only its miraculous juice is beneficial in impure mica-borne disorders by drinking it for three days. And mixing bividang and licorice powder and honey mixed with juice for one month increases age and strength. Along with this Krishna Sarpavasa and honey mixed in the eyes, it is beneficial in eye diseases.
Fresh Indian gooseberry is anti-diarrheal, diuretic and antiphlogistic. Along with this, the proven Kwath mixed with Giloy and Motha is digestive of defects, trisha, distaste and mukha virasya. A concoction of moong dal strained with ghee, mixed with sugar, removes thirst and induces sleep and sweating. Mixing curd with it and eating it in blood bile; Consuming sugar mixed with acidity, distaste; in excess of thirst after eating it mixed with salt or sucking it in the mouth; Consuming old jaggery mixed in gallstones; Eating dry grapes and sugar mixed is beneficial in vomiting. After roasting it in ground and mashing it, mixing it with ghee and sorghum, adding salt and drinking it after flavoring it with fragrant incense, inflames the gastric fire. Its marmalade or pak made with silver work and drinking milk on top of it cures heart disease, gonorrhea, leucorrhoea, constipation, impotence, gall disorder and weakness and fever after the disease. Grinding it and applying it thickly under the navel in urinary retention; And its consumption and coating gives special benefits in inflammation called Jalgardabh. Grinding fresh or dried Indian gooseberry in water and massaging it on the body and taking a bath cures bali palit disease (wrinkles in the body and whitening of hair) in a few days.
Kashtha-Dhatri (Kath-Amla) – Sweet- astringent, charari, cool and removes the defects of blood bile.
Kakat (small gooseberry) – , appetizing, super-deepening, mild, beneficial to the eyes, cool and anti-cough.
Both of these are used after drying.
Dry amla- fried in aloe and grinding in water, applying it on the navel stops the blood coming out of the excreta. By burning it and rubbing it in oil, or by mixing it with boiling water and taking a bath with hot water, itching and itching go away and the body’s radiance increases. By giving its powder with lemon juice in blood dyspepsia; Consuming it mixed with honey or sugar causes gallstones, acidity and leucorrhoea; giving dry ginger powder mixed with curd and honey causes diarrhoea; Headache after consuming ghee and sugar mixed; Consuming cow milk resulted in dissonance; If you eat sugar mixed in fried in red oil and drink a little hot water on top of that, then in blood bile; Consuming Kadli juice mixed with acidity; Consuming twice the amount of sugar and ghee mixed, then there is bile outbreak; And consuming sattu mixed with barley is beneficial in obesity. Consuming equal parts sesame powder mixed with ghee and honey daily in the morning for 20 days cures heart palpitations. Wisdom increases and a little disease gets destroyed. Asgandh powder mixed with powder, Ghee and honey increases body’s radiance in winter. Soak the powder in cow urine at night, grind it in the morning and mix coconut water and apply it on the body, it is beneficial in gallstones. Mixing the powder of logha with the powder, grinding it and applying it on the ulcer, and by rubbing it or rubbing it, the torn anus and the ulcer of the anus go away. Rinsing the vagina with decoction of powder and taking the powder with honey or sugar candy at both the times is beneficial in leucorrhoea.
Kwath- Mixing jaggery in decoction of decoction and drinking it cures blood bile, burning sensation, colic, urinary retention and tiredness. Mixing fragrant white sandalwood and honey mixed in its decoction is beneficial in oppression. Drinking curd and Trikatu powder mixed in Yup prepared by mixing grapes with powder lubricates the dry cell, the cell becomes soft. Ground fresh Kush-root mixed with amla or dry amla powder is diuretic, savandhanya mixed kwath is virukshan or traction and when mixed or mixed with peepal, kwath or drink is beneficial to the throat and kharbhang or yamak hikka respectively is beneficial in.
Seeds or Ming- The seeds which are in the kernels of Amla, they are astringent, sweet, seminal and leucorrhoea, suppression, talk, bile, fever and kaas, respiratory killer. Bhavmishra ji says that whatever fruits and qualities are hot or cold, the same is the quality of the meringue of those fruits.
Grinding the seeds mixed with sugar and honey and consuming it provides relief in leucorrhoea and leucorrhoea, and licking the powder of seeds and red sandalwood mixed with honey provides relief in distress (nausea). Licking the seeds mixed with ground honey repeatedly is beneficial in polyuria. Raisins and sugar mixed with seeds and making Gandush (Kullae) on its own, removes the dryness of the mouth that occurs after fever. Grinded kanji fried in ghee in seeds and applied on the forehead provides relief in epistaxis (bleeding from the nose). Grinding the seeds and boiling them in water and filtering them and washing them is beneficial for many days of sore eyes.
Leaf- and indigestion and diarrhea are decades. By applying juice extracted after grinding and squeezing the leaves of Indian gooseberry, the ulcer or wound becomes clean and heals soon. Grinding green fresh soft leaves and consuming it with butter, curd or fresh buttermilk is beneficial in indigestion and diarrhea. Mixing a little water with camphor, grinding the leaf and applying it on the head is beneficial in nosebleed and boiling the leaf in water and gargling with that water is beneficial in ulcers and ulcers inside the mouth.
Flower-They are cool and soft. It is used in oral form with other medicines.
Bark – The customer is hesitant. Grinding black pepper and clove in bark juice and giving it is beneficial. The root or the bark of the root is ground in water and applied on scorpion’s bite or on inflamed swelling.
The fresh fruit of amla being astringent, diuretic and laxative, is beneficial in chronic constipation etc. abdominal diseases. Dry Amla – It is cooling, digestive, astringent and stimulant.
A paste made by grinding gooseberry well with saffron, neelkamal and rose water is beneficial for headache. Its poultice is done on the habitation area in urinary retention and urinary retention. A sherbet made by mixing mango juice and honey in water and mixing it with crushed mangoes is given in place of water, especially in fever and diarrhoea, it quenches thirst. Like Khadirsar (story), the essence of amla wood is extracted. It is astringent and columnar. This essence is used in cough and diarrhoea. By putting branches or wooden blocks of amla in dirty water, the turbidity of the water gets removed and the water becomes clean.
In Konkan juice of fresh bark mixed with honey and turmeric is given in gonorrhea. Dry mangoes soaked in water overnight and filtered in the morning, cumin powder and sugar mixed in it for taste are given on bile disorders. Sharbat prepared by mixing honey and sugar in amla fruit juice is the best drink for patients, it is said to be diuretic.
Amla wood does not rot in water, that is why Neemchak etc. in wells are made of it. Leather is also taught with its leaves. In Baroda, fenugreek along with its leaves is ground and mixed with water and given in Paratan Pravahika. Pati Tikt Bal (Bitter Tonic) is considered. Wife’s juice is considered best for infected wounds.
The fresh fruit of Amla (in Turkistan) is used in pleurisy, and is used topically in conjunctivitis. In Persia, its fruit is used as an anthelmintic, for this purpose the juice of its fruit is often mixed with honey and given in the quantity of 1 to 3 drams. The font of its seeds is given in diabetes and in febrile form. The same font is also useful in eye drops and other eye diseases. The juice or extract of its fruit, mixed with honey and pepper powder, is given through Hikka door in painful respiration. Dry fruits are soaked overnight in a new earthen pot and put in the waking eyes in the morning after filtering. The dry fruit is useful in haemorrhage, diarrhea and diarrhoea. Its use with iron is especially beneficial in anemia, pandu or kamala and indigestion. Liquor prepared from its root is useful in Pandu, Ajirna and Kaas Prabhriti. Ghee mixed with fresh Indian gooseberry juice is a good remedy.
Amla powder and myrabalan powder 4-4 drams, and Rebandchini powder 1 dram, the decoction prepared by cooking these three in a pint of water is laxative and diuretic. It is given to the patient in ounce quantities. (1 dram is about 31½ masha and 1 pint is about 51 tola). Grinding the bark of the root with honey is used as a mouthwash etc. in diseases of the mouth. A decoction of the leaves is useful for mouthwash. Amla seeds, Chitrakanmal, Harad and Peepal, their decoction is given in fever; And the powder made by mixing rock salt with the powder of the above four substances is also given in fever. The fixed oil produced by the fruits of amla strengthens and lengthens the hair, and the volatile oil produced by the leaves is widely used in perfumery.
The fresh fruit of Amla is Deepan, Digestive, Pittasamak, Anulomic, Urinogenic, Rochan, Balya, Nutritious, Anti-inflammatory, Dermatological and Bajikar. All these qualities are found in it in more or less evidence. If a healthy, healthy person eats fresh mangoes daily, then all the functions within the body improve and the nature remains good, no harm can happen. With all these qualities, fresh gooseberry has been considered as ‘chemical’. Dry gooseberry is erect, mucus dense, shonitasthapana and there is a large amount of choleretic and srangasana.
Amla has excellent properties to reduce mucus. In more evidence, thin phlegm comes out of the mouth and nostrils, and decoction of dry amla, barberry, turmeric, giloy and licorice is given in gonorrhea and leucorrhoea. Decoction of dried Indian gooseberry and turmeric is given in Bastisoth. With this experiment, the turbidity of the urine is removed by clearing the loose motions. Consuming this decoction in the condition of cholecystitis, bile comes out through stools, and the patient gets peace. In the case of heavy periods, about 1 tola of dry amla powder is given with honey 3 or 4 times a day.
The use of Amla fruit on many diseases is described in the medical science. But my Guruvarya late Pt. Bhagwan Lal Indra ji believed that amla fruit should not be used at all for heart disease. The reason is that its effect slows down the work of the heart.
Ripe fruit of Indian gooseberry contains tannic acid in very less quantity as compared to unripe fruit. But in its leaves, this acid is found in the proof of 18 percent. That’s why Professor Hryumal used to say that if dried and powdered mango leaves are sent abroad, they would be sold immediately.
The complaint of indigestion is often found in women. In my opinion, they should use mangoes in a variety of ways. It cleans the stool, like other fruits, it does not even cause loose motions. There is no complaint of constipation due to its use. By using Amla in the morning, taking Amla chutney etc. with food, eating Amla Murabba or Chyawanprash after the meal, the disturbances that occur after the meal have to run away. These types of experiments are successfully researched on pregnant women. Use of Amla along with Banslochan provides relief in fever, constipation and vomiting of pregnant women.
If a diet of only fruits is kept during the period of use of amla medicinally and food intake is stopped by reducing it, then starch gets great power, therefore, to remove chronic inflammation and constipation and weakness of starch, light digestible fruits should be taken. Amla should be used methodically with food.
Amla has a unique power to remove the bad scum of the kidneys. Scholars have given the name of Amla in chemistry with great thought and understanding. The stool accumulated in the kidneys is easily destroyed by this. But for this situation, juice of ripe mangoes should be taken with sugar syrup, or with other necessary preparations. Boiled water of mangoes is also fine, but it is beneficial only in one tenth of the juice of fresh fruits.
It has been proven by experience that amla is bile-killer, removes the heat settled inside the fever, removes the inflammation caused by the rotation of the sun and is beneficial in burning of the eyes. Weakness caused by a little effort, menstruation on the days of menstruation or for a long time is cured by this. Amla should also be used in insomnia of traveller, indigestion and other diseases related to it.
I have seen many doctors and healers that they use only Amla or Triphala snow in the medicine of Pichkari to cure Gonorrhea. In eye disease also, a decoction of gooseberry or triphala alone is sprinkled. Eyes are washed in its decoction and opened and closed. In sermons, a decoction of amla is given to open the penis, ulcers are also washed with amla’s decoction. If the urine turns yellow, then sugar is added to the ice of amla.
Amla squash should be drunk to avoid heat in summer. If squash is not available, sort out the dry gooseberries and clean them. Separate the kernels and wash them in water to get rid of the soil. Soak it overnight in a glass jar or blank pot. Filter it in the morning. Add salt or drink it like this. People who are rich and fond of new ideas, who do not like old methods and old things, can mix sugar or honey in this cold remedy (ice) of gooseberry and keep it in ice and drink it after cooling. People who suffer a lot due to heat, discharge a lot of bile, lose their appetite and are always restless due to thirst, they should drink this cold water of Indian gooseberry every morning.
The higher amount of ‘C’ vitamin remains in Amla, possibly not in any other fruit. Fresh gooseberry juice contains 20 times more ‘C’ than orange juice. In one gooseberry, ‘C’ remains equal to one and a half seer oranges (big oranges). Heating, cooking or drying of fruits and vegetables destroys most or all of their vitamins. But Amla is an exception to this topic. Its life essence does not get destroyed even after cooking. Due to the extraordinary situation caused by the war, when there is a general shortage of fruits and vegetables, and the common man does not get enough of this essential substance (Vitamin ‘C’) for life, then we have the most resources to meet this deficiency. Amla fruit is cheap and widely available.
Like fruit drinks (squash) made from the juices of many fruits are being sold in the markets, similarly gooseberry squash is not being prepared. I would advise people doing fruit preservation work on a large scale and manufacturers of squash etc. fruit drinks that if they keep gooseberry squash in the market like mango, orange, lemon etc. It will be a good profitable business for the manufacturers.
By washing the face with gooseberry snow, the pimples, pimples etc. of youth go away. Grinding gooseberry and sesame seeds soaked in milk or water like a boil and rubbing it removes smallpox spots, etc., and the glow of the body increases, the face starts shining. Grinding amla and applying it on the affected part calms the headache caused by bile or after surgery on the throat or nose.
Those whose blood reaction is acid, or those who feel heaviness in the stomach after eating rice, or who have pain in the joints after eating sour foods, then the use of Amla is of little benefit to them. In such a situation, if you have to use Amla in any form like Chyawanprash, then never give milk along with it. Milk can be given after half or an hour.
If the pulse of the heart has increased especially, the digestion process is slow, then it should be used with great care. It is not good to consume it in excess. In such a situation, the quantity of its powder should not be given more than 1 or 1½ masha. Consuming it in small amounts for a long time increases the heartbeat excessively.
Those who have indigestion, constipation or agitation, have frequent nausea, and are addicted to betel nut, tea, beedi etc., then leaving these addictions gradually, instead of eating fresh or dried mangoes daily, and By making tea or sherbet and drinking it, all the above complaints are removed and there is a complete improvement in nature.
Cut the worm-free and moist (juicy) tree of Amalak Kalpa-Palash (Dhaak) from the top of the stem (slightly above the root) (cut at least 1. or 2 hands above) the parts attached to the ground. Make a pit two cubits deep in such a way that a two-inch edge is left around it. Then fill freshly ripe big gooseberries in this pit. Close the mouth by plugging some part of the stem which was cut from above. And tie the best leaves of Palash around the root and wrap it with darbha (Dabh). Apply a thick layer of soil (about a finger) of lotus root on it, dry it normally or keep it as it is, put cow dung cakes around it, and set it on fire. Keep in mind that this work should be done in a vacuum. For this, a wall two or four cubits high can be erected around it. If the mangoes are cooked for two or three hours on such a flame, then take out the kernels and mix them in the perfect ghee, and then add equal amount of honey and keep it safe in a glass amritban.
After eating it to the fullest, drink cooked milk as much as you want. Consume it for one month. Stop all types of diet. During this experiment, keep abstinence completely, do not touch cold water even with your hands. By doing this experiment in this way, hair, teeth and nails fall after 11 days, and after a few days new hair and hair are born and the body becomes beautiful. Women’s intercourse has immense power. Strength, intelligence, intelligence and mental power have special intelligence and longevity.
Note- According to the method, it is essential to purify by Panchakarma before using it and follow the rules completely by Kalpa method. From a religious point of view, in place of honey, some sherbet, amla sherbet, Nilofer or Banafsa or old jaggery syrup is prepared for this experiment or other similar experiments. But the best qualities are attained only by honey.
Other method- sweetening the mangoes with the help of Palash tree, take out the kernels and shade dry them into powder. Quantity – From 3 mashes to 2 tolas, consume milk, ghee, honey, fat (sweet oil in its place) and sugar mixed. Do diet of Yavagu on top of this. And do rubbing on the body mixed with yaw powder and ghee. This experiment also provides youth and longevity. It is very beneficial for tuberculosis or decay.
Fill 1000 good quality mangoes in a pot covered with a wet wooden lid, close the mouth tightly and cover it with a woven cloth or cloth, and keep it on a soft fire of cow dung cakes. When the mangoes test the same, then when it cools down, take out the kernels, churn the pulp well. Now, if this anus is 8 seers, then add 4 seers of peepal powder and 2 seers of sugar and up to 4 seers of Bibidang powder and mix honey, ghee and sesame oil 8-8 seers well, fill the ghee in a smooth pitcher and keep it safe for 21 days. After following a proper diet, consuming it properly can lead to a ageless age of 100 years.
Fill one thousand well-ripened mangoes in a pot which has many small holes in its bottom. Then put milk in the second pitcher and place the pitcher containing Amla on it and close the joints of both of them with flour. Put only so much milk in the pot of milk, that it cannot flow into the pot above when it boils. Put them on slow flame. By this process, the steam of milk will go to the same place. Then take them out, take out the kernels and shade-dry the pulp and powder it. After that, mix 1000 fresh mangoes in this powder (i.e. mix it with swaras and grate it so much that all the juice dries up). Then put Salparni, Punarnava, Jeevanti, Gangren, Brahmi, Manduki, Satavari, Shankhpushpi, Pepper, Bach, Baibidang, Konchbeech, Giloy, Lalchandan, Agar, Mahua flowers, Neel Kamal, Malti flowers, Rose and Juhi flowers in it. Sambhag powder (whose weight is one-eighth of that Amla powder) and give it to all 2 || Give the feeling of swaras of mind nag bala. After drying, grind it and mix two parts of ghee and one part of honey in smooth pitchers of ghee, keep the pitcher on the mudra (dig a pit in the ground, spread the ashes of 16 fingers of cow dung cakes in that pit), and fill the whole pit with cow dung cakes. Fill it with ashes. After 15 days, take out the pitchers and keep gold, silver, copper, coral and iron ashes mixed in proper quantity in that medicine.
By consuming this chemical in proper quantity according to strength and having a sattvic diet, a person becomes healthy, long-lived and extremely talented and regains his lost youth. (Charak)
If all the above is not possible, then in the same way, take out the kernels of the gooseberries, mix the same amount of fresh mangoes in the shade dry powder and add fresh ghee twice as much as the powder, and then equal parts of all the best. Mix honey and keep a smooth pitcher or amritban, just the chemical is ready. Gradually increase the quantity from 2 to 5 tolas. Do only milk and rice diet on this. It can be increased up to 10 tolas. Keep only rice and milk in the diet. This destroys all diseases, increases semen and gives strength to the stomach, heart, brain and other senses. This experiment can be done after Makar Sankranti till the end of Chaitra.
Fine powder of new dried gooseberries 1. Take 8 seers of fresh gooseberry juice and dry it by giving as many feelings as you can. Then mix Gaughrit and honey 15-15 seers, 15 tolas of pippali powder and 20 tolas of sugar candy in it and fill it in Amritban and press it inside the keep at the beginning of the rainy season. Take it out after four months and use it. Quantity – from 2 to 4 or 6 mashes. By consuming this, peace of all diseases, increase of enthusiasm and memory power, destruction of impotence and youth is maintained for a long time. Consume it while following a diet for one year.
Amla powder mixed with 5 tolas of pippali powder in 15 seers, after giving 7 feelings of fresh gooseberry juice, dry it and fill it in a bottle of fine kharal. Dose – Consuming 15 to 3 grams of ghee with sugar or honey removes dyspepsia and physical weakness caused by weakness of the liver.
Grind new dried Indian gooseberry to powder with a fine cloth and keep giving the feelings of fresh Indian gooseberry in it daily for 21 days, and keep drying it in the shade. After that fill it in the bottle. Quantity: 1 .. From 1 to 3 months, with cow milk and sugar, consuming it twice a day in a dietary way, quickly pacifies the pitta, removes weakness, and intensifies sexual power.
An Unique Experiment – Charkacharya ji says that for one year Jitendriya remained celibately meditating on Gayatri in the midst of cows only on milk food. After fasting for three days on the best dates of the month of Paush, Magh or Falgun, enter the forest of mangoes (on the full moon day). After reaching there, climb a mango tree full of good big fruits and chant Brahmamrit mantra by taking a mango tree from a branch in your hand.
Until that Amla becomes a nectarine mantra and becomes as sweet as sugar and honey and soft. In this way, when there is good communication in Amla , eat it. The more nectarine mangoes are eaten at this time, the more youth you will get for a thousand years. If such gooseberries are eaten at this time, then man becomes like a god and Saraswati herself always stays near him.
Brahmarasayana, Amalkayas Rasayana etc. are described in Charaka Samhita etc.
Mango-lakavleh- (a) Take as many small peppers as fresh best mangoes are in number and immerse both of them well in Palash Kshar only water. When the alkali water enters them well, then take them out, separate the kernels of the mangoes and shade-dry them to make powder. Mix four times the weight of this powder with honey and ghee respectively. Then mix one-fourth of the fine sugar by weight of the powder, fill it in an earthen pot impregnated with ghee and bury it in the ground for 6 months after making a mudra. After taking out, consume this avleh with milk in the quantity of 6 masha to one tola and eat satvik food. This too is not a prior. Former force increases semen and life.
(b) 4 seer juice of pure mangoes on low flame. Simultaneously, mix peepal powder, 1-1 paan (20-20 tola) of grapes, licorice, peeled ginger and Banslochan 2-2 tola and sugar candy 50 tola. When it becomes thick syrup, take it off and let it cool down. Mix the best honey and keep it in the Amritban.
Mix four times the weight of this powder with honey and ghee respectively. Then mix one-fourth of the fine sugar by weight of the powder, fill it in an earthen pot impregnated with ghee and bury it in the ground for 6 months after making a mudra. After taking out, consume this avleh with milk in the quantity of 6 masha to one tola and eat satvik food. This too is not a prior. Former force increases semen and life.
Quantity- 2 to 4 tola or consumption as per requirement destroys halimak, kamala, pandu disease, water disorders and diarrhoea.
(c) Boil the gooseberries well and separate the kernels. Then mix equal parts grapes and dry ginger with that pulp and grind it very finely. After that, mix half a portion of honey in it and keep it. Licking a little bit several times during the day and night provides relief in cough, shortness of breath and fainting. The detailed description of Chyavanprash Avaleh is available in Charak Samhita etc.
Your section – (a) Fry 211 seers of boiled amla without seeds in 64 tola ghee. Then mix 32-32 tola juice of sugar candy and mangoes, and 64 tola juice of petha and cook it. When it starts to be applied with a ladle, add 8-8 tola powder of pepper, cumin, dry ginger, black pepper each, talisapatra, coriander 4-4 tola and grind 1-1 tola of cinnamon, cardamom, Nagkeshar, bay leaf and motha. Mix and take down. When it cools down, mix 32 tola honey in it and keep it safe. Consuming quantity – 1 to 211 tola destroys tridosha generated result colic, vomiting, unconsciousness, breath, cough, anorexia, heart colic, colic and blood bile. This is also a great chemical.
(b) 32 tolas of best gooseberry and boil it and put the kernels in it. Then grind them in two seers of milk and roast them in two seers of ghee, and after mixing two seers of sugar syrup, add 16 tolas of Adusa powder and 1 tola powder of cumin, black pepper, peepal, cinnamon, cardamom and bay leaves. Keep it safe in a container.
Quantity- to 2 tola destroys Duray Dah, unconsciousness and chronic vomiting disease.
(c) very ripe tanturhi mangoes with a conch shell, as is done in making marmalade, (In our country, people do not do this and separate the kernels by cutting the mangoes with a knife). After that, add sugar or jaggery to those mangoes Keep the dishes in the sun in the utensils of. When the juice dries well, then keep that vessel safe in the shade. This is called ‘Aditya Pak Amalki Khand’. Drinking water after eating it during summers reduces thirst and cools the heat.
Amalkyadi Ghrita-(a) Mix 4 seer Gaughrit and 1 seer Punarnava’s kalk in 16 seers of good fresh color and juice of mangoes and cook. When only ghee is left after filtering and cooling down, in that ghee – now Bidarikand Swaras 16 seers and kalk of Jeevanti. Mix it and cook it, and after filtering and cooling down when only ghee is left, cook 16-16 seers of cow milk and bala and atibala in the same ghee, and mix 1 seer of Satavari’s kalk. By cooking in this way a hundred or a thousand times, wonderful seminal ghee is proved. Then mix one-fourth part sugar and honey in it and fill it in a strong, clean and smooth pot made of gold, silver or clay.
Consuming it regularly in the morning in an appropriate quantity and after digesting it, eating Shali rice with milk and ghee, maintains youth up to 100 years, and destroys all diseases. By removing impotence, the ability to beget children is attained. Charak!
(b) First take 16 each of the roots of Kans, dabh, black sugarcane, echo and khus and boil them in 8 seers of water. Sieve 64 tolas of remaining water, and add 64-64 tolas each of amla juice, Vidari tuber juice, satavari juice, cow milk and ghee and cook on low flame. When only the dead body is left, after taking it down, add 4-4 tola powder of licorice, Nishat, Yavakshar and Vidhara and 32-32 tola sugar and honey and keep it safe. This is called ‘Brihad Dhatri Ghrit’.
Quantity- After consuming 1 to 2 tola, Ashoka, Giloy, Adusa root bark, Daru Haldi, Nagarmotha and red sandalwood, drinking decoction made of their powder strengthens the body of women, and destroys all types of leprosy.
The description of ‘Mahatikta-Ghrita’ etc. is available in the scriptures.
Amla – Pak – (a) 500 pieces of the best ripe ripe mangoes and put them in an earthen pot, and in the same vessel add 10-10 seers of milk and water and cook it on a low flame. Take off the milk and a quarter of the remaining water (gooseberries should be thoroughly washed before boiling), then tie a strong thick strainer on a tinned utensil, and mash the gooseberries with the remaining milk and water over it. After filtering all the pulp and coming inside the vessel, fry it well in 30 tola ghee, in which no part of water should remain, keep in mind that it should be fried on low flame only. Then prepare a syrup of two strings of 6 seers of sugar candy, mix this roasted pulp in it, cook a little more. After taking it down, mix Banslochan 16 tola, Peepal 4 tola, sandalwood powder, 1 tola ground and cardamom and bay leaf 2-2 tola powder. Keep it safe in a smooth container of ghee.
Quantity- to 3 tola, twice a day, drink hot cow milk cooked from above up to 1 pav. Those who have stomach disorders, they should drink milk after half an hour of eating it. This is the best semen enhancer, tridoshak, a type of small Chyawanprash.
(b) best ripe mangoes in water for 12 hours. Then take them out and cook them in fresh water for two hours. After it becomes soft, separate the kernels, make a pulp on the cob, filter it in a thick gauze cloth and fry it in ghee. Mix three times sugar candy in the said decoction water and make sugar syrup or Pak, mixed with fried kalak of mangoes and freeze it.
Quantity- to 4 tola. This Pak is very tasty, laxative and removes constipation. Hakim people use it very beneficially in heart and many types of digestive related disorders like acidity, loss of appetite and indigestion etc.
(c) 32 tola pulp of gooseberry after decorating it and grind it. Then after cooking it in 1 milk, when it becomes like mawa, fry it in double ghee. After mixing a sugar syrup, add Adusa bark powder and 1-1 tola powder of cumin, black pepper, peepal, cinnamon, cardamom, bay leaf and Nagkeshar and set it.
Quantity – 1 to 2 tola consumption destroys the burning sensation, unconsciousness, chronic vomiting disorders. Other culinary experiments are available in Ayurvedic and Unani texts like Jawarish Kandi, Anasdaru Lulwa, Faluliya, Mufarrah Barad etc.
Murabba Amla- a handful of ripe mangoes in lime water overnight after crushing them well with a conch shell. On the second day in the morning, keep two seers of flour in a basket on top of water and give it cold. After getting well sweated, wipe it with a cloth or Dip four stars of sugar candy in sugar syrup and keep them in the dead body. It becomes usable after 15 days. It does not deteriorate for 4 or 5 years. This marmalade is digestive, lamp, cool, anti-inflammatory, choleretic and nutritive. It softens the nature, induces pus to fall towards the stomach and intestine and is beneficial in diarrhoea, especially (Zalkul anna) and piles. But in these qualities this marmalade is weaker than myrabalan marmalade.
Unani’s special method-cook fresh mangoes in milk and keep them in the sun for the first three days. Keep changing milk daily. After washing and wiping thoroughly, dip it in honey or sugar syrup. Consume honey marmalade in winter and sugar marmalade in summer.
Sharbat- Amla- Swaras of fresh mangoes (grind them in a wooden or stone bowl to extract the swaras) One loaf and Sevati- Swaras of fresh rose flowers 211 tola to 5 tola both of them got together, 1 seer mishri was found, according to the method Cook on low flame and make sorbet. Quantity- Up to 1 tola, consumption causes pittakopap, heat stroke fever, vomiting and fainting in the navel. This sherbet is beneficial in chronic piles and prevents the discharge of pus towards it.
Density of Amal (Amalaki-Sar) -(a) Crush ripe mangoes and squeeze out the juice by putting it in a stone bowl and when the juice becomes thick, mix fresh juice again and choke it. In the same way, as much as you want to prepare, keep stirring after mixing the juice. When it becomes capable of making tablets, make tablets or dry it and make powder.
Quantity – 4 ratti to 1 or 2 masha. It is very choleretic and is able to quickly remove the increased heat due to cholera or heatstroke in summer. As soon as it is consumed, nervousness or instability of the mind goes away.
(b) the juice of fresh mangoes in bottles. After a day or two, when a greenish-white solid substance accumulates at the bottom of the bottles, then slowly pour all the liquid part above it. And dry the bottom cube and make it rough. Keep safe in the vial.
Quantity- Ratti to 1 Masha. This essence also works best in the above way.
Amalkadi Churna-(a) Amla, myrrh, peepal, chitrakamool and rock salt, if the powder is made in equal parts, quantity 1. From 3 months to 3 months, honey etc. if taken in proper proportion, then it works well on all fevers, makes the fire bright.
If amla and rock salt 1-1 part, Chitrakamool 2-part and hara and peepal 3-3 parts are made into fine powder and consumed with warm water for 1 to 2 months, it destroys dyspepsia and increases appetite.
(b)Consuming equal parts powder of Amla and Sesame seeds with ghee and honey increases speech, radiance and youth. Should be consumed for at least one month.
(c)Make powder by taking one part each of Amla, Khand Sesame and Palash (Dhak) seeds and mix one part ghee in it. Consuming it with proper amount of honey while sleeping at night destroys the sacrifice and there is immense increase in youth and strength of intelligence.
(d) Consuming only amla powder with ghee or honey or water at night increases the strength of the eyes, ears, nasal organs, intensifies gastric fire and gives youth.
Hoarseness goes away by taking only amla powder with milk for 3 months. See behind the use of other powders in the chemistry episode and in the scriptures.
Amalkyadi Vatika- Separate the kernels by freezing or boiling fresh gooseberries. It would be even better if the gooseberries are roasted in the ground. Then this roasted or boiled pulp, white cumin, black pepper, small pepper, cinnamon (Kalmi or Taj) and dry ginger 2-2 pieces, coriander, fennel and small myrrh 4-4 pieces, rock salt 1 tola, black salt 6 pieces, Everyone got 1 tola sea salt and 60 pieces of mint leaves, but grind them very fine and make 1 or 2 tablets. Eating them destroys anorexia. Appetite increases, mouth is purified, indigestion is destroyed.
Make a sauce by tightening the above boiled gooseberries on the Ghiyakas. Then mix cumin, black pepper, dry ginger, rock salt and asafoetida (fry cumin and asafoetida) in quantities suitable for making it palatable and dry it in shade by making 4-4 ratti sticks. These vati are tasty and digestive. By keeping them in the mouth and sucking them, there is an increase in redness, secretion of gastric juice and cholecystitis of the liver, Due to which disinterest, indigestion and constipation go away, appetite brightens and the mind becomes happy. If there is anorexia and agni due to deficiency of digestive juices of the stomach and bile secretion of the liver, then the consumption of these vatis gives quick benefits.
Amalkasav and Arishta – (a) Take out the swaras of 2,000 well ripe gooseberries. Mix one-eighth part of honey, 10 tolas of Peepal powder and 3 to 10 tolas of honey in a greased pot and keep it for 15 days. Filter it and keep it safe in a bottle. Quantity from 2 to 5 weights. This infusion is curative for pandu disease, kamala, heart diseases, cough, dyspepsia, dysentery, hiccups, anorexia and respiratory diseases.
Note – Chakradatta ji advises to cook the mixture of above Rasadi and fill it in a smooth pot. In that condition, it would be fine to put only the nectar of Indian gooseberry once on the fire, after it cools down, adding honey etc, to it.
(b) one seer of dried Indian gooseberry in 211 seer of cow milk for 24 hours, then rub them and squeeze them with a cloth. Add sugar and honey to it after grinding 1-1 tola of rose flowers, nagarmotha, rumimastangi, cloves, small cardamom seeds, jatamansi and fragrant one tola finely. Then after giving some enthusiasm in a galvanized vessel, fill it in a ceramic vessel and keep it for 7 days with a face mudra. This infusion will remain thick. After drinking the quantity from 6 masha to 1 tola, drink 1 loaf of cow’s milk on top of that. It strengthens the stomach, improves the complexion of the body, destroys insanity and is a juggler.
In Greek, this yoga is called Noshdarue Sadah. See other yoga in our Brihadasvarishta collection book.
Amalkyadi Loha Dhatrilauh -(a) Grind Amla, Peepal, Loha Bhasma and Mishri in equal parts or Amla, Peepal 1-1 part, Mishri 2 parts and Lohabhasma 4 parts and keep them fine. This yoga cures many diseases caused by blood purifier, Taurus, fire lamp, forceful, acidic and vatpitta.
(b) 1 part of good freshly dried Indian gooseberry powder, half part of iron ash and 1/4th part of licorice powder and fill it in Shoshi by giving 7-7 feelings of fresh green mango juice and Neem Giloy juice. Mana | Pandu, kamala, indigestion, acidity, etc. diseases are destroyed by consuming quantity 1 to 2 months. Mixing this amount with 3 ghee and 6. ghee honey before meals, the diseases of the stomach and speech are cured. Taking it after meals provides relief in sour belching, heartburn, colic and other abdominal colic.
Oil Amla-Indian gooseberry oil-this is made in many ways. One method is-
Pour Kachari, camphor amla’s swaras, algae (kai) swaras, bhangra swaras 4-4 seers, pure sesame oil 3 seers, fill all these in a large cast iron pan. Then add balachd, small cardamom, clove, cinnamon, bay leaf 1-1 tola and white sandalwood powder, khus and rose flower 10-10 tola, grind them into pulp in water and put it in the middle of the above pan. Along with Nagarmotha, Mulathi, Kamal Pushp, Giloy, Majith, Kevda root and Triphala 2-2 tola, jokut them and make a quart decoction in 8 seer water and filter it and mix it. After that cook on Mandagni. When only oil is left, take it off and filter it. Then put some benzol in that oil and let it lie down day and night. Later, mix Rooh Gulab, Rooh Kebda, Rooh Hina, Rooh Motiya, and Itra Maulsari 6-6 Mashe and Sat Pudina, Rooh Khus, and Rooh Dawanmast (Katli Champa) 1-1 tola well and put a stopper in the bottle. By applying this, the hair becomes very soft and after applying it for a day, its wet smell remains for many days. Hair grows by applying it always and never turns white. This is the only unique medicine for all types of headache, balkhora, fainting, vertigo, etc., for all types of diseases caused by weakness of the brain. This is a self made experiment of Ayurveda Vishwa Koshkar. He did not write the complete method, we have disclosed it on our behalf.
Very simple method of oil – ‘s juice mixed with equal parts coconut oil or sesame oil in 1 seer, cook on Mandagni. When only oil is left, take it down and mix dried leaves of fragrant pandi (five) in it. Filter it after 2 days and use it. It cools the head, darkens and protects the hair.
Diarrhea and polyuria – (a) Sieve the bark of Indian gooseberry tree or grind it to extract swaras. Then grind the leaves of Indian gooseberry with water and squeeze out the juice and grind the fruits of Indian gooseberry to extract juice. Take these three swaras together and cook them in a tinned vessel. When half is left, then after cooling down, filter it and fill it in a pure, smooth pot, mix half a part of it with honey and the powder of milk flowers, and keep it with your face. Filter it after 7 days and use it. Quantity 1 of 3 Mashes|| After consuming up to a tola, drink Dharoshna cow milk on top. It is especially beneficial in gonorrhea and diabetes, but the patient should follow the diet and keep exercising
(b) classical experiments, in the context of Amla’s chemistry, it has been asked to fill in bottles by giving 21 feelings of Amla juice in dry Amla powder. If fresh Indian gooseberry is dried and powdered in it 21 times, then in total 21 times mixed with Indian gooseberry powder, Bangbhasma, Abhrak Bhasma and Uttam Kantloh Bhasma 1-1 tola, 3 tola of pure Suryatapi Shilajit are mixed and filled in bottles. . Honey, ghee and sugar should be licked 3 times a day or 3 times a day for up to 3 months. If the heat is known to be special, then give only ghee and sugar milk and sugar in proportion. Avoid jaggery, oil, sour, red chili and company of women. It is better, before consuming this prayog, the cell should be cleaned by purgation. With the use of this for 20 days only, the fierce prameha and tajjanya impotence etc. are destroyed.
(c) 1 tola juice of Amla or with Kwath of dry Amla. Or consuming 2 mashes of turmeric powder or raw ground turmeric mixed with a little honey is beneficial in menorrhagia. The turbidity of urine goes away. Similarly, mixing dry gooseberry powder and turmeric powder and licking it with honey also gives benefits in 4 or 6 days. Amlaras | Mixing 10 tolas of cow’s whey in pav (20 tolas) and giving it for a few days is also beneficial.
Charkacharya ji has said that the patients suffering from diabetes should keep on eating Amla and Prabhriti fruits by being a vegetarian and a nibar bhoji.
Bahumitra -(d) Drinking the juice of mango leaves after rubbing turmeric in 1 pav and adding some sugar candy is beneficial.
In Shukra Prameha or Swapna Dosh, break the mangoes in the month of Magh and dry them in the sun. After separating the kernels, make a fine powder. Quantity – up to 1 tola, after consuming it with double the sugar candy, it burns up to one foot and drinks it. Consuming it continuously for 15 days gives relief in the condition of nightfall. There is no hindrance of season or nature in this. A man of every season and every nature gets health benefits by consuming it. This experiment is also beneficial on headache, kamala, panda, eye diseases.
For Ayurbal and Pushti – Dry Amla powder, Gokhru and Giloy equal parts of their fine powder, once a day in the morning for 3 months with 6 months of Ghee and 3 months of honey, the heat of the semen is removed and the metal is confirmed.
Mix dry Amla powder and Gokhru powder 2-2 Mashe and Giloy Sat Masha (this is 1 quantity) together and consume it with ghee and sugar every morning.
Consume equal parts powder of amla seeds and ash gourd with ghee and honey. This Taurus is spacious and healthy, especially in winter.
Consume amla powder affected by amla juice 21 times with honey, sugar 6-6 mashes and ghee 3 mashes and drink lukewarm milk on top of it, then the body becomes healthy and strong.
Boil fresh mangoes after removing the kernels, mash them in a plain cloth and filter the pulp. Then fry this pulp in quarter ghee. After it is well roasted, mixed sugar candy powder in it and fill it in a tinned vessel or in an amritban. Quantity – 2 tola, usually in the evening, after eating it with honey, drink cow’s milk from above. After the body becomes strong, the hairs that are ripe in a small stage turn black in a few days. This marketing is the ultimate chemistry.
Consuming Amalaki Rasayan, or Amalkyadi Churna or Chyawanprashavleh, along with following a diet, for 3 or 4 months peacefully makes the body strong and radiant, and chronic impotence goes away.
Take fresh gooseberries as per your wish and soak them in water at night, and in the morning pour that water again and wash it 7 times. And methodically make vegetable by adding more ghee. In this way, the body is nourished even by consuming mangoes 5 or 7 times in a month.
Keep in mind, after consuming Amalaki Rasayan etc. age-enhancing experiments, when they go away, then as a diet, rice should be eaten with salt-free Amla and Moong flavored with a little ghee.
Jirne Mudgamalak Yushenalwanelapsnehen Ghrit Vattamodanmashniyat.
Haemorrhagic bleeding – By mixing pomegranate juice with amla juice, the heat in the blood calms down and the bleeding stops immediately.
(a) If there is bleeding from the nose, mouth, anus, etc., then take amla powder for 6-6 months with ghee and sugar in the morning and evening for a few days. Or drink fresh gooseberry juice with honey.
(b) There is terrible bleeding from the nose (hemorrhage), then consume amla juice or powder in the above way, as well as diluted juice of amla (Fresh amla after grinding, keep the juice in a glass vessel, when the thick part settles at the bottom). Let the thin liquid part remain on the top, then gently decant the upper liquid part in another glass vessel and put 3-4 drops in each of the patient’s nostrils with the help of a pichkari. The patient should take the drops that have gone inside upwards. Then after 15-15 minutes keep giving nasya in the same way with nasya method. There is quick profit. And at the same time, after roasting the mangoes in ghee, grind them in kanji or whey and apply a thick paste on the brain. Or grind amla leaves with camphor water and apply it on the head.
(c) If there is bleeding only from the mouth, then the barks of Amla, Mango and Ber trees. After collecting the jaukut, get Ashtamansh Kwath Siddhakar mixed with Mishri and drink it. Make porridge in this decoction and feed it as a diet.
Make a decoction of amla and linseed leaves and mix it with sugar candy.
(d) there is excessive bleeding from piles warts, then amla powder should be consumed with curd cream.
(e) If there is excessive bleeding in raktatisar, drink honey and ghee mixed in amla juice, and on top of that, drink goat’s milk up to 10 tolas 3 times a day.
(f) If a place is cut with a knife etc. and there is severe bleeding, then taking out fresh juice of amla immediately and applying it is beneficial.
Gallbladder – (a) Due to any reason due to gallstones, confusion, darkness in the eyes, etc. symptoms, then amla juice mixed with two tolas mixed sugar should be given.
Soaking 1 tola of dried Indian gooseberry in an earthen pot or any other pot made of iron at night, grinding it and filtering it in the morning and mixing it with 7 tola or 1 pav of cow milk, calms bile disorders and increases strength. Or
Mixing honey or sugar in amla juice completely calms bile-borne hiccups, nausea, vomiting, and trisha.
(b) There is acute burning sensation due to cholecystitis, then take 32 tolas of well-ripe gooseberries (after removing the kernels and seeds) and grind them in cow milk and fry in 32 tolas of cow ghee. Then mix it in 30 tola sugar syrup. Along with this, mix 8 tolas of Adusamul bark, cumin, black pepper, peepal, cinnamon, small cardamom, bay leaf and Nagkeshar in it and keep their fine powder for 6-6 months. Consuming it in reasonable quantity gives quick peace of inflammation. This is the best medicine for burning sensation due to any reason.
Pitjanya Gulm Rog-(c) Take equal parts of amla swaras, sugarcane juice and decoction of haritaki, along with a quarter of the weight of ghee, prove ghee according to the method. By consuming this Amalkyadi Ghrita, gallstones are destroyed.
Pittaj Murchha-(d) part of gaugrut mixed in Amla’s swaras should be given little by little several times a day and lukewarm cow’s milk should be given on top. With this experiment of a few days, fainting disease goes away forever.
Pittaj – Apsmar -(e) Mix 8 seer juice of fresh gooseberry, 5 tola of licorice and half a seer cow’s ghee, prove cooked ghee on Mandagni. Consuming this ghee gives special benefits in epilepsy.
Fever – (a) Consuming the amount of Amalkadi powder mentioned in Siddha Sadhit experiment no. Or make this powder in this way- 5-5 tola of Indian gooseberry and small myrtle, 2-2 tola of Chitrakamool and rock salt and 1 tola of long pepper and consume it with clean water for 2 to 4 months. By purifying the stomach, fever goes away, digestion becomes strong. A decoction of this experiment is also consumed, but salt is not added to the decoction.
1 tola dry ginger powder was mixed in the said Amalkadi powder. Taking it with hot water during the days of malaria, malaria fever cannot come. If there is excess of phlegm in the condition of fever, then putting this powder in the throat with pinches 3-4 times reduces the speed of phlegm, the gurgling of phlegm goes away.
If you want to get rid of fever with sweating, then this powder should be given with decoction of coriander. It is also beneficial in diarrhoea.
Santat Jwar -(b) Mixing honey and pippali powder in the decoction of Amla, Nagarmotha, dry ginger, Katerimool and Giloy is beneficial.
(c) If the mouth is dry in fever, if there is excessive thirst, grind Amla and dry grapes or grapes and lick them after making chutney or make tablets and suck them in the mouth. It also cures intense indigestion.
(d) After fever, drinking a drink made of yaws mixed with ghee after adding Amla and Peepal bundle, clears diarrhea, brings complete peace of fever.
It goes away by drinking the juice of Indian gooseberry sprinkled with ghee. Where is –
Rasamalakana or Ghrit Bhrishtam Jvarapaham (Charak)
Pandu, Anemia or Kamla – (a) Take 8 seers of fresh mango juice, half a seer of peepal powder, 4-4 tolas of licorice, ginger and banslochan, half a seer of seedless dry grapes and 1 sugar candy. Cook the head on a low flame. When it becomes thick, take it off and cool it, then mix half a seer of best honey and fill it in the Amritban.
Quantity – Consuming 1 to 4 tola destroys Pandu and Halimak. (Yoga-Ratnakar)
(b) sugarcane juice and a little honey mixed with fresh gooseberry juice in the morning and evening and following a diet cures anemia caused by chronic fever.
(c)Dry amla powder mixed with songeru and turmeric powder filter the cloth and soak it again for 12 hours. When it becomes like antimony, keep it in the bottle. Wearing this cream during the day is beneficial in kamala, the yellowness of the eyes goes away. Consuming Loh Bhasma along with Amla is especially beneficial in Pandu disease.
Urinary diseases, etc. -(a) Amla swaras mixed with mixed sugar twice a day, Mixing a little honey in amla, or feeding Amla swaras with powdered cardamom powder in 2 tola; The symptoms of passing urine drop by drop, burning sensation in urine etc. subside.
Do not use Amla if there is increased acidity in the urine. And if the liver is weak, reduce the intake of ghee completely.
(b) urine mixed with blood is passed with great difficulty, then mixed sugarcane juice mixed with amla swaras and a little honey should be consumed. Or give sugar mixed with crushed mangoes several times a day.
(c)If there is minor gonorrheal dysuria, drinking the powder of Indian gooseberry with water, and spraying the same water in the senses gives peace to the burning sensation, and the coming of puya and blood gradually stops by planting bran. goes.
(d) Drinking a syrup made of amla, bun, coriander and sugar 4-6 times a day is beneficial in urinary diseases.
(e) If the urine is of red colour, dry amla powder (3 masha), black salt (2 masha) and sandhav salt (2 tola) should be mixed and mixed in 1 pav of water according to strength and given several times.
(f)On vesicuretic urethritis- Soaking one tola of dry amla and grinding 1 masha of Kalmi Sora with it and applying it on the navel opens the stagnant urine of cholera.
Diarrhea – (a) Amla 101. Prove equal part or half part Nilofar Mila Kwath with Masse. Then mixing 3 tola sugar candy in it and feeding it is very beneficial in diarrhea caused by liver or bile deformity or stomach disorder. At the same time, make a bowl around the patient’s navel by grinding mangoes in water and fill ginger juice in that bowl. Very soon the insurmountable diarrhea is conquered.
(b) If you have blood dyspepsia or dyspepsia, mix honey and ghee in amla juice and drink goat’s milk up to 10 tolas three times a day.
(c) Chronic flow or dysentery is very painful when it becomes chronic. In this, deep wounds are often done inside the intestines. In such a condition, amla ice is diarrhoea. It is necessary to keep giving it dietary for at least one month.
Vomiting – Grind white Malayagiri sandalwood in the juice of amla, when it becomes very thick, make big tablets (of about 1 tola proof) of it, similar to that of amla. Consuming it with honey gives quick relief from talk or vomiting of bile. Take amla powder and white sandalwood in equal parts and lick it with honey or sugar syrup for 2 months.
Drink sorbet containing amla and grape sugar for 4 or 5 beats. Due to this, the intense thirst also calms down.
If there is respiratory disease along with vomiting, then take juice of amla or decoction of peepal mixed with honey.
Acidity- 1 tola of dry mangoes at night. Dry ginger, 3 mashes and cumin seeds with it in the morning. Masha mixed very fine grind 7 or 10 locks dissolved in milk mixed with two tola sugar candy and given to drink.
Soak one lock of Agla in 20 locks of water at night and give it in the morning after mixing masala, dried ginger and cumin powder 1-1 times a day.
Amla-Swaras, cumin powder, Masha and Thadi Mishri mixed in 2 tola, should be given to drink in the morning and evening. Full benefits are there in 7 or 14 days.
Amla powder should be consumed in the morning and evening for 6-6 months, with the juice of banana pole or with raw coconut water.
Juice of fresh amla filtered through a cloth 2. Equal part honey was found in the tola (this is the quantity) given to drink in the morning and evening. Keep in mind that any use of amla powder or juice should be consumed by keeping it in a glass, clay or stone vessel. This experiment is also beneficial in blood bile, burning sensation, heart palpitations, flatulence etc.
Eye disease – (a) Amla 4 parts, myrobalan 2 parts and baheda 1 part, remove all kernels and make powder. Quantity – 1 to 6 Mashes, mixed with ghee and honey, or by consuming only ghee with ghee in the morning and evening, and soaking this Triphala powder in water in the evening and sprinkling it in the eyes after waking up in the morning, washes the eyes. It is beneficial for many diseases, the eyes become strong. Or.
Mixing Amla-Swaras, fat of black cobra and honey-tones and applying it cures all eye diseases.
Amla-Swaras Mix 1 pav of Baheda oil in 1 seer and keep it in the sunlight continuously. Filter the oil when it becomes dry. Applying this in very proof gives benefit on almost all the competitions of eye and head. Grind pure rasaut sambhag in fine powder of amla. Then ghee and peacock are included in morning-evening skype life, blindness, blackness, patal etc. pittaj and raktaj eye diseases go away quickly.
Blindness and night blindness -(b) Amla 1/8th part of rock salt mixed with honey and apply it with a needle. It is sharp, apply in very little evidence.
Haze-(c) Grind the amla powder finely, mix equal parts of sugar candy and soak it in sweet almond-oil and keep it safe in a glass vessel. Quantity: 1 .. Consuming Tola with lukewarm water every morning removes the mist of the eyes and strengthens them.
Blossom-(d) Take 7 mashed dried gooseberries and soak them in 10 tolas of fresh water. After two-three hours squeeze the powder and throw it away, and again soak 7 mashes of powder in the same water after two or three hours, squeeze it and filter it. Similarly do 3 or 4 times. After that drop the drops of that water in the eyes 4 times a day. There is definitely benefit in a few days.
On eye irritation -(e) Amla powder. Soak both the half part and the black sesame (take white sesame in the absence) in water, grind it finely in the morning and apply it thickly on the eyes, take bath after one hour. By extinguishing the burning, there is an increase in the freshness and light in the eyes.
On the redness of the eye-(f) Cook the swaras of fresh mangoes in a tinned vessel on a low flame. When it becomes thick enough to make tablets, make long tablets. Rubbing it in water and applying it with a needle, the redness quickly goes away and the eyes become clean.
(g)Eye drops and redness go away by dripping 1-1 drops of supva juice in the eye in the initial stage of ophthalmia.
Note- Rubbing the pulp of Indian gooseberry well on the head and body and taking a bath, the vision power increases in a few days. Where is
Apalkai: Eyesight on continuous bath. (bangsaen)
Gynecology- (a) Mix 6 pieces of amla pulp and 3 pieces of honey and consume it in the morning and evening on the condition of excessive menstruation or bleeding from the uterus.
Amla-Swaras cumin powder in 2 tolas. Mix Masa and Mishri and give it twice a day. In the absence of mangoes, 2 tola dry-amla powder should be given every night after filtering faeces mixed with cumin and sugar candy. Similarly, soak it in the morning and give it to drink in the evening.
Women who have the habit of frequent bleeding due to cholecystitis get special benefit by consuming gooseberry patiently for a few days.
In white leucorrhoea -(b) After grinding mango seeds in water for 3 to 6 months, add honey and sugar candy to it. There is benefit in 3 days only. Give both times daily. There is also benefit in Soma disease.
If there is foul-smelling thick discharge, it is necessary to keep washing the uterus with the use of gooseberry juice with the help of the above experiment or with the intake of ice of gooseberry. No. in proven experiments. Amalkyadi Ghrita of 5 (A) is tested in all types of leprosy.
Soma disease-(c) In this, due to the destruction of the power to stop urine in women, there is excessive discharge. The body becomes completely lethargic. In such a situation, feeding ripe banana mixed with honey and sugar candy along with Amla Swaras or feeding Amla juice mixed with honey and sugar every morning and feeding ripe bananas is beneficial in a few days.
On vaginal irritation – (d) By drinking honey and sugar mixed in amla swaras, the burning sensation of the vagina goes away soon.
Child diseases -(a) On a type of ulcers called Vichchinna, which arise in the form of red lumps on the body of children, they are very painful. Pour cow urine on it 7 times in amla powder and keep it dry in the sun. Grinding it in cow urine or water and coating it 2-3 times a day is beneficial.
Diarrhea of children -(b) 2 parts amla seed, 1 part chitrak root, half part myrabalan, peepal and black salt, their mixed powder should be consumed in appropriate quantity in lukewarm water in the morning and evening.
(c) Amla swaras on the gums at the time of teething makes the children’s teeth come out happily.
Piles (piles)-(a) one loaf of cow’s butter in a pan. When the foam stops coming out, put dry amla powder in it and say: Put it and keep stirring it with a ladle. When it gets a little roasted, then mix two tolas of crushed pulp of soft leaves of elderberry in it and keep stirring it. When both the sides are cooked, take the pan out of the water and let it lie down for 24 hours. Then keep neem tucker in the bottle. Consuming Bhav in the morning and evening for only 6 months, the pain and bleeding stops in a few days. Not only this, Arshankur gradually becomes lifeless and falls after consuming it continuously for a few days (Junglani herb).
(b) the gooseberries very finely and put that kalk in the inner part of a vessel. Whisk well. When the paste becomes dry, fill fresh cow’s buttermilk in that vessel and continue to feed ragi little by little. On the second day, drink buttermilk by doing the same action in the vessel. Similarly, feeding this buttermilk for a few days gives special benefits in diarrhea.
Vata blood and leprosy – (a) Fry dry mangoes in castor oil and powder them. Mixed mishri in it, consume it in the morning and evening for 2 to 6 months. Or consuming old ghee cooked with amla swaras in proper quantity is beneficial in all types of arthritis.
Leprosy -(b) equal parts of amla and neem leaves on fine powder. Quantity 2 to 6 Mashe or. Licking with honey every morning up to a tola gives quick benefits even in severe leprosy.
Itching-(c) there is any kind of itching – wet or dry, then burn the kernels of amla (fill it in a pot and burn it in Gajput) and apply coconut oil mixed in it. Soaking and grinding mangoes and rubbing them like boiling is also beneficial.
Kaas (cough) -(d) Amla powder 2 tola, milk half pav and water 1. Cook the pav on a mixture of all the three on a low flame. When only milk is left, filter it and mix 6 mashes of cow ghee in it. Consuming it like this in the morning and evening cures dry phlegm or fast-moving cough. If there is bleeding with cough, it also stops.
Rheumatism (Arthritis) – (e) amla powder and jaggery 2-2 tola both 1. Cook the bread in water. Filter and drink when half is left. But avoid salt completely. Soon there is profit.
Wounds of the head-(f) A wound on the head is cured by coating mangoes mixed with ground sugar and ghee. Headache also ends with this experiment. (Charak)
If the head becomes particularly hot due to heat, anxiety etc., then grinding dried mangoes in milk and applying it on the head gives quick benefits.
Prasveda – Those whose hands and feet sweat all the time and keep their hands and feet soaked in water day and night, such people should lick appropriate amount of amla powder with honey in the morning and evening and take 10 drops of amla decoction throughout the day. Washing hands and feet 15 times gives special benefits. This experiment is also beneficial in paddari.
Kesh Kalp-(a) Keep 3 tola dry Amla, 1 tola Baheda, 5 tola kernel of mango kernel and 1 tola iron powder in a pan overnight. Apply it on the hair everyday in the second day. The hair which turns white at a young age turns black in a few days.
(b) Soak dry mangoes with bhangra juice in an earthen pot after removing the pits. When the juice dries slowly, soak it again in Bhangra juice. In this way, after giving feelings of Bhangra juice 7 times, shade dry it well and grind it finely and keep it in a vial. Quantity- Consume with fresh water daily for 3 months, and avoiding oil, chili, jaggery, sourness, worry, awakening etc. (If kept for a few days, the hair becomes black from the root root.)
(c) Grinding both equal parts of amla and mango kernels in water and applying it on the head makes the hair black, soft, shiny and big. Apart from these, there are many uses of Amla which are useful in medicine and food.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Apamarg – Chirchira. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
The shoot of this divine herb sprouts at the beginning of the monsoon and becomes about 5 feet tall by the end of the winter season. In winter, more fruit-rich manjaris come in it. We start seeing it after maturing its manjariyas. Its leaves are covered with very fine white hairs, elliptical and somewhat pointed.
The channels of both white and red apamarga emerge from the central part of the petioles of the leaves. They are long and hoarse, thorny. In this, there are small tandulars of subtle and thorny seeds. These seeds are like small rice grains of gray color and are somewhat bitter in taste. Flowers and some red are green or purple in color. The stalks and branches of red apamarg are of some red half and there are red-red micro spots on the leaves. Somewhere in the Nighantu it has been said that Krishna or Kala Apamarg. But I have not seen the path of black character.
Sanskrit – Apamarga, Mayurke, Kharamanjari etc. Hindi – Chirchita, Chichda, Latjira, Onga, Jhaade Adhajhada. Bengali – Apang | Marathi – Half. Gurjar – middle aged. English – Rough Chiaf Tree. Acaranthus aespes –
Apasarjyate Vyadhirneniti Apamarg
This herb destroys diseases by purifying the contaminated metals of the body with its divine effect, that is why it is called Apamarg. This herb is famous in India since ancient Vedic times. It is found almost everywhere in India. virtue
White Apamarg – Bitter, Bitter, Ushnavirya, Digestive, Antiphlegmatic, Grahi, Vamak and Arsh, Abdominal diseases, Kandu, Mango and contaminated blood are preventive, deafness killer and poison killer.
Blood dyspepsia – Acrid, bitter, antiphlogistic, vamka, collector, bran, itching, medrog, heart disease, adhaman, colic and poisonous.
Both types of Apamarg are going to remove the poisons of rats, dogs, barr etc, quickly due to their effect.
The main Sanskrit names of this plant are Apamarg, Kharamjari, Mayurika, Shikharika, Keshparni, Raktabindu, Kshudrapamarg, Shwetaparg, Raktapamarg etc.
Popular names of Apamarg in Hindi language and common people are- Chirchita Latjira, Auga, Chirchira, Ajja Jhara and Chichda. Its botanical name is Acaranthus asperan (family Amaranthaceae). ,
Apamarg plants are generally 2 to 4 feet or more tall and the branches of the plant are thick in the spreading front part. The leaves are somewhat elliptical or circular, 2-5 inches long and 2-2 inches wide, soft and hairy. The flowers are small with a greenish white color on long stalks. The fruits are small, long and forked, tangled and the seeds are small in size of rice.
In the chemical composition of this plant, potash alkali is specially found in the seeds and the whole plant.
A plant named Apamarga is available in the Vedas and it is one of the useful and important herbs of Ayurvedic medicine. Along with this indigenous system of medicine, the general public is also familiar with it, because it is included in almost universally accessible and self-generating (self-generating) plants.
There are two castes of Apamarg – Rakta Apamarg (red variety) and Shvet Apamarg (white variety). The trunk (stem) of Raktapamarg is red and there are blood dots or marks (red marks) on the leaves. There is greenishness (whiteish green color) on the scandals and letters of Shvetapamarg. Generally Shvetapamarga (white difference) is known as Apamarga and due to its availability in medicinal use, it is used, both types of Apamarga are used in medicinal work. The blood circulation is less than that of the white race.
Apamarg is found in almost all the provinces of India, which is a caste itself. The receipt of blood clots is less or diffusely. The vegetation flourishes as soon as the first rain falls and flowers and fruits come in autumn-winter. In hot summer, the fruits become dry (in the intensity of summer), which also stick to the clothes.
Apamarg’s juice is bitter, bitter; Qualities short, Ruksha sharp; Semen is hot and Vipak is bitter. It is a fire lamp, antiphlogistic, antiphlogistic, antiphlogistic, antiphlogistic, expectorant, blood purifier, heart, diuretic, diuretic, skin, hematopoietic, antiphlogistic, ulcerative, antiphlogistic, antipyretic, purgative, laxative, medohar, diaphoresis, lithiasis, acidity elimination, headache. Virechan Ashon, Dantya and Arttav perform regulatory functions and are used medicinally in disorders related to them.
The flowers of this plant are broken and crushed, and by brushing the teeth with it daily, the teeth become strong.
Mix a leaf of this plant, a piece of a conch, a piece of the root of this plant and some manjaris by filling a large glass of water, then boil it in a pot, and after about a quarter is left. After that the decoction is filtered. Drinking this calms asthma.
By boiling (cooking) the seeds of this plant in milk, Bhasmak disease is pacified, Bhasmak disease is a perversion of the fire, in which the food is digested immediately due to abnormally intense gastric fire, that is, everything eaten or drunk is consumed by the fire of the stomach. Due to pathological intensity, it gets consumed and the appetite increases abnormally (Agni is of three types – Samagni, Mandagni and Attagni, in which the first one is healthy, and the rest two are harmful. Apamarg is used in case of excessive appetite. goes.
Consuming kheer made of the seeds of this plant reduces appetite (desire to eat), so it is also considered as a medicine to control appetite, hence it is known as appetite suppressant or appetite suppressant plant. Its use protects the radiance of the body.
Grind the seeds of this plant with rice washing (tandulodak) and consume this mixture in bloody piles (Raktarsh), it stops bleeding (bleeding) in bloody piles and provides relief.
Grinding or grinding the root (root) of this plant in water (root kalk) the pulp of the root is applied on the place of scorpion bite (scorpion sting-dashtra ang) or applied, tying it, burns etc. Get instant benefits.
Placing the leaves of this plant in the vagina provides relief in vaginal colic in women; With the use of leaves, even the severe vaginal colic becomes calm.
Grinding the root of this plant in water and giving it is beneficial in dysentery (vomiting-diarrhea or cholera).
This plant is used to remove snake venom in snakebite.
The use of the plant is beneficial for pacifying the scorpion venom (scorpion poison) in scorpion sting. Taking a green branch of Apamarg, it is rotated from top to bottom on the bitten part (the place where the scorpion stings). The vegetative branch is rotated in an upward (downward) motion and then after going down, after separating it from the organ, it continues to rotate again and again from top to bottom (i.e. taking it down should not be brought up while keeping contact with the organ) ) This experiment is effective.
Apamarg Kshar is prepared from the almanac of this herb (by Apamarg Kshar method – a process or manufacturing method like burning the plant to ashes or ashes). Drinking water with stone and urinary sugar (stones and related disorders) is beneficial. There is also a law to give this alkali with avimutra (sheep’s urine).
Apamarg Kshar is beneficially used in ear disease, especially in the treatment of tinnitus-deafness (deafness of the ear). Apamarg Kshar is cooked in oil and a few drops of it (Karnabindu Patan) are put in the scan. Apamarg Kshar oil has been prescribed in the treatment of ear diseases.
By tying (wrapping) the excrement (H) of this herbal medicine in blood thread (red thread),
The juice and pulp of the leaves of this plant (Patra swaras and Patra kalk) are used for bleeding wounds and bleeding (ulcers and haemorrhages) caused by cuts and bleeding (vran patra kalk). – Beneficial in the form of preventive and ulcer planting. The grafting effect is important to this.
Grinding the root of the plant in honey (honey) and giving it in proportion to tandu lodak (wash with rice) is beneficial in piles. Consuming the root of the plant with Takra (whey or buttermilk) is beneficial in blood loss.
In Siddha (leprosy with spots of white or copper color), the seeds of the plant, especially alkaloids of Panchang, are applied externally. Along with this, by mixing Apamarg’s blood seeds (reddish or blood seeds) in Apamarg alkali, or by making a mixture in Kadlikshar (banana alkali) and Haridra (turmeric) and applying it externally on the affected body parts of the body, the diseased (skin) There is benefit in Vaivernya.
Mixing the alkali of Apamarga with alkali of Kadali, Palash and Yava, giving it with Aavi urine (sheep’s urine) or with suitable ratio is beneficial in stone and sugar (disorders related to stone and urinary bladder in the initial stage).
Apamarga root is used with milk in urinary tract (urinary tendency with pain).
In Kamla (jaundice), mix Apamarg root and Shami (10 grams) and consume it with Takra. Its use is beneficial in Kamla, Shoth (inflammation in the body – Sarvangsoth) and Pandu diseases.
At the time of delivery – applying a paste mixed with Apamarga’s root and Punarnava in the vaginal colic arising in the neoplasm.
It is used in abdominal pain. Mixing decoction of Vanaspati and long pepper, make ghee and consume this ghee.
Apamarga patra swaras (juice extracted after squeezing the leaves) are applied on the wound in Alark poison.
Cooking apamarg fruits (seeds) in oil (using oil-baking method) and rubbing them on the head is beneficial in headache.
In Shastra or other Abhidhataj-Kshataj wound, oil smeared from the root of Apamarga (use of Apamarga swaras in addition to the aforesaid) is applied. This beneficial use stops bleeding, wounds heal quickly and pain subsides.
Insomnia (in the state of not being able to sleep) Apamarg is consumed by making decoction with Kakjungha and Kokilaksh.
Apamarg is used in difficult delivery (including difficulty in delivery due to stupid pregnancy). By keeping the root of this plant in the vagina, childbirth is done happily. Applying Apamarg on the navel, waist and vagina of a pregnant woman (imminent delivery) helps in giving birth happily.
Apamarg is used in eye diseases. The root of Apamarga is rubbed (rubbed) in water with sea salt (Sindhut salt) in a copper vessel, using it locally (externally) on the eye is beneficial in eye inflammation.
Apamarga’s fruits (seeds) are mixed with cow’s urine and applied in vascular ulcers (especially in canker sores, old wounds, etc.). Similarly, a mixed paste of sesame and apamarg seeds is applied in pulse ulcers.
Apamarga is used in cough and breathing diseases. Apamarg alkali and sugar (both equal parts of half a gram) are mixed (grinded well) and mixed in a cup of hot water (hot water) and given two or three times a day. It can also be given mixed with Vasa (Adusa), Bankasha (Vanapushpikavansika) and Madhu (Honey) (with any or all of them) or honey can be used in place of water. This yoga helps in liquefying Kapha (congested mucus) (expanding mucus), relieving difficulty in breathing (relieving shortness of breath – asphyxiation) and cough and khas beg (recurrent cough and shortness of breath). profit is made.
Apamarga has medicinal use for pregnancy. This plant is used in the establishment of pregnancy for reasons such as irregular menstruation or other disorders in women, deformity of reproductive organs and (in men) Shukra-disorder (lack of sufficient sperms etc.). New leaves of blood apamarg (freshly plucked leaves of red caste plant) washed in water with milk (or mixed with cow’s milk) after retirement of menstruation (season – menstruation) (after being purified by bath) about 5 Day, which continues for a total period of 10 days. The quantity of letters can be kept 10-15 grams and cow milk or milk 100-250 grams. Similarly, Apamarga root is grinded in milk and filtered and fed to a woman in suitable quantity for a long period of time.
Apamarg is the use of letter, scandal etc. in dental diseases. (aforesaid). Dantdhavan (by Daton-Apamarg Kand Kurchika) is done with the branch of its plant. Dental disease, looseness of the teeth (shaking of the teeth), looseness of the gums, disorders of the teeth and gums, pyorrhea (blood, pus coming out), toothache, watery teeth. It is beneficial in toothache etc., and helps in maintaining dental health.
Apamarg Kshar is the main and useful classical medicine prepared from this plant. The preparation method of Apamarg Kshar is simple and this medicine can be prepared at home for everyday use.
Amamarg collects and cleans the almanacs (root, stem, branch, leaf, flower and fruit, ie the whole plant) of the plant and dries it in the shade. It is incinerated (by burning with fire) by fire (by keeping it in a clean place or vessel) and by dissolving the residual ashes (ash left after burning) in eightfold water (eightfold water) in the vessel and washing it thoroughly by hand. completely mixed in, In which ash-particles become solution in water. This mixture is kept stable for six hours, and then carefully remove the top water and put the residual sediment (material accumulated at the bottom of the vessel) in a pan along with the bottom water and heat it on the fire, it is finally saved. The water will also burn and after that the medicine is taken out by scraping. It is made into a fine powder by churning it in a kharal and this immense alkali is kept in a safe container (packing) for use.
This Apamarg Kshar is used for the treatment of various disorders. Generally it is given in 500 ml. Gram. (or 250 mg in children) up to one gram, and one to two grams can also be used in special pathological conditions. Similar to other alkalis (due to pungency), according to the dosha-disorder, they are consumed in appropriate proportions, such as with water, honey, sherbet (panak), sugar (powdered sugar) etc. This war is cooked in oil and used as a point; Alkali is external.
Apamarg Kshar is used alone or in combination with other medicines in Kaas, breathing, agnimandya, abdominal disease, colic, liver disease, splenomegaly, appendicitis, ear disease, siddha and other disorders with suitable dosage and proportion.
Almanac, root, letter, fruit-seed and alkali of Apamarg are used medicinally. Its normal quantity is 10-20 ml. And the powder is 3-5 grams.
Head worms are destroyed by the nasya of Apamarg’s swaras. And rubbing its root (especially the white Apamarg root) and applying it on the breasts increases milk.
White Apamarg is bitter and bitter in Vipak and Red Apamarg is sweet. But the seeds of these two, being honey in juice and vipak, are harsh, vicious, talkative and angry, they are blood-cholesterol. Compared to white, red is said to be inferior in qualities. Therefore, in ordinary experiments, only Apamarg is used for special effect. By making fine powder of its fruits (seeds along with the peel) and giving nasya for the brain or head, painful worms along with phlegm frozen inside the brain fall out. Due to this, heaviness of the head, migraine, pinus, etc. disorders also go away. For the simple plan of nasya, trikatu bidang etc. cough extract and anthelmintic substances are mixed with the above seeds, grinded with water, four fold sesame oil and quadruple cow urine mixed, prove the oil. Nasya of this oil gives quick benefits.
For the prevention of labor pain – When there is severe pain at the time of delivery and there is excessive delay in delivery, then on Sunday and Pushya Nakshatra, its root should be dug with purity (it should be dug slowly with wood and not with any iron) in the region of the woman’s groin. Or by tying it on the head, delivery becomes easy immediately. Remove the root immediately after delivery, otherwise there is a fear of the uterus also coming out.
A strange effect of this herb has been seen in the state of pregnancy. Grinding its said root and applying it on the pelvis of a woman also gives the same benefit. But immediately after delivery that paste should be wiped with water.
The anti-toxic effect is also unique in this. Many doctors say that scorpions can be easily caught by licking the leaves, their poison has no effect. By applying its juice on the bite site of scorpion and as far as it hurts, the pain remains only at the bite site. In that condition, by grinding its leaves and tying the pulp, it also goes away. Along with keeping a piece of its fresh root in the mouth, it should be chewed slowly. Or instead of betel nut, pieces of its root should be given to chew for 2-3 months by keeping it in betel leaf. Soon there is profit.
Powder of its root on dog poison. Tola and powder of lemon seeds, lick both of them mixed with honey. Grind its seeds on rat poison and consume it with honey.
Medicinal Quantity – leaves, root, seeds, alkali and ash are used for medicinal purposes. Swaras of leaves up to 1 tola, powder of leaves up to 3 to 6 months, powder of roots up to 2 to 6 months, seeds up to 3 to 5 months , Give 5 to 10 tolas of Kath or Sheetakshay, 2 to 4 Rattis and Bhasma from 5 Rattis to 2 Mashes. For Kaath, take 2 tolas of its leaves, branches and boil it in 40 tolas of water with the method of Kwath, when Ashtamansh or Chaturthansh is left or for special effect only Ashtagun (16 Tola) water is mixed in it.
Kshar preparation method and its effect- burning the Apamarg Panchang, mix the ashes in Ashtagun water and let it lie down for a few hours. Then after draining the clean water from above, cook it on Mandagni. When all the water gets burnt, take it down and scrape off the alkali from the pan and keep it safe in a vial.
This alkali mixes quickly in the blood of the body and increases the nutritious particles of the blood and in this way it can stimulate all the bodily functions. Clarifies disorders like rheumatism, arthritis etc. Due to this alkali being benign and diuretic, it is used for gonorrhea, colon and urine accumulation, by consuming aliphatic and diuretic substances, the pain subsides and urine delay decreases, its quantity increases. Similarly, it also gives excellent benefits on disorders like phlegm, cough, ascites, liver enlargement, wind ball etc. Consuming kanji mixed with cow urine (2 || or 3 tolas) in the morning and evening for 3 months with the amount of alkali on Vayu Gola or Koshthavat gives quick benefits.
Breath, Kaas etc, (in disorders of airway, larynx and lungs) – Cough arises again and again, phlegm comes out with pain, it has become thick and juicy, in such a condition or in the condition of pneumonia, alkaline and sugar should be taken. Mix 4 ratti mixture in 211 tola hot water and drink it. Consuming this 7 times a day gives rapid benefits. This experiment is also beneficial in the condition of inflammation of the respiratory tract and larynx. The thick phlegm accumulated inside starts getting thin and comes out. The above experiment is given only with honey.
Intensity of breathing rate – Smoke its fruit by cutting it or keeping its dry leaves in the hookah. At the same time, the powder of its root mixed with 7 pieces of black pepper powder from 6 mashes, taking it in fresh water in the morning and evening gives complete benefits during the day. In this experiment, sometimes the internal phlegm comes out due to vomiting. It is also beneficial to massage the chest and throat with heated ghee in the morning and evening.
Nasal disease – By frying the juice of its leaves in sesame oil and giving nasya to the thorn of this almanac, as per the method, due to burning sensation in the nose, cold, nasal discharge or burning sensation, the breath air comes out like smoke or bleeding from the nose mixed with blood. ) goes away, or if there is difficulty in breathing due to excessive saturation and dryness of the olfactory source, then the said nasya is beneficial. Apamargasava is also very beneficial on breathing. See his work ahead. See also Malla and Tal Bhasma.
Ear disease- Due to the condition of the air in the ear source, sound like Bheri, Mridang etc. is heard inside the ear, there is deafness, there is ear discharge, there is foul-smelling discharge from the ear, then it is proved by the said alkali, by pouring sesame oil in the ears. There is benefit. Rubbing this oil on the part of the body where there is numbness (lack of touch) is beneficial. If alkali is not available, mixing 4 parts of goat or goat urine and half part of swaras with sesame oil mixed in its swaras, proving oil on Mandagni, and putting it in the ear is also beneficial.
Eye Disorders – Rubbing its root with curd mixed with a little salt in a clean copper vessel is beneficial for eye disorders, conjunctivitis, kandu, discharge, redness of the eyes, puffiness, night blindness etc. This use of Charak is a tribute to the ancient physicians. Acharya Kaviraj Shri Hardayal ji has published the above experiment in a special way for the benefit of the general public in the following way.
Its root was thoroughly washed with water and cleaned. Put the tola in a clean tinned vessel. Soak the pav overnight with parishrut water. Cook on slow fire in the morning. When 10 tolas are left, take it off and rub it and get dressed. Put it in a vial and mix 10 ratti pure Sandhav and 1 tola Vastraput clean milk (Mastu) on top. After 2 days filter it with flannel or blotting paper and keep it safe. Dripping 2-2 drops of it on the above disorders of the eyes gives quick benefits. In the condition of night blindness, the powder of its root should be consumed with water before sleeping for 6 months at night. In this way, only 3 days of consumption gives benefits.
Disorders of the stomach and gall-bladder- burning in the abdomen, colic, laxity, indigestion, acidity, anorexia, anorexia, withdrawal, ascites, incinerator etc., its action is quick. In such a situation, using it with bitter substances like Kutki etc. works very well. Its almanac or only in the quantity of the powder of the root by mixing a quarter of the powder of Kutki with the food. Or giving it with water 2 hours before, indigestion, looseness of the stomach, colic (especially phlegmatic colic) and burning sensation are also removed. In the condition of acidity, anorexia, appetite loss, Uggar Bahulya, consume this experiment after 2 hours of food or make decoction and consume it. Keep in mind that it should not be used in large quantities for stomach disorders. In large quantities it becomes caustic. Making Kwath only of Apamarg Panchang and mixing black pepper powder, Masha and 4 ratti Nausadar in it, it is beneficial. There is no need to mix kutki in it.
If colic is very intense, then grinding its root powder and 6-6 leaves of colic, white cumin 3 pieces and black salt 1 piece with water and making 3-3 pieces of abuse, it gives quick benefits.
Gallbladder or liver disorders – action is very beneficial. By improving the function of the liver, blood circulation starts to happen properly. Therefore, it also gives benefits on gallstones and urticaria. In such a situation, a quarter of Katuki mixed with Kwathya liquid in its Kwath prove Kwath. After that a little Navsadar mixed in it should be fed in small amounts again and again and again and again. In this, by removing the swelling or other obstructions of the biliary tract of the liver, there is a quick improvement in the process of bile secretion and blood circulation, and all the liver related disorders are pacified. If there is acute colic in the liver or gall bladder, giving its decoction with basic alkali in its initial stage is beneficial soon. It should be consumed in small amounts every half an hour.
If there is acute pain in burning sensation (inflammation) in the urinary bladder or urinary tract, drinking 4 tola decoction of its almanac or root and feeding it with the milk of Dharoshna goat provides quick relief. Keep in mind that Apamarg should be used along with aliphatic and diuretic medicines to reduce the pain in the swelling of gonorrhea and inflammation.
Filter its fresh root solution in water for 6 months and drink it 2-3 times a day, small pieces of colony or stone come out from the urethra.
Gynecology – If there is bleeding related disorder, then its fresh leaves 2. Tole. Mixing 5 tolas of water and 10 tolas of cow’s milk (fresh) and 1 tola of sugar candy mixed with 1 tola of durva on a stone and giving it daily in the morning for 7 days is beneficial. Or – Make a fine powder by grinding all the three equal parts of Panchang, Sonageru and sheep’s hair ash of white Apamarg. The quantity should be consumed with warm milk up to 6 months.
If there is burning or itching in the vaginal tract, applying a little butter mixed with the pulp of its fresh leaves inside the vagina is beneficial. Vaginal colic also goes away. Bringing its fresh root every day and wearing it in the vagina (at the time of menstruation) soon removes colic by making it suitable for secretion of blood.
Santanaarth- Women who do not get pregnant due to irregular season or return, they should get fresh leaves of blood apamarg produced in the best land on the day of Ritusnan. Take one tola and grind it with 10 tola cow milk and consume it for 4 days. Consuming this way for a maximum of 12 days i.e. in three seasons leads to pregnancy. In place of the leaf, its root is fed after grinding it in milk.
In skin diseases like boils, pimples, medogenya durganthya, Kanda Kanthmala etc – after rubbing it with sesame oil, which has been proven by the imagination of its leaves and fruits, put a cloth of oil on the boils.
In the condition of scrofula and dyspepsia, its almanac and the bark of Sirrus should be consumed daily in the morning by mixing 2 tolas of water in half a seer and adding honey to it.
Its almanac to be applied from above. Grind pav or mansil and vermilion 1-1 tola and mix them in 20 tol (1 pav) of sesame oil. When it starts getting thick, stir it in the pan itself, when it becomes like an ointment, take it down and add 6 pieces of opium to it, keep it safe by mixing it well. Applying this on the ulcers of indigestion 2 or 3 times a day gives quick benefits.
In case of bleeding in any part of the body, irrigating the juice of its leaves stops the bleeding.
Arsh – Especially on Pittaj or Kafanubandhak blood, its root is grinded with rice washing and mixed with honey.
Or – Grinding 6 pieces of its leaves and 5 pieces of black pepper with water and consuming it is beneficial.
Taking the powdered quantity of its seeds for 3 months with washing rice in the morning and evening also stops bleeding.
Grind its seeds, roots and leaves and grind them into fine powder and mix equal parts of sugar candy. Give it with water in the morning and evening for 6 months.
Antidote for chicken pox or chicken pox – Its root and turmeric equal parts are ground together, applied on the nails of the hands and feet and applying a tilak of it on the forehead and tongue does not cause chicken pox. If it has come out, then washing its root with pure water and grinding it on a stone, applying it on smallpox gives peace.
Kamshakti Vardharth- Hingul ash made from its combination is very beneficial- Mix the best Hingul in extract milk and make a cake and shade dry it. Keep 2 tola cakes in a strong clay aravale (sakore) by spreading 10 tola Apamarg Bhasma. Press this much ashes on the top and close it with another saravale, dust it with cloth and blow it in 10 or 15 kg of cow dung cakes. Of this Hingulbhasma. Consume Ratti’s quantity with cream.
Soak 3 to 6 grams fine powder of Apamarg’s root in it for 125 to 250 ml. Gram. Consume Bang Bhasma with melted butter in the morning and evening.
Akik Bhasma on weakness of the heart – Put 1 tola of Akik in 1 pav of Apamarg’s kalk, wrap it in the above way and blow it in the flame of 8 seers of cow dung cakes. Its quantity should be consumed with butter up to 2 ratti.
Similarly, making Malla Bhasma in its combination is beneficial in breathing, cough and fever. Amamarg is also the best beneficial on breathing.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Durva – Dub. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
The main Sanskrit names of this plant are- Durva, Shataparvika, Shataparva, Shitveerya, Sahastraveerya, Shatavalli, Ananta Durva’s popular names in Hindi language and in general are- Doob, Dubda, Durva (Durba).
Its botanical name is – Sindon Deck Aylan (Family Gramini Poaceae).
Glucose is found in the chemical composition of a plant called durva.
There are many castes of it in scriptures – Durvatraya (Durva, Neeldurva and White Durva). The main distinctions of Durva are according to the classical mention – White Durva, Neeldurva, Gandurva, Golomi (Durvabheda), Maladurva etc. (Classical name and difference are related to each other).
Vitamin A and Vitamin C are abundant in dub. Due to the presence of all types of vitamins and other elements in dub, this vegetable is full of nutritious elements.
Green and soft leaves of dub should be brought after washing them thoroughly and eating them mixed with salad – coriander, green chillies, tomatoes, onions and other commonly useful vegetables for raw food, then it is considered very beneficial and healthy. It can be eaten by mixing it in vegetable-vegetables (slowly gradually increasing the quantity), gradually its astringent taste becomes favorable or balanced. Apart from this, dub can also be used in dry state, soft and green dub is collected and cleaned and dried, and its chutney can be eaten with taste.
If lentil is consumed in any form on a regular basis for a few days, then the health improves, disorders are alleviated and the vitality in the body increases, energy comes. This type of experience has been of those who consume durva.
There is a concept about the special quality and nutritional properties of dub that when even an animal like an elephant gets intoxicated by consuming durva, a horse also becomes strong and hardworking by eating it, cows, goats etc. have milch animal power and milk-producing power. Receive. Then why shouldn’t humans gain strength by using this type of easily available plant everyday.
It has immense power to save life, everyone can see its benefits by taking some time. In the scriptures, the medicinal properties of Doob include Balya, Jeevaniya, Prajasthapana, Kantivardhak, Dahasasasak, Raktashuddhikar (blood evil) – Raktaprasadin, Sartapana, Medhya and various other qualities, and due to this quality, Doob is considered to be strong and all-body protector-enhancer. Power is useful.Due to being a major anti-inflammatory medicine, it is used in diseases and in many disorders, in which burning and irritation (burning and heat), is used in many ways, and the internal use (consumption) of Durga’s juice is mostly. Happens in practice as well as using durva’s baha lep or any other type.
Kalk or swaras of Durva is suitable for external use in Van, Kshata, Arsh, Dah, Visarp, Shitpitta, Paittik, Shirorog, Skin disease etc. External use of dub juice is beneficial
Durva Swaras is useful in eye diseases, especially in pittaja disorders, burning sensation of eyes, laalagi, Pak etc. In netrabhishyand, the juice of linseed is used as an eye drop and soft leaves of linseed are also applied on the eyelids.
In piles (arsh), paste made by grinding dub leaves is applied on piles warts (arshankur). In bloody piles (hemorrhagic piles), grinded dub leaves and mixed with curd are used internally.
Grinded rice is applied in the swaras of durva (especially white durva) in Visarpa, Vyang, Neelika, blood disorders and skin disorders.
To remove scabies of smallpox, grind it with rice and turmeric and apply jasmine oil mixed with it.
Heat and Pittolvanata Janya (heat-heat and Pitta’s head: Shral (headache) grinded with yaw (barley) with cold water and applied.
Its leaves are applied in solar and skin diseases, it stops bleeding. In Amatisar, it is to be fed after kneading it with dry ginger and fennel.
To cure fever, the root of the crematorium is brought and tied on the wrist (manibandha) of a person suffering from fever.
In brain weakness, diarrhoea, flatulence, fever, ascites, menorrhagia, abortion, hematuria, hysteria, dysentery and pain-predominant diseases and in general physical weakness and poisons, durva’s swaras are taken out and fed to the patient. According to the appropriate quantity ratio and co-drug mixture (drugs to be mixed together), the juice of dub is used in these different disorders in pathological conditions as required.
Durva’s swaras are dripped in the nose in case of heat-induced nasal bleeding or nosebleeds, and durva’s swaras are given mixed with sugar candy. This use of durva proves to be very beneficial for those who have nosebleeds and that is why the use of durva is widely seen in medical practice.
Decoction of its root is taken on inflammation of the urethra, gonorrhea and blood disorders.
Durva root juice. Mixing honey in gram is given in case of hiccups.
White sandalwood powder and sugar candy are consumed in the swaras of Durva in Raktapradar. Durvadighrita is present in blood bile, this yoga is used in the treatment of other diseases related to bleeding.
In the case of abdominal diseases, a panchang of durva’s almanac or pant or juice is given to the patient, due to this, the tendency to urine increases (more urine starts coming) and the stomach starts to become light. In addition to this, taking black pepper powder mixed with durva’s phunt or juice, along with ascites, is also beneficial in Sargansoth.
In Bhaishajya Ratnavali, there is a text on the treatment of dropsy and inflammation. This rasa yoga is prepared by methodically mixing Hinglotth Parad with many other major botanical and mineral substances giving the feeling of white durva’s swaras. Its quantity is very small (50 to 100 mg or as required) and should be given to the patient with sugar syrup or other suitable proportion.
In normal urinary tract, after grinding durva in original curd, it is licked. In the case of urinary tract infection and gonorrhea, after proving milk in decoction of Durva’s root, or by grinding and filtering the root of dub in milk, it is given. If blood comes along with urine in hematuria, it is filtered and fed with sugar candy.
In Shukrameha, mix green lentil root with other substances- Murva root, Kusha root, Poppy root, Majithmool, Semal root.
Durvadya Dhrit and Durvadya Tail are some of the major classical yogas of Durva.
Durva’s almanac, root and letter come in medicinal use. The normal quantity of Durva’s swaras is 10 to 20 ml. Is.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Ashwagandha-Asgandh. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
Its main types are – (1) A small odor. Due to its small size, it is called small odor. But its root is big. In Nagore (Rajasthan) it used to be very common and due to the effect of the climate there, it was particularly effective and that is why its Nagori has become famous as Asgandh.
Due to the effect of time, this bad smell has disappeared from its place nowadays. (2) The second is the big or native asgandh. Its trunk is big but the roots are small and thin. It is commonly found in orchards, gardens, fields and hilly places.
The Asgandh that is sold in the markets of Bombay contains the roots of Kakanaj (cheese). But his qualities and religion are somewhat different from this.
In Latin, what is called Convolvulus Asgandha is a creeper of Nisoth class. He doesn’t have tears. The root of this particular creeper is poisonous. It is called Ghorakun in Gujarati. Its coating is beneficial on swelling, gland, lump of plague etc. and not native or Nagauri asgandh. But it is a matter of regret that by mistakenly considering both these, the doctors have created a big mess by using their medicines. It is produced in greater proportion in Karachi and other countries. Towards Karachi it is called Aankhdi in Hindi. Its vine is convulsive and eating it causes stomach cramps, nausea. Consuming it causes convulsive vomiting symptoms. That is why its above is meaningful in Latin and Hindi. It is known that it smells like Asgandha, that is why the word Asgandha has been added in front of its name in Latin. Some have given it the name Nagori Asagandha. But actually Nagori Asgandha is being described here.) It is different from that. Due to the predominance of marketable qualities in Asgandha and its smell being like the smell of urine of some horse (horse), in Sanskrit its names have been kept related to Baji or Vaji. And the apabhramsa of ashwa has become asagand in Hindi.
Sanskrit – All the compound words that are formed by adding the word ‘Gandha’ at the end of the words ‘Ashwa’ or ‘Baji’ are its synonyms. Apart from this, Pivari, Pushtida, Bajikari, Barahkarni etc. Hindi – Asgandh, Nagori Asgandh | Marathi – Aaskandh, Aasgandh. Gujarati – Asandh, Asun. Ashwagandha. English – Winter Cherry. Botanical Name – Withania somnifera, Physalis flexuos, Physalis somnifera.
Berar, Khandesh, Nashik, Bombay, Sindh etc. in the western regions of India, native Asgandh and in dry and hot regions like Bengal, Assam, Burma etc. Nagori Asgandh is produced.
Its buds are 2 to 3 feet high and are born in the rainy season with many crooked branches. In some places, under the big trees near the reservoir, it remains green for 12 months. Then they get destroyed after 3 or 4 years. In shape-type, these are small like a small bowl but without thorns.
Leaves – are opposite to each other, elliptical, 2 to 4 inches long and hairy.These leaves are elongated and round in shape, somewhat similar to pig’s ears and in some places similar to palash leaves, it is also called Baraharni and Palashparni in Sanskrit. The petiole of the leaves is very short.
Flower – flowers are small and some are of long chilam shape and are of yellowish green colour. These flowers grow on the front of the branches, coming out of the leaf angle.
Fruits – Small round like peas or fruits of Makoy, first green smooth and then turn red when ripened in Kartik or Margashirsh. These fruits are in the shape of a fugue, covered with the membrane of the anther and open on the upper part. Inside the fruit there are innumerable yellowish white seeds like Luab and Katari seeds.
Root – 4 to 8 inches long cone-shaped, thick in the lower part and thin, round, smooth in the upper part. Its outer bark is gray and white from inside. The wet fresh root has a pungent, disagreeable odor like horse urine. It is bitter in taste. This is taken for medicinal purposes.
Qualities – Astringent and slightly bitter in Rasa and slightly pungent in Vipak, hot and mild in semen, extremely semen enhancer (Shukra), chemical in effect, radiative, nutritive and is beneficial for arthritis, talk, phlegm, cough, breathing, decay, inflammation, leprosy. , Poison, Worm, Kandu, Brana and Pramavatanasak.
By consuming it regularly for one year, the body becomes diseaseless. At least in the month of Aghan and Pus, the body becomes fat by removing weakness.
All these qualities are said to be of its origin. According to Ayurveda, it is also included in the substances which have been asked to be taken always moist (freshly wet). But in our opinion this rule can be specially applied in the case of Ghodakun Asgandha (figure) and not in the case of this Asgandha. Yes, it is also more beneficial if it is found fresh.
Consuming the powder of the root with milk, ghee or ushnodak, in the weakness of the child, and in the weakness and old age of the elders; Licking the powder with goghrit and sugar in sleeplessness and colic; In tuberculosis by consuming the powder with its decoction; By taking it with sugar candy and aloe vera, colic, colic; Liquorice powder mixed with it, consuming it with amla juice, results in visual impairment; Mixing honey and ghee in it for a month (in autumn) consumes it; Baheda powder mixed with it, taking it with jaggery, the matter of the heart is in pain; Along with this Giloysattva was found in all diseases by consuming it with honey; Asparagus powder mixed with it and consuming it with honey cures disease; By giving it with gooseberry, in the water; Giving it mixed with milk in leucorrhoea and sterility and giving it only with warm milk in constipation; There is benefit.
Quadruple ghee found in decoction and kalk of the root, after cooking it according to the method, gout goes away and the woman becomes pregnant. In inflammation caused by grinding the root in cow urine; Consuming ground root with hot water in heart rheumatic diseases; Chop-sugar mixed with the root made a decoction in the blood; Along with this decoction mixed with Vidarikand and licorice has been proved and taken with cow’s milk, in breast destruction (deficiency of milk in women’s breasts), And feeding it by grinding it with takra is beneficial in the abdominal poison obstruction of animals. Feeding its fresh root with fodder cures the disease of patient, bull or cow. Grinding its root, mixing honey and snake’s bambi soil in it and heating it in the urustambha; Grinding root in buttermilk or oil and applying it on the affected part is beneficial in narcissism. In case of shortness of breath, by preparing an indigestion alkali of the root and taking it with ghee and honey; Consuming powder of big peepal and mixed with ghee and honey in decoction of root is beneficial in decay. Massaging oil mixed with the powder of the root is beneficial on skin diseases. Due to lack of blood cells in the body, there has been loss of sleep in the body, then use of Suvarnamakshik with decoction or powder of Asgandha and use of Chandraprabha Gutika along with it on neuralgia and paralysis; And decay caused by sexual intercourse, in kas and in kshatjanya. In decay, the use of Brihad Suvarnamaliti Basant with it is very successful.
Asgandh leaves- Grinding and coating it destroys gland, goiter and indigestion. Grind tender leaves and mixed with jaggery, make a pill like wild berry and take 1-1 tablet in the morning with stale water, it provides relief in scrofula. Consuming honey mixed with the juice of leaves is beneficial in sleeplessness caused by typhus.
Almanac of Asgandha – After crushing it, squeeze out the juice in a thick cloth. 2|| By consuming up to 5 tolas, arthritis goes away.
Chemical organization – Ashwagandhin or a bitter alkaline substance called somniferine is found which has hypnotic sleeping properties. In addition, it contains resin. Settled, and contain some coloring matter.
It is a stimulant, a chemical and a depressant. By taking the powder of its root with milk or ghee, the child’s body becomes strong. Soaking its leaves in castor oil and keeping it on the edema, that place becomes dormant, there is no knowledge of pain. Nasya of Narayan oil made with the addition of Asgandha in ear deafness, and its massage in vata diseases like paralysis, sciatica, sciatica, and it is treated as enema (anuvasan basti) in amraktatisar and Bhagandar. This Narayan oil is consumed in the quantity of 15 to 60 drops on Krishta, Jarajanya debility, leprosy and arthritis.
Its powder gives good sleep and the mind remains happy. It does not have any side effects like other sleeping medicines. By this, the urine comes out clean and the heart becomes strong, the pains are suppressed. Pain in the body, tingling, discomfort while getting up and sitting, etc. are better with this.
Ashwagandha powder (Kalp) – (a) Make a mixture of very fine flour after grinding the powder of Ashwagandha. Then mix one-fourth part of the best cow’s milk in it and keep it in a box after grinding it a lot. Consuming this quantity with warm water or milk for 1 to 3 months cures all kinds of pains etc. air disorders. The strength of semen increases.
(b) Asgandh and Vidhara Samabhag into fine powder and fill them in a vessel greased with ghee. Consuming quantity from 6 masha to 1 tola in the morning and evening with warm milk or cow’s dharoshna milk for about four months cures diseases, problems of old age, and rejuvenates. Consuming this powder mixed with 6 pieces of ghee and 3 pieces of honey destroys the semen and increases the strength of semen. This powder can be taken with Samabhag Mishri.
(c) half a part of sesame powder in the fine powder of Asgandh and mix equal parts of both of them with jaggery. Consuming 1 tola of milk with the method of Kalp destroys all diseases.
(d) the fine powder of Asgandh along with amla juice in increasing quantity up to 1 tola regularly, then man becomes divine vision and germ free. That is, he is saved from the special troubles of old age.
Ashwagandha Gutika – Fine powder of Ashwagandha, Peepal, Clove, Cinnamon, Tejpat, Nagkeshar, Deodar, White radish, Banslochan, Balchhad, and Sat Giloy 3-3 each of Mashe, Satavar, Vidarikand, Talmkhane, Kaunch Beej and Big Gokhru in 12 tolas. Taking 5-5 tolas of fine powder, collecting all the powders, mixed 12 tolas of pure Shilajit in it. Make tablets of 1-1 mashe by grinding the extract of pav with rose.Consuming these with milk removes semen disorders and makes the body strong and strong. To make it especially effective, 1 to 2 tolas of proven Makardhwaj is also mixed in this experiment.
Many other uses of Gutika have been given in the scriptures.
Ashwagandha, Ashwagandha powder, 20 tolas of dry ginger powder, 10 tolas of peepal powder and 4 tolas each of black pepper, cinnamon, small cardamom, bay leaves and colocasia powder, first cow’s milk 211 seers, Gaughrit 25 tolas, both of these are put on fire. But cook When half the milk is left, mix the above powders in it and cook on very low flame while stirring with a ladle. And quickly put down cumin, peepal root, talis patra, clove, tagar, nutmeg, khara, belgiri, kamalphool, coriander, midwife flowers, banslochan, amla, khairsar, punarnava, chitrak, asparagus each 6-6 mashes and rosindoor. Grind 2 tolas very fine and mix. Then after it cools down, mix 50 tolas of honey and 11 seers of rab in it and fill it in a smooth utensil. Quantity – 1 to 1. Taking it with milk up to a tola, cures cough, breathing, indigestion, gout, iron, gout, rheumatism, inflammation, piles, pandu, kamala, vatkaph disorders, increases the sex of women and men with low semen.
The remaining uses of Avleh are available in the scriptures.
Ashwagandha Ghrita – (a) 5 seers of Ashwagandha and mix about 13 seers of water in it and make a fourth decoction. Then filter it into 64 tolas of Gaughrit, 31 seers of cow milk and 4-4 tolas of Bidarikand, Mulathi, Satavari (these are taken in the absence of Kakoli, Ksheer Kakoli etc.), Kaunch Beej, Adusa, Munakka, Ghamasa, Peepal, Nutmeg and Khairati. Grind 2-2 tola of these with water to make a pulp and mix and cook on low flame. Sieve it when only ghee is left. Diseases like decay, debility, heart disease, ura:kshata, impotence, cough, breathing, rheumatism, sterility of women, etc., go away by its use.
(b) Mix 1 seer of ghee and 4 seer of milk in 1 pav of Ashwagandha, cook and filter it when only ghee is left. By giving it to the children, they become strong and strong. This is called Balamrit Ghrit. If the same experiment is made with goat’s milk, then it becomes profitable and growth-enhancing.
Other uses of aloe are available in the scriptures.
(c) Cook 1 seer of Ashwagandha’s kalk, 4 seer of sesame oil and 16 seer of Ashwagandha and 4 seer of cow milk on low flame. Sieve when only oil remains. Its massage increases the growth of semen and the power of ejaculation. Apart from this, it is also very beneficial in injury pain, gout, colic etc.
See the use of oils like Ashwagandhabalakshadi oil, Narayan oil etc in the scriptures.
Ashwagandha Pak – (a) Mix the fine powder of Ashwagandha in 32 tolas and 6 seers of milk and boil it slowly on the fire. When it becomes thick, add cinnamon-sugar, bay leaves, Nagkeshar, cardamom 1-1 tola and nutmeg, saffron, banslochan, mocharas, jatamansi, white sandalwood, khairsar, nutmeg, peepal, peepalamool, clove, kaunchbeej, walnut kernel, water chestnut, Gokhru 6-6 Mashe powder mixed and prove Pak in 2 see sugar syrup. To be particularly effective, juice vermilion, asbestos, snake ash, bangabhasm and lohbhasm are also mixed in it. Taking 1 to 2 tola with milk or fresh water destroys all gonorrhea. By destroying chronic fever, decay, gulm, talk and bile related disorders, metal growth takes place.
Ashwagandha Cut the head and cook it in 20 heads of water. When 2 seer is left, cool it and filter it. Then mix 2 tablespoons of sugar in it, cook it, when the syrup becomes very thick, freeze it. This culinary sugar is very beneficial for children in front of mercury.
Their strength increases, they become strong. The best experiments of Pakistan should be seen in place.
Ashwagandha sorbet – Take fresh Ashwagandha juice (in absence of its decoction) and mix 2 times sugar in it and cook. When the syrup of sorbet comes, fill it in the glass. quantity 1 to 2 || By pouring milk up to a tola and giving it to drink, diseases like cough, breathing, rheumatism, gonorrhea, semen defects, insomnia etc. go away quickly. This is very beneficial for children.
The uses of Ashwagandhasav, Arishta, Arka, Ashwagandhabhrak, Ashwagandha Nasya etc. are available in the scriptures.
On weakness, semen depletion and old age – Ashwagandha has the strange power of thickening and increasing the thin metal due to constipation. Consuming it with good manners continuously for one year, there is communication of unique strength and enthusiasm in the body. If one consumes its powder for 3 months with warm cow’s milk, Vata nature with pure sesame oil and Kapha nature with hot water, then all diseases are cured by removing weakness.
Ashwagandha powder, sugar candy and honey 6-6 mashes and 1 tola of cow’s ghee were mixed together. Consuming these four regularly in the morning and evening for 4 months in winter, a weak old man starts enjoying youth.
Its powder is 2 tola, sesame 4 tola and urad 16 tola, grind these three into fine powder and mature it in ghee according to the rules. Consume fresh large mass. Or – Mix its powder, sesame and ghee 1-1 tola and honey 3 mashes together and consume it daily in winter.
Collect equal parts of its powder and absinthe powder and keep it in a smooth vessel. Quantity . Take the weights with milk in the morning and evening.
Mix 1 ratti of Bangbhasm in its 1 masha powder and add sugar candy and consume it with churned milk.
Consume Ashwagandha powder, Pak, Ghrit etc from the above proven experiments.
Impotence and penile dysfunction – Consume the said Ashwagandha powder or pak or keep the fine powder of Ashwagandha clothed and mix equal parts. Cow’s milk mixed with fresh sugar candy in proportion to 1 tola. Keep eating a pinch of powder 3 hours before the morning meal, keep drinking milk from above and use the following tila or paste at night
Ashwagandha 1 tola, Vidarikand and Kaunch seeds 6-6 Mashes Fine powder of these three collected Lion’s fat 1. Put it in a box after weighing it and rub it on the senses.
Ashwagandha, alum, lodh and castor root peel each 3-3 mashes, grind and make a cake with water, burn it in 10 tola sesame oil and filter it, massage this oil slowly on the penis daily.
Grind ashwagandha, cinnamon and bitter gourd in equal parts and filter and mix in cow’s butter leaving betel nut in the morning and evening and rub it on the remaining penis. Before and after rubbing it, the penis should be washed and wiped with warm water.
Simply grinding the fine powder of Ashwagandha in jasmine oil and applying it removes the laxity of the senses, it becomes hard and firm.
Grind Ashwagandha and soak it in the juice of black peppercorns and dry it in the shade. Soak it in fresh juice like this 20 times and dry it. At the time of sexual intercourse, take a little of it and grind it very finely and rub it on the penis after saving the betel nut mixed in your saliva. Then have sex after 3 hours. The penis will remain very hard. And semen will not ejaculate quickly. Cow’s milk must be rubbed on the penis after sexual intercourse.
For pregnancy – Make 2 tola powder of Ashwagandha and cook it in 1 seer of water and 1 loaf of cow’s milk. When only milk is left, Gaughrit and Mishri are mixed in it for 6-6 months. Consuming it for three days after the purification bath of the season, having sexual intercourse with a man leads to pregnancy.
Grind 2 tolas of Ashwagandha mixed with cow milk and make a pulp, then cook it in a very slow fire by adding half a seer of cow milk and 1 tola cow milk in a cast iron pan. After taking a ritual bath, a woman should drink it early in the morning for 4 days and eat milk and rice, then it will definitely remain warm.
Cook Ashwagandha 1 tola powder in 16 tola water in Mandagni. When 2 tolas of water is left, filter it and add 1 loaf of cow milk and 1 tola cow’s milk and heat it and give it to drink for 5 days of the season. This removes the defects of the uterus and leads to pregnancy.
Consuming Ashwagandha powder lubricated with cow’s milk daily for 4 to 6 months with cow’s milk or with fresh water continuously for one month after menstruation, pregnancy is definitely established. Some make him eat it for three days only in the season and give him diet milk and rice.
If you have miscarriage or miscarriage, take 1-1 tola swaras each of Ashwagandha and white bitter gourd root and consume it every morning for five months from the first month, then there will be no abortion in famine and by consuming it at the time of abortion, the falling pregnancy will stop. goes.
Menorrhagia, bloody discharge and white discharge – Fine powder of Ashwagandha 2 Mashe 6. Ratti is another friend. Consume the mixture of these two (this is one quantity) in milk for a few days in the morning and evening. It can also be taken with fresh water.
Grind Ashwagandha 5 tola, Pathani Logh and Vidhara 3-4 tola and take it with cow’s milk in the morning and evening.
Sandhivat – Asgandha powder mixed with 3 mashas of ghee and 1 masha of sugar should be consumed in the morning and evening. Or
Tender leaves of Ashwagandha. Cook the tola in 1 pav water. When the leaves become soft, filter and drink hot. In this way, only 3 or 4 days of consumption is beneficial. Phlegmous cough also goes away.
Cough – Ashwagandha. Mixing 1 tola sugar candy in half a seer of water after proving Ashtamansh Kwath and drinking it little by little gives special benefits on whooping cough or gas. Or
Make 4-4 ratti pills after proving a decoction of Ashwagandha leaves, adding half of the powder of beheda, half of the powder of the catechu, half of the black pepper powder from the catechu and half of the sandhammak mixed with ginger juice. Sucking these cures all types of cough. It is also very beneficial in decay.
Fever – Ashwagandha’s powder 5 mashes and Giloy’s bark powder 4 mashes collected and consumed with warm water daily in the evening cures chronic gout fever.
Pain in hemorrhoids – Grinding Nirgundi’s bark, Katari’s fruit and Peepal and mixed it with ghee and putting it on the fire and giving it in the anus, the pain of piles goes away.
On the subject of poison – Vachhnag (Batsnabh), drinking its root juice for 1-1 hours to 4 times for 6 months is beneficial.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Agnimanth – Arni. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
Nighuntukars have told two types of it with the difference between big and small Arni. There are two types of large arni, and two types of small ones. Description of these four types of Arnis is done here.
This (Arni) is also a part of the Brihatpanchmool of Ayurvedic Dashmool experiment. This is a special medicine of India, and since ancient times, its treatment has been different according to Ayurveda. done on diseases.
In Sanskrit ‘Arni’, this churning stick is called, whose churning or friction with each other produces fire. is born. That’s why Arni has been given the famous Sanskrit name ‘Agnimanth’, That is, by churning or friction by which fire is produced. The sacred fire for Yajna work is produced from the wood of Arni or Shami, hence it is called Agnimanth, Bhimanth, Tejomanth etc names have been given.
Gamble states that the villagers of Sikkim still use its wood to make fire.
Bunches of bunches of Arni leaves and flowers are a spectacular sight. That’s why probably many of its names have been kept in Sanskrit like ‘Vaijayantika’, ‘Arniketu’ etc. It occurs abundantly on the high banks of the river, due to which it has a Sanskrit name ‘Nadeyi, Nadija’. It conquers diseases, hence it is also called Jai, Jai Vijaya. Due to having hot semen or destroying diseases like fire, it has been given names like ‘Pavak Jyotishka’ etc.
The special difference between big and small Arni is also that the trunk of the big Arni tree is big and strong and its sharp branches are widely spread opposite to each other. The small Arni tree is in the form of a very small gulm.
Sanskrit – Agnimanth, Gaanikarika, Jaya, Nadeyi. Hindi – Arni, Ganiyari, Rain, Ganial. Marathi – Tankla, Thor Eran. Gujarati- Arni, Eran. Bengali- Ganir, Aggant, Bhoot Virkhi. Latin – Premna interfolia, Clerodendron phlomydis
Sanskrit – Kshudragminth, Vijaya, Tanu, Skin, Krishanuma. Hindi- Small Arni, Urni, Pirun, Tekar . Marathi – Jaghu Eran, Narbel, Takli. Gujarati- Nahani- Arni, Irun. Bengali – Chhote Ganiyari. Sindhi-Gharayat. Latin – Premna spinosa Premna serratifolia.
Big Arni is found in Bengal, Bihar, Awadh, Garhwal, Rajputan, Madhya Pradesh, Bombay etc. South India and Ceylon. Chhoti Arni is found in almost all the states except Bengal. But in the foothills of North-Western Himalayas, Mathura Brajmandal and some places of Uttar Pradesh, Orissa, Ratnagiri, Thana district near Bombay and other especially hot places are found in abundance.
Big Arni trees are 10 to 30 feet tall, and two types have been considered with the distinction of purple or black and white flowers. Usually 3 or 4 branches emerge from its root, so its trunk is not very thick. Botanic expert Late Shri Rooplal ji says that the reason for this is that due to the presence of many microscopic seeds in its fruit, plants are prepared by sprouting together. If some attention was paid to its population, this tree could be a bit bigger and thicker columned.
Where there is its forest, its trees are organized with each other in such a way that it becomes difficult to cross them. The new twigs that come out on these old branches, they often dry up and fall off and the remaining parts of 3-5 inches long, which are attached to them, become like strong thorns. Its wood is also strong. There are small thorns of the above type on the old branches also. The root is deep from the ground, strong and consists of many roots. The original wood is gray to khaki in color and is circular and porous from inside. Native student herb, pochi, some white or black colored aromatic, astringent in taste, bitter and somewhat bitter.
Root and upper branches- Pale white color with long vertical cracks. And the bark on top of them is thick, pochi and hard. The wood inside them is of pale white colour. The tender branches are dark green and hairy.
Letter – They stand face to face on the twigs. These are wide in the lower part and somewhat narrow towards the front, usually triangular, cold, of pale blue color from both sides. In length, they are from half an inch to 5 inches long and from half to 4 inches wide. Its new leaves are cut along the edges and are brittle, when these leaves get old, their ridges disappear.
Chaitra- In Vaishakh and at some places in the south, in Kartik and Margashirsha, its trees are very attractive and well-flowered.
Flowers – Small blue spots emerge in clusters of white color and in others purple color. The one with purple flowers is called black arni and the one with white flowers is called white arni. These flowers are usually covered with 5 petals from outside. These often smell like jasmine flowers. But the smell of the flowers of Kali Arni is not very dear.
The stalk of its leaves is half an inch to 2 inches long. By crushing the leaves, a sticky juice of blue or dark green color comes out. It is fiery in smell, pungent in taste, seems bitter with some salinity.
Fruit – Looks like the fruits of Makoy in earrings. These are green in raw condition and on ripening, they turn yellow or khaki in color and turn black in the end. These fruits fall in the beginning of the rain and their dry, fine earrings remain attached to the branches, then gradually they also fall.
Seeds – white in fresh condition and then turn gray. The seeds inside the fruit are divided into four parts. Only 4 seeds emerge from the fruit of a tree. Often, by ripping the white Arni fruit in the middle, 4 parts are clearly visible inside and each part has 1-1 seed. This big white Arni is called Chlorodendron phlomoyadis in Latin. Many small seeds are found in the fruits of Kali Arni. This is called Premna Integrifolia in Latin.
Introduction (Small Arni) – It is 3 to 7 or 8 feet high in the form of a gulm or bush. Its letter is 1/2 inch to 1 || Up to an inch long and as wide as the elliptic and appear concurrently on the twigs. The flowers are thin, tubular, fragrant, white in color or slightly pink in color.
There is a distinction of small Arni which is called Tejomanth in Sanskrit and Narbel in Marathi. Its tree is a bit bigger. The leaves are small, elongated and ridged. Its branches spread all around like a creeper. Chutney and greens are also made from their leaves. The greens of its leaves are beneficial for respiratory patients.
Just like there is white arni in big arni, similarly white arni is also found in small arni. In a small arni, only flowers grow, the fruits are not visible.
Since semen and juice of both big and small types of arnias have similar properties, they should be used according to where they are used.
Badi Arni- Charari, Tikta, Bhari, Sarak, Kasali, Ushnatirya, Agnipradipak, Uterus depressant and matter, cough, pandu, atrophy, agnimandya, arsh, fecal attachment, rheumatism, catarrhal, febrile meadow disease and is an antidote.
Chhoti Arni- Its properties are similar to that of Uka Badi Arni. It is specially used in coating, application and swelling.
Arni Mool – purgative, agnivardhaka, liver pain reliever, heart-strengthening and nutritious. It is added to nutritious Pak and Kwath etc.
Ikshumehi, Basamehi by getting the decoction presented by the bark of the root; A little Shilajit was mixed in this decoction; Mixing a little dry ginger powder in this decoction, consumes it on Mandagni; Mixing a little jaggery in this decoction and giving it hot, it is beneficial for Tridoshaj Gulm.
Consuming the root or its bark with grinded (Kalk) Gaughrit for 7 days on the gall bladder, abdomen and pelvis; And making a paste of the root and feeding it is beneficial for flatulence.
Mool – Root of Matulang (Bijaura lemon) mixed with bark and grinding in kanji is applied on rheumatism ulcers; Applying crushed leaves of Adusa with root bark on gland pain; With this, grinding the root of Punarnava and applying it on swelling; Grind karanj leaves mixed with cow urine and apply it (before this root should be decontaminated and watered) then on the pillar; Grinding the root bark in goat’s milk and applying it on the black spots of the face, and grinding the root in water and applying it on the scorpion’s rash is beneficial.
Mixing sesame oil in the colocasia of the root of black arni, massaging it and baking it after crushing and heating its leaves and tying them is beneficial in rheumatism, inflammation and paralysis. By tying black or white Arni root on the forehead or in the crest, cold fever goes away.
Arni Patra – There are diarrhea, constipation, rheumatism, medrog and antidote. Women’s colic, vaginal diseases etc are beneficial on disorders.
Taking a warm decoction of its leaves gives special benefits to the patient suffering from menstrual pain, but first the patient should be given oil bath. By making a poultice of leaves and tying it on the bed, its creation goes away. By tying this poultice on the eyes, eye ointment is beneficial. It is also tied on headache and nausea.
Massaging with the juice of the leaves (especially of small Arni is better) or sesame oil prepared by the juice of the leaves gives special benefits on ascites, heart disease, swelling etc. By massaging it on the stomach of children, stomach pain and worm disorders go away. Grind small Arni leaves with a little salt and tie them on the bite of a tiger or lion.
Consuming the decoction of the leaves removes indigestion, afra and colic of the stomach. Arhar’s bark mixed with the letter Kwath Sindh tax on constipation; On the weakness of the heart by drinking coriander mixed with the letter. And by feeding Takra (buttermilk) mixed in the decoction of the leaves, the animals get relief from the disease of Sheetla (large lumps arising on the body).
Consuming leaf juice mixed with honey cures cough and blood disorders by grinding leaves with black pepper or consuming leaf juice mixed with black pepper powder, catarrh, cold and In fever, taking sorbet prepared with the addition of leaf juice is beneficial in colic and dyspepsia.
Consuming some secret by making bhaji of small arni leaves, increases milk in the breasts and calms colic.
Arni’s fruits and flowers – Grind its raw fruits and flowers together and make a cake and tie it on the ulcer (which is on the back). Giving the powder of flowers with aloe gives benefits in gallstones. Drinking decoction of flowers or ice for a few days cures dyspepsia and dyspepsia. And by repeatedly compressing the flower, the pain of the head due to catarrh is calm.
Arni’s almanac – Decoction of its almanac is beneficial on arthritis, neuralgia. By feeding its almanac or making decoction, the flatulence of animals goes away.
A variation of Chhoti Arni, which is called Tejomanth (Narbel), is characterized by anti-inflammatory properties. The juice of its leaves up to 4 tola is given to the woman on blood pressure. This juice also cures colic and worm disease in children. The vegetable of its leaves is especially beneficial for respiratory patients.
According to modern opinion – In its chemical composition – resin, alkaline essence and cupain (tannin) are found.
Its action on the stomach is stimulant, digestive, lamp, and adhyaanahar. It is a changer, that is, chemicals and force.
Burst of its leaves in the quantity of 2 tola to 5 tola is given in fever, colic and abdominal pain. The decoction of its root is used in gonorrhea and weakness after fever, rheumatism and arthritis.
This phlegm thing is suitable in predominant diseases. It is consumed on goiter and swelling and applied externally due to the presence of research. Being carminative, it is suitable for all types of vata disorders, such as rheumatism, medullary colic and painful hemorrhoids. Being febrile, it is also consumed on explosive fevers like simple fever, virulent fever and masurika etc. Due to mucilage, it is beneficial on cough disorders like cold and cough, and due to being deep, it is beneficial on dyspepsia, indigestion and dyspepsia. By taking this for many days, all the functions of the body get improved and Pandu, Ikshumeh etc. disorders are destroyed. Its special useful action is on the uterus. It removes the disorder of contraction of the uterus and the pain of contraction. Abortion cannot be caused by its use. Along with this, cool, fragrant liquid should be given. Opium is another substance that can stop abortion like this. Therefore, planning opium with it is the best thing to do. Or give lotus flower with it. Its action on the uterus is opposite to that of cotton root bark. Its use is beneficial on hyperventilation, dysmenorrhea and labor pain.
By boiling 4 ounces (10 talas) of its root in one pint (half seer) of water for 15 minutes (and eating it), taking 5 tola to 10 tola 2 times a day, it is digestive and astringent. functions as For this reason its letters also come in handy.
Matra- The quantity of letter swaras from ½. Tola, original bark from 211 tola to 5 tola, quantity of original bark powder from 3 to 6 months.
(1) Fevers – (a) If there is vat fever, then the bark of its root. Collect 3-3 tolas of Tola, dry ginger and myrobalan and cook it in 32 tolas of water. Sieve the rest and consume 10 drops of small peepal powder mixed in it. Fresh Kwath should be proved twice in the morning and evening.
(b) Fever or Vishmajwar- For this, 10 pieces and 5 pieces of black pepper, collected in 5 tola 22, after filtering, put in a hot red pot and cover with another vessel, drink Samsotishan. Appetite also increases by its use.
Finely grind 15 pieces of its leaves and 9 pieces of black pepper and make pills equal to gram, taking the pill 4 times in the morning and evening before the onset of fever is beneficial.
(c) Masurikadi explosive fevers- giving decoction of Arni leaves or font 2 to 11 in 5 tola twice a day is beneficial.
Inflammation – (a) If there is an all-round inflammation, keep both Arni Pancham and Punarnava Panchang in the shade and burn them in a vacuum, then prepare alkali by alkaline method. First, the patient should purify the room by purgation, and consume this alkali in appropriate quantity in the morning and evening with warm water. And purify oil with this alkali and make it manly.
Make a fine powder by grinding the bark and leaves of its root along with black cumin, dokimal, sarfonka root and equal parts. Mix this powder in water and heat it and apply it on the body. If the patient feels cold with this paste, then make him sleep on the cot and consume it. This paste is also very beneficial on the body or abdomen of a pregnant woman.
(b) there is a research on Udra, make decoction of its bark and consume it mixed with Punarnava. Heat the bark on the abdomen and keep applying it for 3 days.
Upavamsa – on the old teaching – Drinking up to 1 tola juice of small Arni leaves twice a day for a few days is beneficial. The patient should follow a diet.
For purification of blood, take quart of its root bark mixed with honey. Or mix 7 pieces of black pepper in this bark, filter it and consume it for a few days. This increases the force.
Stone (Ashmari)- By grinding and drinking the powder of its seeds in Mathit (without adding water) for 2 to 4 months, as well as eating a decoction of its leaves, it removes the stone.
Udard – Erysipelas (this is a difference between cold sores) but its root mixed with 2 tolas of fine powder should be consumed in the morning and in the evening, lick Triphala powder mixed with 2 mashes, 3 mashes of honey and mix 5 tolas of cow urine on top. Take moong rice porridge, rock salt in small quantities in the diet. Grind mustard, turmeric, pawand seeds and sesame all over the body and rub it mixed with bitter oil. Avoid sunlight. There is complete benefit in 7 days. See further experiment on simple urticaria.
Affection or seasonal obstruction – 25 leaves of large arni, 25 leaves of small kateri, 2) nuts and baibidang, kalonji and radish seeds, after taking 3-3 pieces each, make a decoction in half a liter of water and prove it as an eightfold decoction. Found a tola old jaggery, 3 days before the time of season, menstruation becomes clear by feeding mother in the morning.
On Vata disease – Dry the bark of its root in shade and powder it. Then make a fine powder by giving 7 expressions of its letters in this powder. Quantity from 6 Ratti to 1 Masha, should be consumed with hot cow milk in the morning and evening. This experiment is also beneficial in catarrh (cold). If there is pain in the head, see Nasya Nasya mixed with a little ghee and rock salt.
Gandavridhi and obesity – Grinding and heating small arni leaves and tying them on the testicles, as well as heating a copper rod on fire and staining it on the forefinger of the ring finger of the side where there is ovum growth, gives quick benefits. If the patient has flatulence or medrog, then decoction of Arni root bark and Tentu root, both of these mixed with honey should be given to drink.
Bhagandar – Grind small Arni leaves and soak them in butter washed one thousand times for 24 hours and keep it in a glass bottle with a big mouth. Prepare fresh paste after 5 or 6 days. Along with this, the patient should be given decoction of Arni root bark mixed with 1 tola and 3 mashes of honey in the morning and evening. Shatponak fistula is also cured by this experiment.
Hysterectomy – Grind and dry the fine powder of Majufal with decoction of big Arni and leaves of Patra. In the same way, by giving 7 feelings and feeding a pill like a small berry, the hanging uterus or the uterus sitting here and there sits in its place. This experiment is the experience of Bhagirath Swami ji.
Treatment of baldness and boils on the head – Grind about 10 tolas of fresh leaves of small arni, 4 tolas of coconut kernel and 2 tolas of sugar candy in water and keep them in a glass cup. After some time, filter the water above the talent of the cup and apply it on the head separately. Wash your head in the morning and apply it again. Similarly, applying it for a few days is beneficial.
Eye drops – Take out the juice of its fresh leaves and soak a cotton wick in it and dry it 7 times. Then light this lamp in the lamp of sesame oil and cross the kajal. Applying this kajal is beneficial for puffy eyes. This kajal is very beneficial for small children.
Swara bhang – Grind its flowers and drink 3 mashes of powder daily in the morning and evening with 10 tolas of cow milk (Sukhoshna). In 7 days, hoarseness is destroyed and the voice becomes very sharp.
On vata disorder of vagina and uterine colic – due to entry of air in the vagina, there is pain in the uterus, for its prevention – preparing a paste of fresh green leaves of arni and placing it in the mouth of the uterus in the form of a pill like gram gives quick benefits. It happens .
Cholesterol – Keep the powder of big arni’s root and roasted cumin seeds together in fine powder. Quantity: 1.. Lick it with honey 2 or 3 times a day for 2 months to 2 months, it is beneficial in hives, rashes on hot body, disorders caused by application of cold water, etc.
Visceral ulcers, vascular ulcers, etc. Large ulcers, 3 parts of big or small arni leaves and gram. Grind both the parts together with water and keep them on the ulcer and tie a cloth with a peepal leaf on top. Due to this the ulcer ripens and bursts and becomes good on its own. Rotten throat ulcer is also conditionally cured by this experiment. The ulcer which is left by the big doctors as incurable, that too is definitely cured by this simple experiment.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Vasa – Adoosa. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
Sanskrit – Balakaḥ, Vasa, Sinika, Ramarupaka, Vaishvamata, Kasanotpatanaḥ Vrishaḥ. Hindi – Adoosa, Rusa, Bisonta | Marathi – Adulsa | Guj-Ardusi. Bengali – Vasak | Punjabi – Bhikdar | English – Malavarant Tree. Latin – Adhatoda Vasica.
It is almost everywhere in India. In all the places of Bengal, in Central India, Uttar Pradesh, Bombay province, it is abundant in the higher regions of the Himalayan foothills above 4000 feet. It is found abundantly in old ruins, wasteland and on the banks of fields and rivers.
This universally accessible, great quality divine herbal medicine of small caste is almost familiar to all. But it is a pity that many great people mistakenly consider Pio Bamboo (Katasaraya) to be one and consider it to be the same as white, yellow, blue (Kaula) and red. But keep in mind that it is completely different from Piyabans.
Adoosa is usually of two types, white and black. The leaves of white Adoosa are somewhat rough, green in color and have white spots. And the flowers are absolutely white. The leaves of black are of dark green colour, some are black and soft, flowers are also some black. All ordinary people call it Hada Bamboo.
Purvacharyas have mentioned Raktapushpa or Tamrapushpa Vasak, which is considered best on the basis of medicine, and which they used specially in Raktpitta disease. But nowadays it is rare and black is also very rare. White is easily available almost everywhere.
Adoosa’s buds are 4 to 10 feet tall. At some places its small medium size trees like up to 20 feet high have also been seen. Its fence is put around the bungalow, house, garden, garden, farm etc. Animals do not eat it, as a result, trees and plants etc. remain safe behind its fence.
Its stem is firm and solid, and often on the top of the root, near the earth, branches and sub-branches start coming out, due to which it becomes like a small bush, whose herds keep on forming.
Letter – Its leaves are front-facing, 4 inches to 8 inches long and 1 to 3 inches wide and pointed. Both the sides of the letter are smooth and somewhat rough. The letter stalk is subtle. Some strong smell comes from the leaves, that is why it is called ‘Vasak’ in Sanskrit. When the leaves are cooked in water, a kind of yellow color comes out, if a little indigo is added to it, it becomes blue-green.
At some places its leaves are first spread in the rice field. Then the plow is run. Mixing in the soil in this way, often those grasses which are harmful do not grow in the field. This proves that if leaves are mixed with the land of the field before sowing the grains, then the harmful plants do not grow and the crop is good.
Knowledgeable people keep Adoosa leaves in clothes and books to protect them from insects. Fruits ripen best in these leaves. They neither rot nor do they get moldy. In Bengal, Uttar Pradesh etc., sails are often kept in its leaves. Guava and custard apple keep well in this, and good fruits like banana, mango etc. are also kept in its leaves.
Flowers – Flowers are well planted on the front of the branches. They are like the open mouth of a lion in shape. That is why it is called ‘Sinhasya’ in Sanskrit. These flowers appear opposite in clusters. The taste of honey comes from plucking the flowers in spring. Bees carry its juice. It flowers twice a year (in spring and autumn).
Fruit – about 1 inch long, somewhat thick in the front and flat in the back. Wood – white in color is soft and light. Water does not penetrate into this wood, so it does not rot if put in water. In ancient times its coal was used to make gunpowder.
It is bitter, astringent, cold semen, mild to digest (short), beneficial to the heart, good for voice and cough, breath, blood bile, decay, phlegm, bile disorders, kamala, fever, discolouration, discharge, leprosy, anorexia, thirst, vomiting. , blood disorder and cancer killer.
Flowers – Bitter and bitter in Pak, and Kaas are decaying and phlegmatic.
There is brittleness in the bark. Both the bark and the leaves are expectorant, laxative and carminative, so their use is good for chronic congestion and phlegm disorders. Decoction of bark or leaves works well for leprosy, indigestion, febrile weakness and obstetric diseases.
It has been considered a futile medicine for biliousness, decay and cough.
Mixing only honey in its decoction and consuming it destroys blood bile, decay, kaas and phlegm.
In Ayurveda Shastra, about 25 uses of Vasadi Kwath have been prescribed for diseases like blood bile, phlegm fever, decay, cough, shortness of breath, odd fever, colic, acid reflux, eye drops etc.
In chronic fever, it has been asked to consume aloe vera in its leaf juice. Consuming only honey and sugar mixed in its letter Swaras calms the hard blood bile. Making ice out of it and consuming it with sugar candy in the morning destroys cough, blood bile and fever. (B.P.) If there is pain in the anus due to phlegm, if there is a very difficult tickle disease, then baking with bundles of its leaves gives quick benefits. (bangsaen)
Consuming Adoosa’s swaras with honey cures diabetes insipidus, leucorrhoea, biliousness, shortness of breath, phlegm, dry cough, leucorrhoea, etc.
By heating its fresh flowers and tying them on the eye, cholecystitis of the eyeball is removed. By giving the flowers cooked with dry ginger, split ends disappear.
In atrophy, decay, by taking its almanac and proven ghee mixed with honey, it destroys cough, breathing and pandurog. (Sushrut)
The leaves or vegetable of its leaves are of cough bile, cold semen and Kat Vipak. (Charak).
Its flowers are first class cool. Beneficial in decay, raktapitta, raktana and pragaha and are choleretic. Its root destroys cough, shortness of breath, fever, prmeh, kaphapittajanya gatli or vagaan, pandu, urinitis, gonorrhea and rajayakshma. To protect children from cold or cough, its seeds are sometimes hung around their necks. Gargling with decoction of the leaves ends toothache.
Decoction of its root is beneficial in whooping cough and common fever in children.
After soaking the bark of its root for 7 days in sugar syrup, dry it and make fine powder, its quantity. Consuming Masha daily cures chronic syphilis. Or on leprosy, both its root and shaved herb are mixed with ghot, honey and given daily.Grinding the bark of its root and soaking it in water and drinking this water sip by sip is definitely beneficial in nausea and vomiting. If one foot of its root is prepared and consumed regularly in appropriate quantity after making 1 bottle of sorbet, then breath and chronic cough are destroyed by the root.
Soaking its leaves in rogan babuna and coating it provides peace in pleurisy. Take out the juice of its leaves and cook it in sesame oil. After removing only the remaining oil, filter it and keep it. Massage of this oil ends convulsions, abdominal pain and cramps of hands and feet.
Grinding its leaves with melon seeds and drinking it, urine starts to flow freely, and it is beneficial in urinary diseases. If its Mixing 6-6 mashes of fennel sora and chicory with tola patra and drinking it after drinking it, urine comes with excess, and kamala disease goes away.
If you apply its leaves after grinding them with water on the boil in the beginning, then it settles, and there is no pain.
Its flower is the destroyer of Rajyakshma, the heat of gallstones and blood. If the flowers are soaked in water at night and taken in the morning after filtering, then the irritation and pleasure of urine goes away. After filtering its dried flowers, mixing two parts of bengash in it and consuming it with molasses, kahu, khurfa and cucumber destroys spermatorrhea. Prepare sorbet of a bottle full of ripe flowers. Then mixing four mashes of sherbet with 6 mashes of rooh crab and proper amount of well water and drinking it early in the morning ends heart palpitations, shortness of breath, nervousness and chronic heat. Prepare Gulkand by mixing two parts of sugar candy in one part of its flowers. It is beneficial in cough, shortness of breath and tuberculosis.
Adoosa harms sexual power. Pure honey and black pepper are its mirrors.
According to modern opinion, Adoosa being a stimulant, mucilaginous, inhibiting growth inhibitory or anticonvulsant, its action is similar to English medicines named Ipecacuan and Siniga, and its planning is done in their place in ancient cough, breathing etc.
According to modern opinion, Adoosa being a stimulant, mucilaginous, inhibiting growth inhibitory or anticonvulsant, its action is similar to English medicines named Ipecacuan and Siniga, and its planning is done in their place in ancient cough, breathing etc.
Separation of its bark has come to know that the bark of the old tree contains more useful substance than the new one, so it should be used for medicinal purposes only.
By looking at the properties of leaves and bark, it was found that both have almost similar properties, so it is even better to use a mixture of both. There is a slight difference in the properties of its leaves, flowers and roots. Flowers are acrid, bitter, febrile, diuretic, reduce the heat of the blood and inhibit growth. Its feverish religion is well visible in the fever which is odd or ascending.
Mool – antipyretic, diuretic, mucilaginous, antipyretic, antihelminthic and antiphlogistic. Compared to the leaves and roots, the anticonvulsant dharma is more in the flower. The root has more expectorant action than the leaves. Dilution of phlegm and reducing the velocity of kaas, these two religions are mainly found in Adoosa. Mixing peepal powder with its juice increases its virtues. It is more suitable in chronic phlegm-diseases than in new phlegmatic diseases. In chronic phlegm disease, there is often weakness in the heart, it goes away from the use of its root.
By giving juice of leaves in decay, the stagnant phlegm starts coming out. Organ-burn and rising and falling fever reduces. On cough diseases of small children, giving its leaves mixed with sugar syrup gives quick benefits. Prosperous people have a type of cough, to get rid of it, its leaves are consumed by adding fine powder of Sheetalchini (Kawab-sugar) to Swaras. Putting its juice in the ear is beneficial in nosebleed. To remove the redness of the eyes in Netrabhishyand, its fresh leaves or flowers are tied above. Its root-bark powder is given in cold fever. Leaf paste and root bark powder are used in rheumatic diseases. Patra-Swaras is planned for prevention of diarrhea. Intestinal worms are destroyed by its juice and rot does not come in the diet. If its leaves and branches are boiled in water and children are bathed with that water, then they do not get itching etc. contaminated animal diseases.
It has the unique power of anthelmintic drug. It has been tested as follows. A little bit of water was taken from the pond, which was full of small insects, then the juice of its leaves was put in it, then all the insects died and started landing on the water. The red spider which harms tea cultivation also dies from Adusha Swaras, this is also a felt talk. Therefore, wherever insects cause sorrow, we should sprinkle its juice mixed with water through a fountain, then these sad creatures will not even be detected.
Bedbugs run away by keeping its small twigs in the cot. One of it’s formulations is mushaak – excrement, whose method is such that by grinding its leaves in goat’s urine, catch a mouse, leave it in the house after smearing it with this presented paste, then all the mice will run away from the house.
For sprinkling on plants etc., its juice is used in this way- after crushing its leaves, leave it lying in water for 6 hours or more, then that water should be sprinkled in the shower.
After soaking half a seer of its dry leaves powder in 5 seer of water for two hours and using it in the above way, the same pest destroying work is accomplished.
If cows and bulls have any stomach ailment, then mixing the powder of its leaves in their fodder is beneficial. Bullocks also have stomach worms, they also fall due to this experiment.
Compared to its flowers, leaves and roots, flowers have the characteristic of anticonvulsant properties, they are planned in many stages of respiratory disease and in rapid recurrence in hay fever. They are given by making an oblation. Avleh tea spoons are equally twice a day.
“It has proved beneficial for patients suffering from bronchitis (bronchitis and cough) and shortness of breath, but the great praise given to it in relation to the destruction of tuberculosis is very doubtful,” reports the Indigenous Drug Committee of India.
The author of ‘Pharmacopeia India’ has specially praised it on respiratory disease and wrote that it does not benefit that much in those who have cough or fever with breathing. But this experience of our doctors is a complete statement that those who have cough with fever also get special benefit from it. But this fever should not be caused by air.
It has been written in the ‘Indian Journal Medical Research’ that the alkaline acid present in it loosens the speed of the blood, and brings the speed of the heart to a minor level. This . Alkaline is also the destroyer of heart related diseases, and dilates the air tubes in general. The juice of its leaves is beneficial on cough disorders. It loosens the phlegm, so that it can be thrown out without any discomfort.
According to Indian Medicinal Plants (Major Vasu and Dr. Kirtikar), it is beneficial in vasculitis, blood disorders, leprosy, heart disease, thirst, breathing, fever, vomiting, loss of memory, decay, pandu, oral disease, urinary tract and leucorrhoea, and its leaves regulate menstruation and flowers regulate blood flow and fruits are especially useful in vasculitis.
Ten of its leaves are especially useful in amatisar and raktatisar. Drinking fresh leaves crushed in water destroys phlegm. Boiling its ripe leaves in water and inhaling its steam, or soaking a cloth soaked in that boiled water and squeezing it, gives ultimate benefit on arthritis (joint pain) and painful swelling.
Consuming its flowers, leaves or roots with dried ginger provides relief in tremors, flatulence, cough, breathing and other healthy mucous diseases.
Red flowered peach is more useful. Its font is used in cough and decay. It is more favorable to use the liquid essence of its leaves and flowers.
Vasarishta has a good effect on breathing. If there is no benefit even after giving it in 3-4 doses, then it has been seen that using only Kankasav mixed with Vasarishta gives quick benefits.
Vasa Putpak – Make a ball by crushing its fresh leaves. Wrap the green pieces of banana or castor on it, wrap the cloth on top. Apply 1-1 finger of cow dung soil on the cloth and sprinkle ashes on top and heat it in the fire. Take out the capsule when the soil turns red. Some coat castor or banana leaves with urad flour and bury the ball in the ground. When the top dough is cooked, then take out the samput and extract the juice by squeezing it. Mixing it with honey, it is consumed in blood bile, cough, fever and decay. Quantity from 6 masha to 2 tola.
Vasavaleh – Mix 64 tolas of swaras, 32 tolas of sugar and 8 tolas of peepal powder and 8 tolas of ghee, and cook on Mandagni. If the sugar syrup becomes thick and smooth, remove it and mix 32 tolas of pure honey in it and keep it safe. Consuming 4-4 mashes in the morning and evening and increasing it gradually, has great benefits on Rajyakshma, cough, shortness of breath, catarrh, heart disease, biliousness, indigestion and chest pain.
Grind 61 seers of Vasapatra and bark and cook in 32 seers of water. When the quarter is left, filter it into 6 | Got sugar candy, cook it again. When it becomes thick, take it down and add 211-211 tolas of Trikatu, Trisugandha (Cinnamon, Cardamom, Bay leaf), Caraway, Nagarmotha, Dry ginger, Kabila, White, Cumin, Harr, Talispatra and Coriander powder and after cooling 1 Add a spoonful of honey. Quantity – 1 to 2 tola, proportion – hot water. Kaas, hoarseness, tuberculosis, agnimandya, urinary tract, afara, heart disease etc. are killers. Similarly, there are many other uses of ‘Vasavaleh’.
Vasahim – Grind 1 tola fresh leaves of it and soak it in 6 tola water and keep it in dew at night. Sieve it in the morning before sunrise. Mixing sugar and honey up to 4 tolas in 1 tola or sugar candy mixed with 1 loaf of cow’s milk and drinking it is beneficial in blood bile or fever.
Vasa Ghansatva – Grind 1 seer Panchang and cook it in 16 seer water, filter it when the quarter is left, and cook the filtered decoction again with Mandagni. When it is ready to make tablets, then keep making tablets. Make bullets from 4 Ratti to 1 Masha. Take 3 or 4 tablets a day with honey in cough, dyspnea and dyspepsia.
Vasakwath – Take 2-2 seers each of its leaves, root, bark and flowers and cook it in 20 seers of water. When it remains half, mash it and filter it. Put 1-1 seer of the above mentioned three things in this filtered decoction water and cook again, when it remains half, filter the sewage and cook again by adding eight seer each of leaves, bark and flowers. When half is left, filter it and fill it in bottles. Only till 211 tola, should be given 3 times a day. It removes cough, fever, vertical biliousness, bloodthirst and increases digestive power.
Other Vasadi Kwaths are available in the scriptures.
Basa sorbet: Mix 1 seer of stale juice and 4 seer of pure sugar, filter it and fill it in a bottle when the sherbet syrup comes.
Vasapatra 1 Ser, Liquorice. Collect 10 tolas of pav, small bowl and cook it in 6 seers of water. When half is left, filter it and mix 6-6 mashes of kooth sweet, gavjwan, small peepal, kakadasingi and pohkarmool and bharangi 6-6. When two seers of decoction water is left, filter it. Mix sugar candy and make sorbet. Dosage – 1 to 5 tola, giving it 3-4 times a day cures cough, cold, sore throat etc. quickly. Due to this, Kaphasrava is done in the best way, it is good for taking out Kapha in cough, breathing and decay.
Vasakshar – Burn its almanac and soak it in quadruple water in a Chinau or earthen vessel. Keep stirring it with a stick in between. On the third day, after filtering the water, filter it with a thick cloth, in which no part of ash can come. Add two times water to the remaining ash and dissolve it, and after filtering the water, taste a little on the tongue and see. If alkali is found in it, then mix that water also in the first water. In this way, after tasting 3 or 4 times, take water and mix it in the above until the alkali is known. But every time add water in half proof. Then burn all the collected water in a clean pan in a low flame. In the end, scratch out the strong white alkali remaining in the pan.
Quantity – 1 to 3 ratti. It is like nectar for cough, asthma and bleeding gums. Taking it with betel leaves provides relief in all types of cough and breathing problems.
Mix its almanac with double water in a lohapatra and keep it in an open place for 21 days. Shake it in between with this stick. After that put this wood or ber acacia wood on the stove and give it on low and medium flame for one hour. After everyone leaves, when all the almond powder falls down on the floor or on a wooden board, scrape the black colored crust at the bottom of the vessel and keep it safe in the bottle. The quantity of this Vasa Patti is half a ratti to 1 ratti. After consuming empty stomach in the morning with butter or curd cream, drink it from above till fresh (faded and thick). Consume more of it in the diet. Reading of acid and oil is unhealthy. In this experiment, there is benefit on breathing and breathing.
Vas Ghan-Kshar – While burning its almanac, keep pressing it with ash wood, when it becomes black after burning completely, then mixed with eight times the water, let it remain in sugar or earthen vessel for three days. Keep stirring it in between. Then drain all the water from the top and put it in the pan. When it becomes thick, then store it in a vessel. Just the alkali is ready.
Quantity – 1 to 4 ratti. Ratio ginger juice or honey. Instantly stops the dreaded velocity of all types of cough, it is also beneficial in respiratory diseases. It is very useful if throat is blocked due to phlegm, speech is stopped, if no medicine is beneficial.
Basa extract – Crushing its leaves 1 seer, flower 10 tolas both, let it soak overnight in 4 seer water. In the morning, by giving an enthusiasm, 4 sher of cow’s milk was found in him. Draw 5 seers of extract through Bhavka (Nadi Yantra). Quantity-up to 5 tolas. It is beneficial in the first and second grade of Rajayakshma.
Vasa Khand Pak – its Swaras or Kwath in 5 Ser in section 2 || Mix 13 drops of sage and haritaki powder and cook on low flame. When it becomes smooth, mix honey 8 tolas, Banslochan 4. tolas, peepal cinnamon 1-1 tola and Talispatra, small cardamom and Nagkeshar 6-6 mashes and mix their powder.
Quantity – 3 mashes to 1 tola. Beneficial in heart disease, decay, breathing, cough, catarrh, blood bile.
Vasa Dhrita – Root, including leaves and branches, after grinding 2 seers of almonds, cook it with 32 seers of water. Sieve when 4 see remains. Then mix 4 seers of ghee and half a seer of peach flowers in it and cook it on a low flame. Sieve it when only ghee is left.
Quantity – Consuming 1 tola, quarter honey mixed with it destroys breathing, cough, catarrhal, tertiary and quadruple fever, blood bile, decay and poison disorders. If it is mixed with honey and sugar, it cures bile cough and all bile disorders.
See the use of other Vasadi Ghrita in the scriptures.
Vasadi Vatika – In its density 8 tola, powder of peel of acacia root 2 to, pure opium and camphor 1-1 to make all of them sour and make 2-2 pills. Quantity-1 to 2 tablet. Beneficial on urakshat, breath, blood bile, diarrhoea, blood leucorrhoea, kaas, prahani etc.
Vasa Tincture – Crush its leaves on a clean stone and take out the juice. Or take swaras extracted by Putpak method, mix half of rectified spirit, fill mouth mudra in a bottle, keep it for 7 days. Then filter it and fill it in another bottle. Quantity -10 drops to 60 drops | It is beneficial on breathing, castration etc.
Vasakasav or Vasarishta – worthy of reference in the scriptures.
Vasa Suvarna Bhasma – After heating 1 tola of gold, extinguish it 100 times in the juice of Vasa Mool-Tawk or decoction. Then keep it in the Kalk of the destroyer and prove it to ashes by fire. Consuming this Bhask in proper quantity and in a suitable ratio, the heat of many days and chronic Venus discharge goes away.
Vasa Tamra Bhasma – After extinguishing pure copper leaf in vasa leaf-juice 100 times, put it in the pulp of green mustard plants, cover it with alcohol and blow it in the flame of burning grains. By doing this three times, consuming 1/2 Ratti quantity of Bhasma with proper proportion is beneficial in complete rheumatism, phlegm, cough, breathing, weakness and old age.
Vasa Godanti Bhasma – Godanti – Hartal with Vasa’s swaras and blow it in Gajput. In this way, the ash prepared by giving Gajput after rubbing it 7 times is especially beneficial for chronic fever. Quantity – 1 ratti. It is given with sorbet Anjubar in Raktpitta.
Vasa Kand – Mix double sugar or sugar in its flowers and keep it in a glass or ghee smooth pot and keep it in sunlight for a month. This is Vasa Kand. Mother-6 Mashe to 1 So. till | It is the destroyer of all Kaas, breath, blood bile, pinus, and pathological Rajayakshma of the lungs.
Use in cough, breathing, tuberculosis and semen disorders
(a) Mix 15 tola Vas Mool and 1 tola Giloy and cook them in 20 tola water. 7. Sieve the remaining weights. Consuming 3 doses of this mixed with honey 4 times a day, 4 times a day, cures phlegm and wet cough.
Mix 1/4th Jauhar Nausadar with its flower powder, keep it in the quantity of 2 Ratti Batashe and feed it.
Its root bark 2. So very fine grinding, opium 1 in it. Mix the masa in water and make it very sour. Then make 20 pills by adding ghee to make pills. Give 1-1 pills in the morning and evening, there is a quick benefit.
Take its fresh yellow leaves and put layers in the Bhavka and Varuni Yantras and fill only the leaves so much that the Yantra remains empty. Make clean letter-vaap by Mandagni. Then mix equal parts of Parishrut ordinary extract with honey. This ‘Kasari honey’ has wonderful miraculous benefits on cough, breathing, tuberculosis, cough, cold, whooping cough in children etc.
Dosage – Give to children from 3 months to 6 months according to their age Its leaves (dried) 2.
Take a tola and boil it in 10 grams of water, and mix dry ginger, black pepper 2-2 mashes and sugar 6 mashes in it. Only – 311, Chronic cough and shortness of breath are frequent. Beneficial in bronchitis.
Its density. In Tola – Peepal, Black pepper, Mulathi, Kakadasingi, Pomegranate and Jawkhar Mix 2-2 mashes and make tablets by grinding. Cough goes away quickly by sucking it.
Mix the almanac of Sambhag Kateri in half a seer of Vasa letter and cook it with 4 seer of water on Mandagni, keep the lid closed on top. After cooking for about 3 hours, when two seers of water remains, filter it and mix two seers of sugar in it and make a sherbet. Quantity – 1 to 2 tola is best for cough with breath, removes phlegm quickly. If chronic cough (bronchitis) and low fever persists, then it is especially beneficial.
Give its bark to Tola. Cook the bread in water, when 5 tolas of water is left, then mix a little rock salt in it, drink it hot, give something and lie down covered. There is a unique benefit on cough.
Thick powder of its shade dry leaves should be mixed in half a seer of water. Sieve half of the remainder and mix dry ginger and peepal powder 1-1 masha and 10 tolas of honey in it. Quantity – This shroud is up to 5 tola. Excessive phlegm is beneficial on cough and breathing.
After drying its leaves in shade, grinding and sieving, mixing sugar candy in equal parts of the powder and consuming it also provides relief in cough.
Note – If phlegm has increased in chronic breath, then to remove it easily, put dried leaves in a chillum and drink it (add some leaves of ghatura to it) or powder of dried leaves of it, 5 tolas of Giloy juice and 2 Make a cigarette by mixing Tole Kalmi Sora and smoke it. If the phlegm has become especially thick, then drink hot tea mixed with its juice, sugar candy, honey and a little black salt.
Among the above proven experiments, Vasakshar, Vasa-Kwath, Vasa Sharbat, Vasarishta, Vasa Tincture and Vasadhanasatva are particularly beneficial.
(b) In Rajayakshma – the above-mentioned Vasavaleh, Vasark, Vasakvath, Vasarishta, Vasakand and Vasakhand are especially useful.
If a tuberculosis patient has a special cough, phlegm does not come out and the appetite is less, then in place of water, give Vasa-Parishruta water. The method is to cut the Vasa tree along with its root, dry it, clean the earth in a vacuum and burn it. When it becomes smokeless, collect the fire and cover it with an earthen pot. By doing this the fire will be extinguished. Then blow the ashes. Take out the coals. Out of these, fill 1 seer of coal in an empty earthen pitcher and put a thread in the hole in the bottom of that pitcher with a nail that hangs down a bit. In the same way, pierce the bottom of the second pot and put a thread through it. After that fill water in that pot and place it on the pot containing coal and keep the third pot without hole below the pot containing coal. First the water will trickle down to the coal, then it will collect from the pot below. Drinkable water for the patient will have to be prepared daily in this way. Once lit, the coals of Adusea give equal work for 7 days. After that the coals should be changed. By drinking this water phlegm starts coming out easily, the throat gets cleared. But if there is semen in the urine of the patient, do not give this water.
The place or home of a tuberculosis patient should be filled with Vasa Kwath, Tutiya and Kalai’s lime mixed together and Vasapatra’s dhuni should be given there. It is very beneficial for him to take air of Aduse, making a hut of Aduse leaves in Aduse’s forest.
(c) Semen disorder:Consume appropriate quantity of its density daily in the morning and evening, drink cold water from above and eat nutritious food.
Raktpitta – Mixing 2 tola juice of its green fresh fruits with 6 mashes and 2 tola honey, drinking it daily in the morning or 2 or 3 times a day cures bleeding and all its problems.
Its root bark 1 tola, licorice, infinite-root, bay leaf and grapes 3-3 mashe, jokut and cook in 32 tola water. When 8 tola water is left, after filtering, mix 2 tola sugar candy and give it to drink.
Its bark 4 tola, blood sandalwood, pitta papada 1-1 tola and 6 mashes of khus, after making all these, keep them soaked in dew at night in 5 tola water. In the morning filter the ghot and make 2 amounts of it. In the morning and evening, mix 1 loaf of cow milk and 4 tola sugar candy and drink it.
Or 7 drops of Basasatva or Vasa Kshar solution prepared by 200 times Sura, adding 1 c.c. By giving hypodermic or intramuscular (intramuscular) injection, there is a great benefit in blood bile.
Apart from these, the above-mentioned Vamahim, Vasa Sharkhet, Basakhand, Vasavaleh etc. are also useful in blood bile.
Gynecological diseases – If there is amenorrhea, there is no menstruation, then Adoosa leaf 1 tola and radish seeds and carrot seeds 6-6 Mashe, they should be given decoction for a few days.
For a happy delivery – Inviting Adoosa plant on Saturday morning on Sunday morning Bring its root and tie it with a red thread around the woman’s waist, and at the same time rubbing its root in water, below the navel and it on the vagina, gives a quick and happy delivery.
In obstetric diseases, the juice of its leaves mixed with 6 pieces of ghee, give it to drink once a day. In 7 days, any type of obstetric disease is completely destroyed.
On leucorrhoea – If shevat is far away, then the juice of its root bark should be consumed with honey. And if there is bleeding, mix equal part sugar candy in 1 tola of leaf juice and consume it like this 3 times a day. full benefits in 7 days.
Use in Kapha disorders like hair box etc. – 20 drops its swaras extracted by Putpak method and 2 ratti of honey and 4 mashes were collected, according to the power of the child, it should be licked 4 or 5 times a day and grind its leaves, heat it and apply it on the chest, it separates the phlegm stuck in the chest.
In fever Grinding its leaves with sugar candy and feeding it after filtering, the increased nervousness due to the heat of fever ends.
In stomach fever – Cut its leaves and amla and soak it in a kulhad in the evening, squeeze out the swaras in the morning and mix 1 tola sugar candy in it.
In typhus fever – Its juice extracted by putpak method and a little ginger juice and Collected Tulsi leaf, mix licorice in it and give it to drink after mixing it with honey.
Its root bark 2 tola, dry ginger 3 masha, black pepper 1 masha, make a decoction of these and consume it after mixing it a little sweet.
When phlegm stops in guilty fever, then its voice. Tola, ginger juice and honey 6-6 mashes and honeydew kheel. Mix the masha together and lick it several times.
In influenza – 7 pieces of its leaves, dry ginger, fennel peel, 2-2 pieces of turmeric and muladi and 4 pieces of bitter gourd root, grind them all and mix them slowly in 10 tola water. When the water dries up a lot, then squeeze it in a cloth. Then that thick juice should be consumed at both the time in a pleasant way, but mix 3 mashes of honey in it, this is proof of quantity.
In the state of fever, whenever the patient feels thirsty, then after adding Adsa leaf, he feels boiled and the fever also subsides quickly.
Itching, dryness, scabies and inflammation – Mixing its soft leaves with a little turmeric and cow urine and applying it is also beneficial on itching, ringworm, itching and inflammation of the calf (kachchu) and eczema.
Ordinary itching goes away only by taking a bath with decoction of its leaves.
If there is excessive dryness in the body, then its leaves should be taken in 6 months. Mixing loaf milk, 2 tola ghee and 6 tola sugar candy, consuming it destroys the dryness of the body during the day. By mixing a little conch shell powder in its leaves and applying it, the bad smell of the body goes away quickly.
In diseases of the mouth – due to swelling of the gums and blisters in the mouth, by making a decoction of the root of Adoosa, gargling it or chewing its root in the mouth gives special benefits.
If there are only blisters in the mouth, then chewing its leaves and sucking its juice is beneficial. Folk should spit.
When there is a hollow in the molar or tooth, fill its essence in that place. Many mouth diseases are also cured by teething its wood. By taking ocher and honey mixed in the decoction of Vas, mouthwash, nerves are destroyed.
Renal colic- Adoosa leaf juice mixed with 6 pieces of honey, and the steam of its leaves should be baked on the pelvis, then severe kidney pain ends quickly.
Consuming fine powder of Arsh- Adoosa leaves and white sandalwood together, 4 mashes a day, is very beneficial for bloody piles, and bleeding stops. If there is swelling in Arshankur, give steam of decoction of its leaves.
Vata disorder – Basa Kshar with 4 ratti. Consuming it up to Masa cures vaat-borne fever, especially heaviness in the stomach after eating, dull pain. If Vasa Kshar is not ready, make powder of its bark, mix one-fourth part of caraway powder and half part of rock salt with caraway powder and mix it well in lemon juice and make 1-1 tablets of the paste. Consume 1 to 3 tablets after meals.
Shirarog – (a)Make 4 tablets by drying the flowers of Adoosa in the shade and mixing a little jaggery in the size of 1 tola in the shape of Mahin. The attack of headache starts as soon as eating 1 tablet gives real benefit.
(b) Taking two tolas of its root, grinding it well in 20 tolas of milk and mixing 3 tolas of sugar candy and 15 pieces of black pepper powder in it, diseases like headache, eye disease, colic, hiccups, cough etc are destroyed.
(c) By drying its leaves in the shade, making it like tea and drinking it, any pain related to headache or headache goes away. You can add some rock salt to this tea for taste.
(d) If there is a headache due to normal night time, then taking 1 tola decoction of the above leaves mixed with honey and sugar candy at both the times cures the cold quickly.
Small Pox Prevention –If there is an outbreak of small pox in the surrounding, then to save the child from its attack, 1 leaf of Adoosa and licorice should be given to each of them daily once after making an eightfold decoction in pounded water.
Note – There is also a white small Adoosa which is called Justicia Picta in Latin. Its shell is small, it is applied on the left side. The leaves are small with whitish green colour. White-crimson flowers almost always bloom in it. Its properties are similar to those of Adoosa. They have the specialty of being warm and loving. These qualities are in its leaves. By making a poultice of the leaves and tying it to mastitis (inflammation caused by obstruction of milk inside), it cures purulent inflammation. On any other swelling, grinding its leaves with coconut fruit and tying them in water, the swelling goes away quickly. The quantity of its swaras is 10 to 20 drops. In kaas, lick 1 to 4 ratti honey mixed in its swaras.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Aragwadha – Amaltas. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
This is India’s useful herbal medicine. Its details are available in Charak Sushruvadi ancient Arsh texts. Perhaps the Arabs had obtained its knowledge from India only, after that the Greeks came to know about it.
Ayurveda Nighantukars have given it a name Karnikar and have said that it is a variation of Amaltas, ‘Kshudra Amaltas’. There is a lot of difference of opinion among the scholars in this matter. There are two reasons for this difference. One, ‘Karnikar’ has been given the name ‘Talatkambal’ by some of the modern scholars. Late Mr. Umeshchand ji has also given the name ‘Kanikar’ to Ultakambal in his drug word Sindhu, and has given its second real name ‘Dramotpal’ and has written its qualities according to Rajnighantukar. Next see the Ultkambal episode. Ayurveda Nighantukars have given it a name Karnikar and have said that it is a variation of Amaltas, ‘Kshudra Amaltas’. There is a lot of difference of opinion among the scholars in this matter. There are two reasons for this difference. One, ‘Karnikar’ has been given the name ‘Talatkambal’ by some of the modern scholars. Late Mr. Umeshchand ji has also given the name ‘Kanikar’ to Ultakambal in his drug word Sindhu, and has given its second real name ‘Dramotpal’ and has written its qualities according to Rajnighantukar. Next see the Ultkambal episode.
The second reason is that a commentator has given the names ‘Mahakarnikar and Dramotpal’ below the word ‘Karnikar’ which has come in the synonymous names of Amaltas in Bhavprakash. Actually Drumotpal may be the name given to Ulatkambaka and not to Karnikar or Mahakarnikar.
Big Amaltas and Small Amaltas are two such distinctions of Amaltas. The older one is called Mahakarnikar and the younger one is called Karnikar. Small Amaltas or Karnikar tree is found in sand-mixed land (Madhya Pradesh Chanda forest and other similar forests) of lesser height than big Amaltas. Its pods are smaller in length and roundness than those of large Amaltas. Its garland is as beautiful as the garland of big Amaltas, but it is odorless.
Late Mr. Umeshchandra ji has rightly written about this Karnikar (he himself named Ultakambal as Karnikar and then elsewhere in the same medicine word Sindhu) that ‘Hrswa Swarnabhushan Vriksha (a kind of Amaltas) which is called Chhota Sonalugach in Bangla, Laghuwahwa in Marethi, In Telangi it is called Kirugke etc. and in Rajnighantu the qualities called Sar, Tikta, Katushna Kaphashulaghna, Udar Krisimehaghna, Vranaghna and Gulmaghna are of this.
‘Amaltas’ is a Greek name and it may be a corruption of the Sanskrit word ‘Kritmal’. Due to its resemblance to a garland, it has been called ‘Kritmal’ in Sanskrit. Its trees on the ‘giri’ (hills) are specially adorned with their garland-shaped golden flowers. That’s why it is called Girimala. And Garmala in Gujarati seems to be a corruption of the same. Being the destroyer of diseases, it is called Avaghatak etc. and its main Sanskrit name, Aragwadha, is also due to this reason.
Sanskrit – Aragwadha, Rajvriksha, Chaturangul, Karnikar. Hindi – Amaltas, Dhanbehera, Vanarkakdi.Marathi- Bahva, Bhaya. Gujarati – Garmalo, Garamako, Gudmalu. Bengali – Sonalu, Bandarlati. Punjabi – Amaltas, Karangal, Kaniyar. English – Pudding Pipetree, Indian Lebanon, The Paging Cassia. Latin – Cassia fiscula.
It is often found in the whole of India, Brahmadesh, Bengal, West Indian Islands, Brazil region of South America and tropical regions of Africa.
Description – Its plain trees are of small stature (called Karnikar or Chhota Amaltas) and hill trees or Bada Amaltas are about 30 feet tall. The roundness of the tree is from 3 to 5 feet. The branches are very dense, thick and thin. A type of red juice emerges from the branches which solidifies and becomes like palash gum. It is applied on molar pain.
The roots of the original tree are very deep in the ground. The wood of the root is very hard and the bark on top is grayish red in colour. The smell of the bark is pungent and somewhat astringent in taste.
Leaves – The leaves of Jamun are shaped like elliptical, face-to-face pairs on longer coins. There are 12 to 18 pairs on the hook holding the letters. The length of the leaf is 3 to 5 inches (the length of the leaf of Karni-kar is 111 to 3 inches) and width) to 2 inches. The surface of the leaf is smooth and the stalk is decaying. Both the sides of the large Amaltas leaves are covered with white gray hairs. The upper part of the letter is of dark blue color and the lower part is of slightly pale color. The soft leaves are very shiny, beautiful with the luster of gold and are densely hairy. The smell of the leaves is pungent, the taste is some what spicy and astringent. The leaves usually fall at the end of winter.
Flower – The whole tree looks very beautiful with a garland of yellow flowers, usually in the month of Vaishakh or Jyeshtha when the leaves fall off in Karnikar or small Amaltas. It appears as if the tree has put on a bright Pitambar. but it doesn’t smell
In large Amaltas also, these flowers come out in yellow colored, long garlands, usually along with the leaves in Chaitra or Vaishakh. These flowers usually adorn the tree till the end of Jyestha month. Each flower usually has petals. 1 to 1, slender, conch-shaped, garland-like stem that bears the flowers. Long up to the fur, the leaf is derived from the angle. This stick of dark green or blue color is covered with very soft, shiny and white hairs and attracts the eyes by swinging here and there with the gust of wind laden with flowers. These flowers have a natural sweet smell. This smell is sweet like ripe melon on first smell but after special smell it seems a bit fierce and pungent. The flower stalk is 1 to 2 inches long, soft and bent down. The basal part of the flower stalk has three flower leaves which are 1/8 to 8/16 inch long and are covered with gray, shiny hairs. The middle flower leaf is a bit longer.
Vegetables (greens) are made of these flowers, Gulkand and Kwath are made for medicinal use. But these flowers are going to rot very quickly. Storing and keeping them safe is a very difficult task. Therefore, whatever use has to be made of them should be done immediately.
Pods – In the month of Jyeshtha, when the flowers usually fall off, these pods emerge in the beginning, of a thin needle-like blue-green color, which become 1 to 2 feet long at the end of the rainy season. In small Amaltas, these beans are more than 1 foot long. In rounding 3/4 cm. Or is tubular up to 1 inch.
After ripening and drying, at the end of winter, their blood turns black. And their surface becomes hard like wood. The front of the fruit is notched. Small food remains inside the pod and on both sides of the food or layer, sticky sweet pulp of opium-like black color or fall is attached, which is taken in the main medicinal work.
Seeds – There are 2-3 seeds in each layer of the pod. A total of 25 to 100 seeds in each pod. Vinegar seeds like, ringed; The blood vessels are very smooth of gray colour. These seeds are very hard. Yellow lentils come out from inside by whipping.
Wood – The wood of the tree is very strong. It comes in the work of thatch on the houses or in the work of applying it on the surface of the water inside the well. Wood ash is used as a colour. By rotting the upper bark of wood in water, fiber is extracted and rope is made and this bark also comes in the work of shellac dyeing.
According to Ayurveda – it is sweet in Rasa, bitter in Vipaka (some consider it sweet in Rasa and Vipaka), cool in semen and Guru, aliphatic, laxative, anti-inflammatory, and is beneficial in fever, burning, heart disease, vatodabarta, worm, colic, Abdominal disease, Vishtambha, Prameh, Utrikruchhu, Raktpitta, Kaphodar, Gulm, Pittakopap, Tridosh, Kandu and Leprosy. Its successful planning is done to remove constipation during fever.
It removes raw and solid stools stored in the bowel. It does not come out in the feces after digesting the mango. In the condition of fever, it is even better if the contaminated urine is not digested and it is thrown out soon, fever cannot take a more extreme form, therefore, in the condition of fever, it is also used for bowel modification and to bring out common stool. It is used fearlessly to soothe gastroenteritis as well.
“Just as in modern medicine, liquid paraffin and castor oil are used to remove stool by rubbing it slowly, in the same way, the pulp of Amaltas gives astringent properties. But the amount of liquid paraffin It is digested, it is not beneficial for the body, it has this defect and after bleaching, castor oil causes contraction of the intestine, due to which constipation occurs on the second day. Both these faults are not in Amaltas. That’s why it is considered better than both of these in Amaltas for abdominal research in fever. Purification of Amaltas does not lead to over-purification and never leads to weakness, that is, it is a mild mind medicine. It gives the attainment of sransan quality in the intestine, due to this colic, udrat and udvartt are also retired. For this reason, it is planned for purification of the abdomen in the Kshatra also, if necessary.
Abdominal feces and worms are removed from Amaltas. Then opinion poison or germ poison does not enter the blood and it also does the work of blood donation to some extent. All the skin diseases (leprosy) caused by the said poison are destroyed by these two reasons. It reduces the sharpness and heat of the blood. That’s why it is given to remove the disorder by making the upward trend of blood bile.
In rheumatism, flatulence and colic, colic and various gout diseases, the heart becomes relaxed by hitting the heart. Consuming Amaltas in such a condition purifies the stomach and saves from heartache.
There is some heek in its anus, so drinking a little Gulkand mixed with it after boiling it with water is especially beneficial during consumption. Many doctors mix jaggery in it and consume it, due to which there is no pain in the stomach.
In Ayurvedic texts, many medicines have been mentioned in virechana class and all of them are beneficial. But in all of them special superiority has been given to Amaltas. It has been said that it is more beneficial in diseases like fever, heart disease, rheumatism, diarrhea etc. because it is soft, sweet and cool. This child does not cause any harm even to young and young children, on the contrary, it only benefits.
To consume it specially (in the form of Kalpa), take well mature pulpy pods and bury it in a pile of sand for 7 days. Then dry them thoroughly in the sun, take out the pulp and keep it safe by filling it in a pure vessel (pure earthen vessel). According to Ayurveda, its pulp extracted in this way never causes any harm. Its quantity for a child up to four years is one Prasut or one Anjali ie from 1 tola to 2 tola.
In the pulp – By mixing juice of sambhag grapes or by giving it with suramand, or direct of gher or dadhimand or juice of amla or cold kshnav or kanjo, or drinking it mixed with nishoth’s astringency or mixing salt and honey in it. By drinking it with the decoction of the fruit or by consuming appropriate quantity of Nishoth powder and jaggery mixed in its decoction or By cooking it in milk and extracting ghee from it, or by consuming that ghee again after proving it with juice of amla and its pulp, or by consuming the same ghee after proving it with the astringency of dashmoola, kulthi and barley and nishoth etc. By consuming it or making it Arishta (see Arishta Vidhi Aag), the achievement of good physique is achieved. The aforesaid Dwadash Kalpa Siddha medicine for the patients suffering from diseases like Dah Udavart etc. has been given in Charak Samhita. And in the end, it has been said that the person who likes sweet, bitter or salty type of food, he also gets desired success by consuming its pulp along with it. The body gets purified by perfect purification.
Pulp of pods – given with warm cow’s milk only purifies the cell of a fever patient. By giving it in abundance with honey and sugar, in vertical blood bile; Its decoction in pittodar; By giving it with the juice of sugarcane or Bhumikushmand or Amla, in Kamala Roga; Consuming this decoction mixed with carom seeds proves to be beneficial in phlegm; Raisins mixed with this in cholera by drinking Kwath Siddham; Grinding tamarind pulp mixed with it and giving it is beneficial in bile outbreak. If the patient has the specialty of phlegm, then a little powder of Nishoth is added to the above mixture. Grinding the pulp with coriander and keeping a little catechu mixed with it in the mouth or keeping only its pulp in the mouth cures oral diseases. Mixing it in warm water and applying it on the stomach ends colic in children.
Grind the ripe fresh pods of Amaltas along with the pulp and seeds and apply it on the lump of the plague. And the decoction of its pulp is given on constipation and unconsciousness of the plague.
Mixing its pulp with Pipramool, Kutki, Moutha, Haritaki and consuming it proves beneficial in mango, colic, phlegm and fever. This is Aragwadhaadi Panchak Deepan and digestion too.
Raw pods – Greens, raita etc. are made from the raw soft pods of Amaltas, which are nutritious, appetizing, laxative, bile inhibitor, phlegm, cleansing the rectum, always dietary and leprosy in fever.
Patra – Dries phlegm and meda, loose stools (milduvrechak), topical fever killer, diet in fever, vranropak, Kandu etc are dermatological and antirheumatic.
On skin diseases like leprosy, rashes etc. by grinding the leaves; Grinding them mixed with ghee and applying it on the snake; By grinding them in women’s milk or in cow’s milk, Sadyovran and Kikis disease (flesh disease); Grinding it in the same way or applying swaras on mixing poison; Grind rock salt, sulphur, saffron seeds, saffron and rasaut with it and apply it on ringworm and eczema by coating it with lemon juice and honey. Grinding it with question and making it like a cake, it is beneficial on cancer. Cheating the ulcer with the decoction of the letter, the dream that is pure from the residence gets fulfilled quickly. Rinsing wounds caused by syphilis by making decoction mixed with leaves of jasmine is beneficial.
Eating the leaves with salt and chilli purifies the stomach. Feeding greens (vegetables) proven without salt and oil to the leaves is beneficial in Urustambha disease. Roasting the leaves in mustard oil and taking it with the evening meal provides relief in rheumatism. The decoction of the leaves is beneficial for Haridramehi. Grinding the leaves with the cream of cow’s milk and applying it on the body of a newborn baby removes pimples or blisters.
Flowers – Tasty soft, some bitter, customer, astringent, carminative and phlegmatic.
Gulkand of flowers is beneficial on intestinal disease, microfever and leprosy. Giving Gulkand up to 2 tola to a Komalangi woman with milk at night clears the quota in the morning. The decoction of flowers is beneficial for polyps and diarrhoea. Their infusion is also made.
Root – Vatarakta, Mandalkushtha, Ringworm, Skin diseases, Tuberculosis, Gandmala, Haridrameh, Soth etc are killers.
Root bark or root – after drinking it after grinding it in milk, grinding it with rice wash on gout and ringworm, and applying it on Gandgala by grinding it with takr in poultices and abhyanga, grinding it in water and applying it on research and Drinking it after making decoction is beneficial for haridrameh.
The swaras of the fresh bark of the root or the clarified butter prepared by giving 100 feelings of decoction is given to the leprosy patient and during its consumption, water mixed with khadir is used for bathing.
Grinding the root of big and small amaltas separately in water and applying it on the penis is beneficial in the pain and soreness of the preaching on the penis.
Almanac – Herpes, itching etc. are skin diseases and leprosy killer. Grinding its almanac (root, bark, leaf, flower and anus) with water and applying it is beneficial on skin diseases like ringworm, ringworm etc. By using the Kashaya of Panchang in bath, paan etc. (washing hands and feet) all types of leprosy, new and old, are cured by benefiting from both internal routes. Along with this, it is also necessary to consume ghee prepared from the original bark.
Chhota Amaltas (Karnikar) – Sarak, Kaduva, Charpara, Ushna and Kapha, colic, abdominal disease, Krimi, Prameha, Vran and Gulm killer. The rest of the properties are similar to those of the above big amaltas. Gulkand of its flowers is not particularly beneficial.
Mixing the pulp of its pods with cow urine and applying it cures gout, hepatitis, pleurisy, hematoma, stupidity, dadru, pama, vascular ulcer, inflammation of the eye and arthritis.
Consuming its bark mixed with honey after boiling it in cow urine gives excellent benefits in dropsy, flatulence, dyspepsia, duodenum, anus worms.
Its pulp and tulsi leaves mixed together 1 to 1 tola each after proving it to be ripe and drinking it cures the perverted fever of autumn.
Note – Taking out its kernel or pulp from the pod, it becomes useless within a few days. Therefore, it should be taken out and used only when it is necessary. Its alkali is anthelmintic.
According to modern opinion – its pulp, root bark, seeds and leaves have laxative properties. The action of the root is rechak, balya and jvagna. Use of pulp only when in large quantities. If 5 tola or more is done from the tola, then it has a powdered effect. Such a large quantity is intolerable to the patient, so it is given in Pak or Avleh form along with other laxatives, it is also given with coffee extract. Its Pak or Majoon is a soft laxative in the quantity of two to four drams. It is also given in diabetes or polyuria. Its Gulkand works as a soft laxative, especially for women with soft nature. Quantity – up to 1 tola. It is given with warm milk at bedtime. Its pulp is applied around the navel to induce diarrhea in colic caused by children.
The decoction of its flowers is given on stomach disorders. Grinding its leaves and bark and adding oil to it is applied on pimples, ringworm, cold-borne condylitis, insect bites, rheumatism and rheumatism. Its root is beneficial on fever, heart disease, blocked secretion and bile development.
Amaltas is given in the form of catharsis when the heat of the blood increases or due to the accumulation of feces in the body, due to diseases like gonorrhea, rheumatism etc. If there is predominance of bile, then it is given with Nishodha and if liver function is disturbed, then it is given with Makoy. It is beneficial in febrile constipation and enteritis.
There is a lot of pain when the glands swell due to phlegm, there is pain even in drinking water. In such a condition its bark. By kneading a tola in some water and putting a little bit of it inside the mouth, the swelling of the glands goes away. The juice of its leaves is given to people suffering from arthritis etc. caused by constriction of the airways, and massage is done at the place suffering from this paralysis. There is benefit from this experiment.
Mixing 2 parts of its pulp with 1.5 parts of sugar provides relief in dyspepsia, flatulence and dyspepsia and strengthens the metal. Its pulp can also be given with coffee or chicken egg yolk. The pulp and the sugar portion are used in the treatment of sugar diabetes (gluten), and bleeding in the urine. Only the powder of its root should be given in blood diarrhoea.
In Konkan, the juice of its tender leaves is used as a pain reliever, and as a remedy for poisoning (soreness etc.) of Bhilava. The residents of Portugal make majoon or pak of its soft beans and flowers. A kind of gum emerges from its tree by spraying it, which swells in water like a katira. Similar to Amaltas, plants from other countries like Brazil, Cassia Mosqueta etc. have been planted in India. By using Amaltas for a long time, urine of all gray color starts coming. Its pulp is used for mixing in the essence of coffee. This pulp collection is beneficial for people suffering from duodenum disease. Quantity from 15 to 40 ratti.
By extracting the extract of the fine powder of the pods, a black-yellow volatile oil with honey smell is obtained. And the aqueous fraction or extract in this oil contains simple butyric acid (this is a fatty volatile acid which smells like rotten butter. This acid is often found in butter. Sugar in its pulp is 60 percent and luab, collector substances, gluten coloring matter, pectin, calcium oxalate, ashes and water.
Quantity – Quantity of pulp from 2 to 6 to 5 tola for gentle purgation. The quantity of pulp decoction ranges from 4 tola to 8 tola. The quantity of Moolatvak Kwath ranges from 5 to 20 tolas.
Pachkavaleh or chutney – Half a seer or pulp of the ripe pod of Amaltas. Or till 1 pav (by crushing the pods) put in one seer lemon juice. After soaking for 24 hours, mash it with your hands, put it in a clean cloth, shake it well and filter it. Then add cinnamon, dry ginger, black pepper, small pepper, small and large cardamom seeds, both cumin seeds (roasted) 2-2 tola each, rock salt and black salt 5-5 tola (any rock salt 2 tola and black salt 3 tola). Grind all these and mix them. If you want to make it sweet, then grind half a loaf of dry grapes and mix it. Someone in this Tola Akarkara is also mixed. Then fried kaladan in it? Tola, roasted asafetida grind 6 mashes and mix. Just this delicious digestive spicy chutney becomes.
Quantity – from 3 mashes to 1 tola. It removes dullness and laziness. By licking it at night, it clears diarrhea in the morning, the mind remains very happy. In case of disinterest in food, licking it two hours before, interest arises. Often the taste of the mouth is disturbed in fever. By licking it, that fault goes away. If the juice of ripe pomegranate seeds is mixed in this avleh, then its heat cools down and the taste increases even more. Do not cook or keep it in any metal vessel. Salt can be reduced according to taste.
Gulkand Amaltas – Take half a seer of the best flowers of large Amaltas and put them in a stone or ceramic pot and add a little white sugar and slowly beat them. When 1 seer sugar is mixed in it and the mixture becomes like Gulkand, then know it is ready. It is yellow in colour. Some prepare it in the same way as Gulkand of roses. It can be given from 5 to 8 months to small boys, 14 tolas to Komalangi women, 2 to 10 tolas to men in old age.
This Gulkand quickly removes the disorders caused by obstruction of stool, urine and air. It is specially consumed to pacify the defects of women during pregnancy. It is also beneficial in cough and fever. Ordinary fever subsides after a diarrhoea. It moistens dry cough. Eating 1 or 1 tola of it while sleeping at night and drinking milk or hot water on top of it, the soft natured person gets clear diarrhea in the morning.
Murabba Amaltas – Take the half-ripe beans of Amaltas, which have not produced any smell, remove the peel and take out the pulp inside, soak them in lime water for two hours. When it turns red, then take it out of that water and wash it with clean water 2-3 times. Then wash two times the sugar candy with rose water and cook it, when the sugar syrup is ready, put the above washed pulp in it and boil it for two or three times. A little musk and amber can be added to make it fragrant. It is a softener and colic killer.
Sharbat Amaltas – Unnao grains 30, Anjirdana 10, Lisodha (Labhera) grains 40, Gaavjbaan and Hansraj (Hanspadi) 5 months each, 2 tolas peeled licorice and cook all of them in two liters of water. When one seer remains, mix 10 tola pulp of amaltas in it and filter it. Then mix 3 tolas of almond oil and half a seer of sugar candy in it and make a sherbet. Drinking Gatra mixed with 2 to 4 tola of hot water purifies the lungs, softens the stomach, removes cough and is a forceful breath.
Majun Amaltas – Rose flowers and Sanaya 7-7 tolas, Coriander juice, Mulethi and Rock salt 1-1 tola, keep them separately after making fine powder. Then 12 tola figs, 9 tola tamarind and 5 tola plum, after soaking them in two seers of rain water for 24 hours, cook until one-fourth i.e. half a seer of water remains and filter through a sieve. Soak 1 pav (20 tolas) of amaltas pulp in this filtered water and take it off after heating it for a few minutes. And filter it again with a sieve and mix the above boiled figs, tamarind and plums in that water after mashing them well, and add a spoonful of sugar and cook till it thickens, then remove it and add 4 tola of almond oil to the above ground powder. Keep it Keep in mind that while cooking, it should not burn in the fire.
Quantity – 4 Masha to 8 Masha. It is very beneficial for Arsh Rongi. By removing the dryness of the intestines, it cures abdominal diseases, it is an appetizer and a carminative. Removes nausea and nervousness. Drink it fresh at night while sleeping. Consume with water or with milk.
Note – There are many other uses of Majun, available in Greek texts.
Aragwadharishta – Take 1-1 seer pulp of Amaltas and root of Jamalgote (Dantimool) first in 32 seer of water after proving a quarter decoction of Dantimool and fill it in a pure smooth pot and fill it with Amaltas pulp and jaggery 211 grams, and cow flowers, black pepper, Mix 5-5 tola powder of dry ginger and peepal and keep it safe for a month by cleaning the mouth of the vessel. Then filter and fill in bottles. Quantity – 1 to 211 tola in the morning and evening, it is a good laxative, cleans the bowels, it is especially beneficial for abdomen, gulm, prameh, udavart etc.
Aragwadha Pushpasav – 400 pieces of Amaltas flowers and 40 tolas of desi betel leaves collected in a pure pot for an hour, crushed and filled in a clean cloth in a porcelain vessel, Gavjwan, Makoy, Mulethi, Chirayata and Dashmool each 25 percent Extract x half-half seer and sugar candy 1. Seal the container well after keeping it safe for 1 month and filter it.
Kwath Amaltas- (a) The pulp of Amaltas, Atis, Nagarmotha and Kutki, their quarter decoction destroys Samjwar, colic, vomiting, burning sensation, Kamla and bloody fever. There are many uses of Aragwadhadiquath in the texts. Greeks add almond oil to its decoction.
Oil Amaltas – Amaltas root 5 tola, conch powder 2 tola, hartal 2 tola their kalk and 1 Prove half a seer of bitter oil with the urine of a seer donkey. Then a fourth part of conch and hartal powder was mixed in this oil, by applying it, the hairs fly away and do not grow again.
(b) Boil, pimples, ringworm, scabies etc. diseases are cured by applying a mixture of leaves of amaltas, pawad leaves, mensil, turmeric, kooth, barberry, peepal and sulfur in bitter oil.
(c) oil made from the kalka and decoction of Aragwadhadigan is given in case of Kafoth inflammation.
(d) Mixing 1 seer of malkangani oil with decoction of Amaltas root (6 seers) and kalk of Guja, Bavchi and sulfur (4 tolas each medicine of kalk) destroys Siddha and Udambara leprosy.
Note – In Unani medicine, many types of ointments like Majum, Mullayan Mubarak, Lahuq, Him, Font etc. are used, which we cannot write here for fear of detail.
Vishtambh or Malavarodh – (a) Amaltas has been found to be the best among all laxatives and it is especially beneficial in summer due to its temperate nature. Its pulp is 3 tola. Add 9 mashes of almond oil (or 4 tola almond kernels after grinding them with water) to the filtered water. By drinking this, after 3-4 loose stools, the room becomes clean, the heat of the blood decreases.
Soak the pulp of Amaltas up to two to four tolas in half a pound of water in an earthen vessel. Then Sanay two tolas of big myrobalan, 9 mashes, munakka 15 grains, circumcision, apricot, banafsa, fennel, white sandalwood powder and gorakhmundi 6-6 mashes, and Unnao 7 grains, boil them in half a seer of water and make this decoction. Mix the pulp soaked in water and two tolas of tamarind in 5 tolas of water after filtering the excreta. Simultaneously, mix two tolas of orange seeds, one tola of sheerkhint, mix these two extracts in 5 tolas of rose, then mix two tolas of Gulkand and give it to drink. This Badshahi laxative experiment is very good. In this, if half a pav of extract of macoy and extract of fennel is given on every loose motion, then the flour becomes completely clean and there is a lot of benefit in the diseases of blood disorders.
Amaltas pulp 1 tola and large myrobalan bakula 6 mashes, mix both of them in half a seer of water and add sugar after proving “ashtamansh kwath”.
(b) If there is constipation in the state of fever, then use its pulp with grape juice, or gulkand or milk. Keep in mind, if the bile of the liver is strong and there is burning sensation in the mace, then with grape juice, if the stool is dry, lumpy, then with gulkand, and if the bile has become very intense, then it is beneficial to use it with milk.
(c) After the fever goes away, if there is dysentery, then its pulp, kuti, nishoth, bark of big myrobalan on Sanaya, dry rose flowers 2-2 tolas (if rose flower balls then 4 tolas) and dry grapes (with seeds removed). 5 pieces and half of Gulkand from all medicines- Out of these eight substances, pulp of Amaltas, Manukka and Gulkand, except these three, grind the remaining things into powder, then mix these three also and make a kalk. About two or two and a half tolas of this kalk, putting a loaf of kalk in water and drinking it after making a decoction, one or two loose motions become open, the stomach defect gets eliminated and there is a lot of appetite. (chemical)
Haemorrhoids – (a) Haemorrhoids are often special in the patient of haemorrhoids and due to this there is a possibility of bleeding due to increased pain. Therefore, if constipation and pain are characteristic, 1 tola of its pulp, 6 pieces of myrobalan peel, and 1 tola of seedless raisins should be mixed together and given as Ashtamansh decoction in half a seer of water. By giving this way in the morning and evening, constipation goes away, after calming the pain of warts, they become soft and shrink. It is necessary to drink this decoction continuously for 3 or 4 days. The same decoction can also be given with success on vertical biliousness or haemorrhage, urinary retention and febrile fecal impaction. Some people use this decoction mixed with 1 tola punarnava for inflammation, and bind the leaves of Amaltas by heating them on the inflammation. If there is special swelling at the hemorrhoids, then using it in this way is beneficial.
In case of fecal impaction of some arsh, without putting dry grapes in the above Kwath, taking only pulp and myrobalan in the said proof, boil it in 24 tolas of water and add 6 mashes of jaggery to prove it as a fourth quarter. This clears up a loose motion within 3-4 hours, and helps in bowel contractions.
(b) If bleeding is predominant, take two tolas of its pulp and mix it in 10 tolas of water, keep it on the fire for some time. After the color comes off, filter it and mix 1-1 tola of ghee and rock salt in it. Then spitting 3 mashes of lavanabhaskar powder and feeding it on top stops the bleeding. By continuing its use for a few days, warts also dry up. It has also been seen to be beneficial in Vatarsh.
Constipation is also removed by eating the flowers of Amaltas fried in ghee along with food for 3 to 6 months.
Cough, breathing and cough disorders – The said ‘Sharbat Amaltas’ is very beneficial. And ‘Aragwadha – Pushpasav’ is best on breathing. Or put 10 tola pulp of Amaltas mixed in water in an earthen vessel and keep it in dew.In the morning, filter the faeces and add 2-2 tola powder each of isabgol husk, almond kernel, aak (madar) flowers that have not blossomed, and after stirring well for eight hours, make 80 pills. Consuming milk from goat or cow 1-1 tablets in the morning and evening gives immense benefits in breathing.
If there is phlegm disorder in the lungs, mix its pulp in water and make a chutney mixed with triple sugar candy and drink it with fennel extract. This experiment removes phlegm from the lungs.
Grind the fruit or jaggery with its pulp and make betel nut-like pills and take it every morning and evening with heat.
Its pulp and sugar candy mixed together and licking it little by little many times in the day and night, the phlegm accumulated in the intestines and ribs comes out through diarrhea. It is very beneficial for cough disorder of children.
Inflammation – (a) Garyngitis or throat gland inflammation, boil 1 tola bark or root bark of Amaltas tree in 20 tola water. Leave drop by drop in the mouth when the quarter is left. As soon as a few drops of it are taken inside, the patient gets a lot of peace in about 3 or 4 hours, and after taking a few more drops in the stomach, the swelling of the red gland of the throat disappears on the second day. This is an amazing experiment on tonsillitis. Especially when a small child gets this disorder, then he cannot drink anything except milk and water, his throat gets blocked. The doctors, out of desperation, could not save the child’s life even after performing horrific operations etc. In such a situation, the above experiment gives miraculous benefits.
(b) If you have kidney inflammation, mix 3 parts of its pulp and 1 part of fig juice and cook it on a soft fire and make a paste. By licking 1 tola in the morning and evening, the inflammation of the kidneys and sardi is removed.
Leparth in inflammation- its pulp and barley flour 2-2 tola, camphor 2 mashe, dissolve all three in linseed oil 1 tola (or mix linseed seed 1. tola and dissolve with water) and apply after heating.
Degenerative inflammation of liver, spleen – Grinding 1 tola fresh flowers of Amaltas with Suhaga Kheel 3 Mashe and taking it with warm water in the morning and evening is beneficial. (5) Leprosy, Visarp, Vichchika etc. – Roots of Big Amaltas and Small Amaltas (Karnikar) 2-2 parts, Dhav, Arjuna, Sarj (resin tree), Palas, Kadamba, Neem, Kuda, Adusa, Khair and Purva, Take 1-1 parts of each root and cook it in 8 times water, filter it and mix a little ghee in it when the eighth part is left.
Mix 2 seers of Amaltas root, 16 seers of water and make decoction, when 4 seers are left, mix 1 seer of ghee and 10 tola of Amaltas roots and cook it. Sieve the amount of ghee remaining. Cook Kwath and Kalk Gila in it again in the same manner. Similarly, after cooking 100 times, the amount of this ghee. Till Tola Consuming decoction of Anupan Khairsar cures leprosy quickly. During the period of use of this prayog of the patient, only decoction of Khairsar should be used for bathing.
Applying equal parts of Amaltas leaves, Lihsoda bark, Sirrus flowers and Kakamachi in water on Visarp is beneficial.
Menstrual disorder and leucorrhoea – If the Raj, amenorrhea or menstruation does not come freely.
(a) Amaltas bark 6 tolas and fennel, safflower seeds 5-5 tolas and madjith 3 mashes, make them all 1. Cook in sea water. If it remains till pav, filter it and give it to drink after adding sorghum to it.
Its pulp 1 tola, peel of walnut fruit, waibidang, cotton flower stick 7 pieces each, carrot seeds, gokhru, melon seeds, radish seeds, kalonji 4-4 pieces and bamboo knot 5 pieces, everyone got Ashtamansh Kwathan. It is proven that after feeding it, menstruation comes freely within 3 or 4 days. Keep in mind, never give it in case of pregnancy.
Amaltas pulp 4 mashes, dry ginger and bark 3-9 mashes and jaggery 1 tola, after proving all these decoctions and consuming them for equal 3 days, menstruation becomes open and the pains of the back etc go away.
Leucorrhoea -(b)> By crushing 2 tolas (or up to 211 tolas) soft swar Sakia of Amaltas, then mixing 2 tolas of acacia gum and catechu mixed with 1 tola in the morning and evening, all types of leucorrhoea go away. Should be given for at least 7 days?
Fevers – (a) If there is vatpitta fever, give decoction of Motha, Mulathi, Khus, Harad, both turmeric, neem bark, Giloy and Kutki.
(b) If there is cough with mango and colic, then mixing the powder of peepalamool, nagarmotha, neem and myrobalan with its pulp can prove to be a decoction.
(c) In the condition of fever with colic, vomiting, diarrhea, kamala, make decoction made of nagarmotha and kutki mixed with its pulp.
(d) If there is common fever and chronic fever, then decoction mixed with harr, kutki, nisoth and aqr along with its pulp should be consumed. This pulp is called ‘Arogya Panchak’.
(e) you have Vata or Kaphajanya fever, make a decoction mixed with its pulp, Piplamool, Nagarmotha, Chirayata, Harad and give it to drink.
Varicose veins or canker sores – Mix the bark of the root of Amaltas, turmeric and makhana in the fine powder of these. Then wrapping it in yarn, before putting the lamp in the canker, the pus gets rejected and the canker gets cured slowly.
Ashadvriddhi – Anus 1 tola in 10 tola water, filter it when 2 tola is left and mix ghee in it and drink it while standing, it is beneficial. Use 7 days.
On Urinary Tract – Consuming Dhamasa, Coriander, Shatachar and every equal part of it along with its pulp and making a quart decoction is beneficial.
Vatshul – Its wet seedless pulp. Or after weighing 2 tola, add Chhatank in ghee, roast it on the fire and put that pulp along with ghee into a loaf of ashes. When the milk cools down a bit, mash it out and mix 9 pieces of black pepper into it and give it to everyone to drink. Due to this the dying air colic patient is saved. (Siddha summation)
By grinding and coating the root of its tree, consuming its pulp three times a day regularly till every month destroys syphilis quickly. The lump that develops along with or after syphilis, tying poultice on the root of Tinpatia herb destroys that lump in 4 hours. (doctor)
Haemorrhage (Hemorrhage) – Collect 2-2 tolas of its pulp and rose flower’s Gulkand and cook it in a loaf of water. When 10 or 15 tolas of water remains, filter it and give it to drink when it cools down. Hemorrhage stops soon and it is also beneficial in burning of urine.
Sunstroke – Licking its pulp mixed with 2 parts of Pashanbhed 3 Masha, Ghamasa 4 Masha, Chhoti Harr 5 Masha and Gokhru 6 Masha and making a paste of these fine powder with honey gives quick benefits.
Stomach worm – 6 mashes of waividang powder was found in 211 tola of its pulp, after filtering it after proving quarter decoction, adding 2 tola of castor oil to it and giving it in the morning along with stool in 3-4 hours, microscopic stomach worms fall off. After detoxification, feed porridge to the patient. If necessary, this experiment can be given for 3-4 days. With this, all the complaints of worms, fire, nausea, penduta, weakness, itching, laziness, sleepiness, low fever etc go away.
Diabetes – Cook its pulp like opium on fire and make like gram.Take 2-2 tablets in the morning and evening with water. Be healthy.
Scorpion’s bite – Grinding its seeds in water and sticking it on a part of the place gives quick benefits.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Aagralam (amarood) – Guava. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
This fruit is famous all over India. Some westerners like Dr. Dimak say that it was brought here by the Portuguese from America. And at the same time it is also said to the buried jawan that it happens in forests in many places of India.
We say that like wild mango, banana etc., it is produced in our country since very ancient times, and it is a native of this place only. Due to this, its crop is very abundant in the whole of India like mango, banana etc. We also believe that in the country of Peru in South America, there is a special type of Aagralam(amarood), which is very long round, very sweet and with very few seeds. ht by the Firangis especially from the Portuguese in Goa province. After getting the favorable condition of water and land, its yield started increasing here. And in South India, this fruit became famous by the name ‘Peru’. The Nighantukars also named it as ‘Peruk’.
Its ancient Sanskrit name is ‘amrit’ or ‘nectar fruit’, and almost everyone in Banaras calls it by this name. We think that perhaps the name ‘ Aagralam(amarood)’ is a corruption of the word ‘Amrit’ and has become popular in general.
There are many seeds in the indigenous Aagralam(amarood) here as compared to the Aagralam(amarood) named Peru. Hence it is called ‘multi-seed’. Aagralam(amarood) is also called ‘Bihi’ in Hindi at some places. But in fact jaggery is different from it, it is a kind of Kashmiri pear, and it is also named as ‘amritphal’ in Sanskrit.
Sanskrit – nectar, multi-seed, hard seed, peruk, flesh etc. Hindi – Aagralam(amarood), Safari. Gujarati- Jamphal, Jamrukh | Marathi – Peru, Jam | Bengali – Piara, Goachifal. English – Gavhna. Latin – Cidium guwahn.
There are many varieties of Aagralam(amarood), such as red and white, without seeds and with seeds, big and sweet etc. The red Aagralam(amarood) whose pulp is red inside is called Sodium palmiferum in Latin and the Aagralam(amarood) with white pulp is called Psidium pyriferum. Accordingly, there has been some difference in the names of many languages due to the difference between white and red.
Its tree is of small stature, the trunk is weak and the branches are thin. The outer surface of the bark of the trunk and branches is smooth, brown in color and covered with dry thin white bark like a feather. The taste of the bark is astringent, somewhat sour. The wood inside is smooth and strong. Gun butts are made from the wood of its young tree.
Leaves – Elliptical, 3 or 4 inches long, with short petioles, fragrant. Rough to the touch, the underside is covered with soft hairs.
Flowers – On each peduncle there are small one to three white flowers. The peduncle is half an inch long
Seasonal fruit – After three or four years of the tree’s production, it starts bearing fruit. The winter and the rainy season come twice a year. The crop of winter season is more and people also eat it a lot, but the fruits of rain crop, people eat less due to the fear of winter or cold.
Fruit – astringent in raw condition and sweet or sour when ripe. The best Aagralam(amarood) are from Lucknow and Allahabad in India. Fruit greens, marmalade etc. are also made.
It is astringent, palatable, acidic, cool, heavy phlegm, pungent, hakr, spermatic and vatal, mania, delusion, swoon, worm, trisha, labor, atrophy, febrile and virulent. Some consider it to be carminative. In fact it suppresses matter. Consuming it in small quantity along with food in Amatisar and Sangrahani gives immense benefits. Appetizer and heart and brain tonic.
Taking out the seeds of Aagralam(amarood) and grinding it mixed with rose water and sugar candy, it gives peace to the greatly increased pitta and separation.
Grinding good ripe fat Aagralam(amarood), mixed with milk, after filtering all the seeds are removed, adding sugar as desired and consuming it increases strength and semen.
Roasting Aagralam(amarood) in hot sand and eating it is beneficial in cough.
Fennel is fed in the Aagralam(amarood)’s ovary. Or eating jaggery also cures its indigestion and disorders.
Grinding its leaves and drinking it cures fever. By chewing the leaves or gargling mixed with alum in the decoction of the leaves, toothache ends. Mixing catechu in the leaves and chewing it like betel leaves heals mouth ulcers. By drinking the juice of the leaves or by eating Aagralam(amarood), the intoxication of cannabis, datura etc. goes away.
Making a decoction of the bark of Aagralam(amarood) tree and giving it to the patient is beneficial in the initial stage of cholera. This stops the tendency of vomiting and diarrhoea. Drinking decoction of root bark provides quick relief in chronic diarrhoea.
According to modern opinion – The tree has a great reputation because of the delicious fruit it produces. But its seeds are harmful. The fruits, after finely chopping them and cooking them on low heat or steaming with sugar, prepare its famous lapsi or mothi chutney, which strengthens the heart and is good for constipation. Ripe Aagralam(amarood) is a mild laxative. The peel of the fruit should not be removed while eating. Peelless fruit is an anti-seizure. Unripe or unripe fruit is given in diarrhoea. Rich fruit is indigestion and produces vomiting and fever. Dr. Gaird has praised its fruits in rheumatism or rheumatism. Aagralam(amarood) should be cut and put in water, then after some time drinking that water after filtering, it is beneficial for diabetes or polyuria.
Its stalk, bark and root bark are collector and astringent. Use of decoction of root bark in the quantity of one dram is beneficial in chronic diarrhea of children. This decoction is also used to stop vomiting and diarrhea (if the color of vomiting and diarrhea is somewhat red) in cholera (Kalra).
The local use of its decoction is very successful on children’s anus, fracture death and blood defects, infected ulcers and swelling of the gums. Excellent poultice is prepared by grinding its leaves.
Cook 11 tolas of its root bark in 15 tolas of water, when half is left, giving it once or more tea spoon 3 or 4 times a day is beneficial in children’s chronic diarrhoea. It (this decoction) is best used externally as a compress on children’s vagus disease. Its leaves have also been successfully used in diarrhea.
Its tender leaves have been considered an antipyretic and anticonvulsant in the West Indies. They bathe the patient with its decoction. It is applied in arthritis. That is, after grinding the leaves, it is applied on the painful place of arthritis and the font of the leaves is used on brain disorders, arthritis, inflammation and physical and mental deformity. Its extract or tincture is given for epilepsy and tremor. Massaging its tincture on the spine of children cures convulsions. Due to the collection of fruit and fruit marmalade, it is especially beneficial for diarrhea and flow diseases.
Dr. Desai etc have said that in acute diarrhoea, in acute diarrhoea, tying Aagralam(amarood) leaves after making a pultus reduces swelling and the anus sits inside. Alternatively, Aagralam(amarood) and Nagkeshar are both finely ground and made into pills similar to Urad.
Many examples have been found. When eyes come (Netrabhishyand) by preparing a poultice of leaves and tying it at night while sleeping, the pain of the eyes: swelling and redness goes away quickly.
Raw Aagralam(amarood) have astringency and slight sweetness along with some acidity. There is a special increase in its sweetness in maturity and it becomes more tasty and beneficial. There are also some sour Aagralam(amarood) which are not beneficial.
Red Aagralam(amarood) is more beneficial than white. It has more quality to bring open defecation. By the way, both types of Aagralam(amarood) are beneficial. Diarrhea is cleared from them, and there is no harm in eating them as long as they are available throughout the season, but winter Aagralam(amarood) are especially beneficial, strong and satisfying. Many people believe that eating Aagralam(amarood) causes abdominal pain, afra, cholera etc disorders. These disorders can be caused by eating Aagralam(amarood) in the rainy season. Because due to the effect of season and time, a type of microscopic white worm is produced inside the Aagralam(amarood) in the rain. But after taking good care and eating them after mixing salt, black pepper, lemon juice, then no disorder can arise. It is said that Vitamin ‘C’ remains in abundance in rainy season Aagralam(amarood).
The best time to eat Aagralam(amarood) is from 8 to 9 in the day. You can eat Aagralam(amarood) in the third hour even after lunch. Those whose body has the characteristic of burning due to pitta outbreak, its continuous consumption for a few days after meals is particularly beneficial. Those whose digestive power is weak or those who are weak themselves should eat it in less proportion, otherwise there is a possibility of pain or upset in their stomach.
Those who have suffered from Vata Pitta predominant mania or delusional disease, consumption of Aagralam(amarood) in dietary form along with proper medicines is beneficial. Soon the progress of diseases stops and benefits begin.
Aagralam(amarood) seeds should be avoided as far as possible because they are not digested quickly due to being very hard. These seeds work to clean the intestines. But if they go into the tailbone, they cause a disease called appendicitis or appendicitis.
Aagralam(amarood) marmalade is beneficial for blood diarrhoea. Half-ripe fresh Aagralam(amarood) is taken to make Gurba, which does not spoil for a long time. Raw or underripe Aagralam(amarood) is eaten as both sweet and salty vegetable, which is very tasty. They are also kept dry. They are cut into small pieces and dried in the sun and whenever they want, they make greens and eat them.
Aagralam(amarood) actually works as nectar on chronic cold (Pratishaya). If a good big Aagralam(amarood) seed is taken out and fed to the patient and fresh water is given on top of it (he should drink this water only after closing his nose), then the stagnant painful cold starts flowing. In this way, he can eat fruits three times a day, if there is no proper discharge, then he should eat them on the second and third day also. When there is a lot of discharge and it is necessary to stop it, then one or two drops of jaggery should be eaten at night without drinking water.
In native Aagralam(amarood) – The percentage is 76.1 water, 1.5 protein, 0.2 fat, 7.8 mineral substance, 14.5 carbohydrate, 0.01 calcium, 0.44 phosphorus and percentage 1.0 mg iron. Vitamin A is nominal but 299 milligrams is vitamin C.
In Pahadi Aagralam(amarood), these substances are present to a lesser extent. Vitamin B is also found in both types of Aagralam(amarood). Therefore, diseases arise due to deficiency of B and C vitamins, among them Aagralam(amarood) is more beneficial.
Its leaves contain resin, fat, starch, tannin, volatile oil, green and mineral salts. In short, it is said that lime and manganese are present in the Aagralam(amarood) tree mixed with Phosphoric, Chakra and Amatsattva.
Gud Bhramsh – Aagralam(amarood) tree’s bark, roots and leaves in total equal to 1 pav after grinding barley and making a semi-residual decoction in 1 seer of water, this decoction should be used to wash the anus repeatedly and keep pushing it inside. This decoction, with its astringent and astringent effect, gives quick benefits to menorrhagia disorders.
Cough and phlegm disorder- If there is a dry disease, the patient becomes restless while coughing, but the phlegm does not come out, then the patient should go to the Aagralam(amarood) garden every morning and break the beautiful ripe Aagralam(amarood) growing on the tree and put a knife etc. in it. While not applying substances, eat while standing and chew thoroughly with your teeth. In this way, with the use of 2 or 3 days, dry to dry cough runs away by pressing the tail.
Extracting the extract of Aagralam(amarood) by grinding and mixing honey in it and drinking it is also beneficial in dry cough.
If phlegm comes out a lot and cough is excessive, diarrhea is not clear, fever is also normal, but the patient is not weak, then he can eat good fresh and sweet Aagralam(amarood) as per his wish. It has also been seen to get miraculous benefits even to a tuberculosis patient who is desperate for life.
If there is a simple cough of cold, then roasting Aagralam(amarood) in fire and adding some salt to it is beneficial.
If you have eye disorders, eye drops, redness of the eyes, swelling, continuous tears from the eyes, eye pain, etc., then grind its tender leaves and mix some water and give it as a wash. If a little alum and opium are mixed in the paste, the benefits are even quicker.
Diarrhea and cholera – Mixing about 2 tolas of its soft leaves or the inner bark of the tree, after proving Ashtamansh Kwath in 40 tolas of water, give it little by little 3-4 times a day in small children’s diarrhoea. If there is a collection, that is, after one or two months, the children have a lot of diarrhea, there is a disturbance in the stomach, there is no digestion of the food and it becomes crunch every day, then this decoction is also beneficial for that. Bark decoction is more beneficial than leaf decoction. There is profit in 7 days.
If cholera is caused by eating too much Aagralam(amarood), diarrhea is felt more, then the decoction of the above leaf is beneficial. It should be given repeatedly in small amounts.
Ajirna – The juice of its soft leaves mixed with a little sugar in about 1 tola, consuming only once daily in the morning gives complete benefits in 7 days. Digestion of food starts getting better, appetite increases (feeling hungry).
Rashushul half vial – Rubbing raw green Aagralam(amarood) on a stone in the morning before sunrise and applying it on the head where there is pain, the pain does not arise. If pain has started, it soon subsides. If there is no benefit in one day, then this experiment should be done for 2-3 more days.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Tulsi – Basil. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
Introduction After analyzing the word ‘Tulsi’, it is known that the plant which can be compared to anyone is Tulsi. Tulsi has got the position of mother of the world in Hindu religion. She has also been called Vrinda. The chapters of Puranas are filled with the greatness of Tulsi and the subtle effects of reason power. All disease preventive and life force enhancer, this medicine can probably be considered direct. It is based on the fact that there is no other such cheap, accessible and beautiful useful plant for the human community.
Tulsi’s flower-like inflorescence is 1 to 3 feet high, branched Ramesh, with purple aura. The letters are 1-2 inches long, molecular or rectangular. Each leaf has a kind of intense fragrance. The inflorescence is very delicate, its length is 8 inches and it is decorated with many colors. On this, very small flowers appear in purple color or blood-like aura. Angle inflorescences are usually heart shaped. Seeds are flattened yellowish ovate with small black markings
Tulsi plant is evergreen, that means it always remains green. Generally it is planted from March to June. It flowers in September and October. The whole plant is covered with fragrant flowers. Its seeds ripen during winters. It can be obtained in one form or the other in all twelve months of the year. Generally flowers come in winter.
Basil has strong smelling flowers, whose branches are straight and spread. Leaves elliptical, flower spikes at the end of branches, in various colors, curved, seeds flattened, blood-coloured.
The following species of Tulsi are commonly found-
(a) Asimum americanum – Black basil, Gambhira or Mamri; (b) Asimum americanum Mammaruva Tulsi, Munjariki or Sursa (c) Asimum gratissimum-Ramatulsi or Vanatulsi (d) Asimum kilimendeskeschim ‘Karpur Tulsi, Kapoor Tulsi and (e) Asimum sanctum, Asimum virdi etc. some other species of Asimum (genus).
Leprosy- Grinding basil root and mixing dry ginger with water in the morning provides relief in leprosy.
Bastishoth – Taking 1 gram powder of basil seeds and cumin seeds, mixing 3 grams of sugar candy in it and taking it with milk twice a day cures urinary tract infection, puya and bastishoth.
Arthritis- 2 grams of carom seeds in 3 grams of basil juice is beneficial in arthritis.
Pride – Vomiting stops by giving basil juice.
Fever – Tulsi leaves 3-9, given with black pepper, cures fever, influenza. You can also drink it by making tea. Rubbing basil juice on the body in chronic or toxic fever has special benefits.
In various diseases – leaves, roots, seeds are medicinal. Patra swaras or fontanelitis, cough, breathing, fever, especially phlebitis, acute and chronic fever), colic, agnimandya, charade, abdominal etc.
Beej- Poyameha, Urination, Ashmari, Durbalya and Krimi disease.
Basil has beneficial use in dental diseases (teeth and gums). Basil leaves are used in pyorrhea, bleeding gums, toothache, looseness of teeth and other similar problems of teeth and gums. Take 15-20 basil leaves and grind them, mix ground dry ginger and one spoon mustard oil in basil leaves. With this mixture, paste is applied on the teeth. This medicinal combination helps a lot in curing dental diseases.
Apart from this, take out basil juice in a spoon and mix it in a cup of water. Keep this Tulsi mixed water in the mouth for some time and gargle with it (Gundush and Kaval Dharan). Continuously doing this experiment for a few days (10-15 days) (in the prevention of dental and dental root disorders) is very beneficial in teeth, gums and other local (organic) diseases.
Mixing basil juice in light warm-lukewarm water and gargling and gargling (gargle and mouth wash) or mouthwash with water, especially in throat-throat disorders. And especially useful in sore throat, hoarseness and other similar diseases of the throat. If you add a pinch of ground turmeric and household salt in this Tulsi Swaras water. Let this mixture be mixed, medicine yoga is very beneficial. It is used in diseases of the throat and teeth and it becomes more effective when mixed with these medicines. This also helps in treating enlarged tonsils in the throat. Lukewarm basil juice (mixed with boiled water) in any bacterial infection in the mouth, teeth and throat It is very beneficial to rinse, gargle or use in any other form by mixing it in water.
Basil’s leaves, root and seeds are useful parts. These parts (organs) of the plant are dried and kept in closed vessels to dry and in cool places. This stored medicine can be used medicinally for one year. Fresh tulsi leaves are very useful, because being accessible everywhere and having more quality in green state, fresh plants especially tulsi leaves are considered to be full of medicinal potential and best for use.
Tulsi is useful in all types of Kapha and Vata disorders. As a local paste, it is applied in ulcers, inflammation, arthritis, pain etc.
In depression and low blood pressure (hypotension) etc., applying or rubbing it on the skin immediately activates the nervous system.
Tulsi leaves or seeds are applied in external worms of the body. It is useful in impetigo, any kind of colic and intestinal worms. Giving basil seeds in Prahika gives instant benefits.
This plant is cardiac stimulant and is used in case of heart depression. By consuming it, the heart gets excitement and strength. It purifies blood disorders.
Tulsi juice has an active effect on the respiratory system and various uses of its leaves, seeds and roots etc. are used in institutional disorders. Its voice is very useful in cough, asthma and stiffness of muscles and spinal cord (pillar-sclerosis) caused by these disorders.
Consuming the powder of basil seeds gives instant benefit in burning sensation in urine (urinitis) and difficulty in urinating (urinary incontinence). In the condition of burning sensation and difficulty in passing urine, soaking 6 grams of basil seeds in 15 grams of water at night and filtering it in the morning is given. ,
Basil seeds are useful in the treatment of kidney stones (bladder stones), the use of seeds also reduces the inflammation of the bladder (cystitis).
Tulsi is considered one of the best medicines for leprosy. It is useful in removing odd fever. It is capable of breaking the cycle of any type of fever immediately. It is successfully used in Rajyakshma. Tulsi increases vitality and does not allow further growth of bacteria; The bacterium becomes capable of inhibiting the prefix.
It is anti malarial. Tulsi plant (Tulsikshup) is planted near the house, which is considered a mosquito-repellent plant. The Tulsi plant has an anti-bacterial effect in the environment. By applying Tulsi Swaras, mosquitoes destroy the active chemical elements (constituents) of Tulsi Swaras when ingested by not humans.
Basil seeds have chemical properties and they are debilitating killers. Using them gives power. Tulsi does not come near, because Tulsi well-known mosquito-seed powder is given in general debility, consumption of seeds is beneficial in debility after diseases.
White basil is hot (hot) and digestive (helpful in digesting food) It is used in children’s cold-cold (catarrh) and phlegm diseases. Black basil is a cough suppressant (expels frozen phlegm or mucus) and antipyretic (relieves fever). It is widely used in cough and fever. Black basil is used for the treatment of these diseases in many forms and forms. Black basil has many important medicinal properties, so its plant is very useful.
The powder of Kali Tulsi (Krishna Tulsi) leaves is used in Pinus. Tulsi is very useful in other nasal and leprosy diseases.
Cooked oil of basil (Tulsi Siddha Oil) is useful as Karna Bindu. In ear diseases, especially ear colic, drops of this oil made from basil are dripped in the ear.
(a) Basil juice has special ability to resist malaria bacteria. Scientific tests of this antibacterial power have also been done. The effect of malaria is greatly reduced by the use of black basil. The air touched by Tulsi leaves acquires such qualities, due to which mosquitoes do not stay in the place where the Tulsi plant is planted or the premises where it lives and mosquitoes do not fly around; This has been found by tests. There is such a volatile element (oil) inside Tulsi that it destroys the germs that cause fever.
(b) The effect of basil is found to be good on fever-causing bacteria, especially in tropical areas, in fever that increases with cold, because mosquitoes are protected by this plant.
The effect of cold in the chest is not affected by the use of Tulsi and the phlegm which accumulates in the respiratory tract, throat etc., and causes pain in many ways, starts coming out, due to which the patient feels relaxed. That’s why Tulsi leaves and Tulsi juice are very beneficial in the disorders of respiratory system, because it is anti-bacterial infection and has effect in diseases related to having every quality of expectorant, expectorant and expectorant. This is the reason why Tulsi Patra, Tulsi Swaras and other parts of Tulsi are used commercially in various forms for the prevention, pathology and symptoms of the respiratory system, and making and drinking tea of Tulsi leaves is a common practice in domestic herbal utility tradition. is included
In the context of Malaria fever, it has been proved by scientific tests that Tulsi juice has remarkable ability to destroy protozoa parasite and mosquitoes responsible for Malaria fever and as a result Tulsi is resistant to Malaria fever.
(a)Tulsi juice and Tulsi essence (essence or extract) have been found to be active against malarial mosquitoes and bacteria and many other bacteria as well. Some of the major bacteria can be mentioned – Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhosa and Escherichia coli. The bactericidal property of Tulsi Swaras is six times more in carbolic acid. The bactericidal ability and anti-bacterial activity of Tulsi has been tested by various researches in addition to these bacteria, and many other types of bacteria have also been tested, and good results have come out.
(b)The volatile oil obtained from Tulsi has a powerful effect on Klebsiella, Candinda etc. Basil seeds greenish-yellow oil about 17.8 Q. Sh. found in quantity.Its constituents are some sitosteral, several fatty acids mainly palmitic, stearic, oleic, linoleic and linolenic acids. Apart from oil, mucilage is abundant in the seeds. The major constituents of this mucilage are – Pentos, Hexa-Uronic, Acid and Bhasma (Ash). Of these, reek is about 0.2 percent. it occurs .
(c)The chemicals present in Tulsi are actually very beneficial, observing whose properties and effects on the body, it can be said that positive help in confirming the classical quality is obtained from the plant’s chemical potential and laboratory tests.
(d)Tulsi ether extract T.B. Of. Bacteria have the ability to inhibit (prevent) the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Compared to all the latest medicines, this extract is best in higher concentration. Tulsi in T.B. The destructive power is extraordinary. This medicine also inhibits the growth of the human strain of this bacterium. Tulsi is very useful in tuberculosis. The quality of Tulsi has been proved as a plant resistant to Rajyakshma’s bacterial infection, and it is well-known as a medicine for respiratory diseases. That is why it is useful in decay and other related diseases.
Some special properties are found in Tulsi, due to which it directly affects the electrical structure of the body. The rosary which is made by cutting pieces like seeds from Tulsi wood (Khupiya Kand), is used for wearing it. The wearing of Tulsi-garland has been considered very effective. Wearing a garland of seeds made of Tulsi wood increases the flow of electrical energy in the body and increases the ability of the body cells to Tulsi-wreath simply wears away many diseases before they attack under this effect and with the effect of rosary the vitality of the wearer (the person wearing rosary) increases and the life span increases.
The powder of Tulsi root is very beneficial in internal use. If a weak person consumes Tulsi root in small quantity, it is beneficial. For this, mixing the powder of basil root with ghee in the morning and evening and taking it for a few days is very beneficial, it destroys weakness, increases strength and it is a factor in increasing energy in the body. At the same time, vitality increases, it is helpful in increasing immunity. That’s why Tulsi is counted among the herbs that increase vitality.
Consuming one gram of basil seeds with cow’s milk in the morning and night, this metal is used in weakness, it cures metal weakness; And Venus increases till the body, gets strength, metal is confirmed. Basil seeds are used in many types of medicines, which are used universally and are nutritious.
(a) Tulsi root has many beneficial elements, its root is very good, that’s why it is useful in many diseases.
In diseases like cough (kaas), hoarseness (hoarseness) and dry cough (dry cough), pieces of basil root (like licorice) are sucked by keeping them in the mouth. Swaras of Black Tulsi is continuously given with one and a half spoon of mirich (black pepper) (juice extracted from basil leaves and ground black pepper mixed with it), which reduces the speed of cough and by giving several times (as per requirement) the speed of cough He becomes completely calm.
(b) The utility of Tulsi in pulmonary pathology (lung diseases) is multifaceted and using Tulsi juice in various forms and methods is extremely beneficial. Dry basil leaves mixed with 4 grams of sugar candy (in powder form) are given two to three times a day (in case of severe cough etc.) when there is a sound of crackling in the lungs and when there is cough. Similarly, this use of Tulsi is useful in other diseases in the respiratory system. In hiccups (excessive hiccups) and breathing (asthma), extracting the juice of basil leaves and giving one spoon full of it with honey (honey) twice or thrice a day provides relief to the patient.
(c) Keeping basil leaves with black salt like betel nut in the mouth provides relief in respiratory diseases. In century-cold, tulsi’s almanac and ginger (Ardrak’s) knot-these are made by participating in the same, and it is given two-three times a day. It is beneficial in breathing, cough and throat diseases.
Home simple use of Tulsi in cold, cough and influenza is generally prevalent, which is very effective and useful. Making tea of basil leaves with sugar, ginger and black pepper is very beneficial. It is customary to add tulsi leaves when making tea in general (usually tea made from tea leaves); Along with this, in case of non-availability of green leaves, dry basil leaves are collected and kept in a closed glass etc. And keep adding them while making tea, this is also beneficial.
In case of not getting green leaves, dry basil leaves are collected and kept in a closed bottle etc.
In odd fever, there is a law to consume decoction of basil leaf after three hours. In addition to the decoction of basil leaves, half a teaspoon of swaras is given with honey at a gap of three hours. If there is constipation even in mild fever, prepare black basil juice (two spoons) and Gaughrit (10 grams) by humming it in a bowl. By taking this in full quantity once or twice or thrice a day, loose motion-disease (constipation) is removed and diarrhea starts to clear and fever also subsides.
In fever and typhoid fever, giving half an ounce twice a day of Tulsi root decoction (decoction made by mashing the root in water) ends the fever. A common experiment is beneficial in all types of fever – Mixing twenty basil leaves and ten black pepper and drinking decoction, the fever subsides immediately. Grind 10 tulsi leaves and half to one gram of mace in water and lick it three to four times with honey in Motijhra or period fever (typhoid), it benefits the patient.
Vamana (vomiting or nausea) and Hallas-Utklesh have beneficial use of Tulsi. The concoction of Tulsi leaves with honey is given to the patient in the morning or when required. When there is a lack of digestive power, swaras or phant of Tulsi leaves are given in indigestion, indigestion and devotion and liver-spleen deformities of children. Basil leaves are given with black salt in indigestion.
In the condition of vomiting, mixing small cardamom, ginger juice and tulsi leaf juice is beneficial in vomiting, nausea and vomiting. In this way, the use of Tulsi calms down vomiting.
Tulsi is also beneficial in diarrhea with vomiting. Apart from this, grinding basil leaves (10 leaves) with roasted cumin seeds and one gram after roasting cumin seeds and licking them with honey (three to four times a day) is beneficial in diarrhea and dysentery.
Grinding basil seeds mixed with cow milk and giving it to children in diarrhoea, is beneficial. Diarrhea stops by taking 1-2 spoons juice of basil leaves in Pravahika in the morning. By consuming the powder of basil leaves in abdominal worms, all the nuisance caused by worms become calm. In colic, basil leaves are given along with sugar candy. Similarly, 2-3 grams of Tulsi seeds powder is given in the collection along with sugar candy in the morning and evening. Giving basil seed powder with curd or with takra (buttermilk) in piles is beneficial.
In leprosy, drinking juice of basil leaves daily in the morning is beneficial. In skin disorders-herpes, eczema, eczema, basil panchang is mixed with lemon juice and applied. Grind one gram of basil seeds and two rose flowers and bind it on the boils (ulceritis) arising in the body.
For quick healing of ulcers (brana rotapan) and local bacterial prefix (for infected ulcers), basil leaves are boiled and cooled and applied. The use of Tulsi leaves on ulcers and wounds by both the juice of Tulsi leaves or grinding paste is beneficial, because Tulsi has the ability to resist bacterial infection and prefix and this quality is helpful in ulceration.
Tulsi is useful in arthritis. In rheumatism or rheumatism, 2 to 4 grams powder of basil almanac is given with milk in the morning and evening. Similarly, in the disease of Gridhrasi mensiatica, tulsi decoction is sweded in the painful vatanadi. Especially Vantulsi (Black Basil) is useful in inflammatory and painful disorders. In case of vitiation caused by defects in Urdhvangavata, Asthivata, Sandhivata and Parad, baffara (vapor sweat) is done with the almanac of its plant.
In men’s impotence or impotence (male cleavage-absence of masculinity), basil seed powder or root is fed with old jaggery in the division, and for about a month or six weeks (as required) one to three grams of cow’s milk. Taking it continuously with milk is beneficial. Similarly, taking one gram of basil seeds with cow’s milk regularly is beneficial in men with metal weakness. Type C (Consumption of basil seeds with one gram of cow’s milk in the morning and night is beneficial in men with metal weakness.
To increase the general strength of the body, powder (20 grams) of Tulsi seeds is mixed with almost twice as much sugar candy (40 grams) and grinded to make fine powder. This Tulsi seed powder can be kept safe in a suitable vessel (vial etc.). It is beneficial to take this Tulsi (seed) powder in the quantity of one gram each (or more as per requirement) for a few days in the winter season. This prevents the diseases of Vata-Kapha and is beneficial for the recovery of physical decline in weakness. Use of this powder is helpful in increasing the immunity of the body and it also strengthens the nervous system.
Headache, especially in headache- Adha CC (Half headache and headache that starts with sunrise) Adhavidheka and Suryavarta) Tulsi is beneficial. Basil leaves are ground after drying them in the shade. Basil leaves are ground after drying them in the shade. Mix it with one or two grams of honey. is consumed.
Tulsi is useful as a medicine. Taking five leaves of Tulsi daily with water is beneficial for intelligence, cloud power and brain power. Tulsi is used in case of incurable headache. Mixing camphor in tulsi leaf swaras and applying it on the head provides relief in varicose veins.
Tulsi tea is an easy, simple, cheap and effective drink useful for home use. In addition to the tradition of mixing Tulsi leaves in the drink of tea (tea-leaves obtained from tea gardens-market), which is commonly used for drinking everywhere, only Tulsi tea is more effective from the point of view of disease treatment – disease prevention, medicinal and health protection. Is.
5-10 Tulsi leaves are crushed in a cup of boiling water and after boiling for 2 minutes, Tulsi tea is made by mixing 1-2 teaspoons of sugar and 4-6 teaspoons of milk (according to taste-interest-compatibility). In this, ginger (adrak) pieces (crushed), black pepper (mirch) crushed, Gul Banfasha (Banpushpa- Vanapsika Pushpa), small cardamom (Elakshudra) crushed – medicinal liquid Household items (Gulbanfasha obtained from outside) one or several can be mixed, And for the purpose of treatment of special diseases and prevention of diseases, tea can be made and given.
Generally, Tulsi tea is beneficial in conditions like cold, cold, cough, fever, heat, tiredness, pain in the body, anorexia, depression, headache (alone or by mixing Tulsi with other things).
Tulsi sorbet is made, and having medicinal properties is very useful. Cook 50 grams of ginger, 25 grams of ginger and 15 grams of black pepper in 500 grams of water along with basil leaf manjari. When a quarter remains, filter the mixture, grind 10 grams of small cardamom seeds finely and mix it with 200 grams of sugar. When the syrup of one string is done, then filter it and keep it in a suitable vessel.
Tulsi sorbet prepared by the above method is especially used for the treatment of various diseases of the respiratory system and diseases of children. Children (according to their age) lick this sorbet in the quantity of half a spoon to one and a half spoon and adults (elders) are made to consume it in the quantity of two to four spoons. It is beneficial in cough, shortness of breath, whooping cough, whooping cough, sore throat, cold etc. It is very beneficial to take it mixed with hot water in cold and asthma etc. This Tulsi sherbet also helps in improving the digestion of children.
Tulsi is very beneficial in chronic cough and asthma (chronic cough and shortness of breath). Ten leaves of Tulsi and three leaves of Adusa (Vasa), one black pepper, 4-6 small pieces of ginger or dry ginger (pea-sized), six inch long stem of Giloy – crush all these substances. Mash and cook in about one and a half glass of water. When half a glass of water is left after cooking, then 10-15 grams of jaggery is mixed in it. Three doses of this mixture are made and it is given at an interval of four hours. It is beneficial in chronic cough and asthma.
Grind 21 leaves of basil, 5 cloves and half a gram of ginger juice in cough-predominant fever and flu, filter and heat, then add 10 grams of honey. Grind this mixture in water Let’s filter it and prepare it.
Basil leaves are cooked in water and when half is left, they are removed and filtered, adding a pinch of rock salt to it. This temperate-kavoshna (lukewarm) is given to the patient to drink, which is beneficial in influenza.
In slow fever (typhoid), black basil, forest basil and peppermint are taken out and consumed for three or seven days.
In ordinary fever and all types of fever, basil leaves, white cumin and small peepal mixed with sugar are given in the morning and evening. To reduce the rate of fever in fever, equal parts of dry ginger powder and carom seeds are mixed in the powder of Tulsi leaves, and the patient licks this mixture with honey in the quantity of 2-3 grams. In this way Tulsi fever, chronic fever, subject fever and various other types of fevers are useful in various method-yoga-ratio.
In case of rib walking (box disease) in children’s pneumonia disease, humming with Tulsi Swaras (juice of black basil leaves) mixed with fresh cowdhrita. Its use provides relief in rib motion and other symptoms in children. This experiment is done for two-three days. If the fever is normal and diarrhea does not come due to constipation in the stomach (or if the diarrhea does not clear up), then mix the Panchang of Tulsi and the pods of Amaltas and make ashes. Then 250 to 500 ml. Gram. The patient licks the child with honey in the quantity of .
In colic (postpartum pain) occurring after delivery in women, basil leaf mixed with old jaggery and sugar in swaras is destroyed by giving it to the woman immediately after delivery (having a child).
Tulsyasav is useful in gynecological diseases and using this medicine is beneficial in labor pain and colic. Tulsi Patra Swaras 2 Km. After filling 500 grams in pure porcelain (or any other suitable vessel), adding 1 kg of old jaggery, 250 grams of fermentation element (alcohol) and 1 kg of sugar, keep the mouth closed for 15 days. After that, after the research is done, the medicinal mixture is filtered and kept in vials. This basil-infusion is given in the quantity of 3 grams to 12 grams. It quickly cures the acute pain of childbirth and colic of Sutika.
Another type of infusion (extract) of Tulsi is made, and it is used in chronic fever, cough and other related disorders. Tulsi leaves, 250 grams each of dry ginger, black pepper and small peepal (three constituents of trikut, shunthi, pepper and long pepper), 125 grams of yavani (oregano) are mixed and soaked in 10 ml of water. After that, Bhavke (by the method of extraction of extract-distillation) obtains the extract of this compound of Tulsi. 6 grams to 12 grams of this medicine is consumed with sandhav salt (sandhanamak) with hot water (hot water).
Apart from this, other infusion-arishta-extracts etc of Tulsi are also made.
Tulsi oil is manufactured and it is used externally. Take 2 kg 500 grams of pure sesame oil or mustard oil. The juice of basil leaves is mixed with 60 to 120 grams of oil. Keeping the mixture of oil and swaras safe in a bottle (closed stopper) is kept in strong sunlight (intense solar heat) for a week, then after filtering it, orange or rose perfume (spirit) is added as needed. Instillation of drops in the nose (Nasya) cures chronic headache (chronic headache and other associated headaches). Vinegar destroys hair lice (Euca lixa shirgat) by applying oil and applying on the face is beneficial. This oil can also be used for applying on the body. Applying this oil also protects against mosquitoes, because mosquitoes do not come near it. This yoga is also beneficial in soft disorders for use on the skin.
Medicines are made by mixing Tulsi Avleh, Tulsi Vatak and many other herbs with Tulsi. In addition to herbal medicines, many formulations of Tulsi are made by mixing mineral substances – juice, ashes, chemicals etc. There are multiplicity of different drug formulations using different parts of Tulsi as the main ingredient (and also as co-ingredient) and they are popular for use in the treatment of various ailments in single and combined (multi-drug formulations). In addition to these, various medicinal uses of Tulsi in various forms of powder, decoction, swaras etc. and especially the spirit of Tulsi leaves (extracting the juice of Tulsi leaves and adding it to the drug-mixture under manufacture) are used for the preparation of many Rasaushadhis – Rasashastra and Bhaishajya Kalpana is done under. In which purification-killing of minerals etc. is also included. Juice of fresh leaves of Tulsi is used in classical methods and procedures, and in addition to this, Tulsi Panchang, root, seed powder, decoction and other forms are used according to the classical instructions and as per requirement.
Use of Tulsi is beneficial in Naharu’s disease (nervous disease) (Nahru or Naru is a painful helminthic disease especially occurring in Rajasthan). Grinding basil root in water and applying it on the mouth of naru and the place where there is swelling (inflammation and worm mouth), it brings out the naru that has entered inside. By first applying the naru, it will come out 2-3 inches, tie it there, and after that again by applying basil root in the same way, in two-three days the sarara naru (complete nerve worm) will come out and the swelling will reduce. Will go After this, this paste should be continued for two to three more days, so that the naru is completely destroyed.
Basil is used externally in skin diseases. Grinding Tulsi leaves, grinding them in lemon juice is especially beneficial, external coating is applied on ringworm, gout, leprosy etc. Apart from this, Tulsi leaves, Swaras, Gaughrit, stone lime – all these are collected and applied by suffocation.
White spots on the body, freckles, pimples, discoloration of the face (discoloration, loss of luster, etc.) This mixture is kept in the sun for 24 hours, when it gets flooded, then it is used externally. By applying it continuously, there is benefit in white leprosy also. By applying this yoga on the face, spots and other skin disorders on the face get cleaned and beauty comes on the face.
For use in night terrors of the eyes, by grinding the powder of black pepper (after removing the peel) in the juice of Tulsi leaves, they make a lamp (Tulsi Vartika) or prepare vati (cake) and dry it. Grinding it in honey, they eat it in the evening. Only the leaves of Tulsi are applied to the eyes several times a day.
Basil Manjari 4 grams in smallpox fever and leprosy (Kuth) 1 gram. Make a decoction of both of them in four times the water and take the bark when a quarter of the water remains. It is beneficial to lick it.
To avoid the production of electricity, the root of Tulsi is tied in a copper tin, it is believed that there is no fear of getting electrocuted.
Dripping the juice of the leaves of Babui Tulsi (Barbari-Bavui Tulsi-Nyaj Vo) in the nose is beneficial in bleeding nose (nasal bleeding-nasal bleeding).
(a) A decoction of leaves is given in colic pain. Decoction of its leaves is given in the pain of joints, ice, cold, exhaustion and bursting.
The juice of the leaves is applied when there is a sprain in any part of the body. Patra Swaras is also applied externally on Dadru (herpes), which has to be applied several times a day. In case of burning somewhere in the body, the juice of firewood leaves is applied at that place. Dripping the sticky juice of its seeds in the eyes increases eyesight. There are many other external uses from its leaves, roots, and seeds in various diseases.
(b) Soaking its seeds in cold water at night and giving it mixed with milk and sugar in the morning provides relief in burning sensation in the body.
Panchang, seeds, leaves and root of this plant are used in various forms and methods in many diseases. This fever, odd-fever, chronic fever, childish fever, enteric fever, cough, shortness of breath, hiccough, catarrh, headache, nasal disease, intestinal disorder, adhamana, abdominal disease, children’s diseases (dry disease, abdominal disorder, liver disease, kukkur kaas etc.) Useful in urinary disorders, menstrual disorders, dysentery, diarrhoea, flow, essay, painful disorders, syphilis, impotence-weakness, semen disorders, trisha, inflammation, helminthic disease, blood dyspeptic disorders, bladder inflammation, virulent disorders and other disorders. The leaves of this basil have a lot of fragrance and are like spices. ,
Tulsi has been used in various types of tumors (cancer). It is believed that if 25 or more fresh leaves of Tulsi are ground and given daily, their growth stops and this is the subject of testing.
Every part of Tulsi has been found useful in snake venom. If the person suffering from snakebite is made to consume Tulsi on time, then it is possible to protect him. The place where the snake has bitten, the basil root should be grinded in butter and ghee and applied on it. As the poison gets absorbed, the color of this coating turns from white to black. The black layer should be removed and then a fresh coating should be applied.
Tulsi is a kind of life-enhancing medicine that purifies the whole body. Tulsi also purifies the atmosphere and balances the environment. Tulsi is one of the plants that purify the environment. Tulsi is counted among the important plants that protect against pollution.
Regarding Tulsi origin or planting place, it is believed that even a little contact of Tulsi with the body nullifies infectious diseases. It is a belief that by eating the soil under the Tulsi flower and applying it on the body, one becomes free from diseases. This aspect is a matter of investigation and there is a scientific basis for this effect.
Importance – In this way, Tulsi is considered as a cure for all diseases and a life-enhancing medicine. The all-welfare form of these herbal medicines is recognized as a divine boon in the form of plants for human beings and the environment – for all living beings. The religious importance of Tulsi is well known and well known. Its classical, cultural, spiritual and social importance is also universally recognized, on the basis of which Tulsi has got a special place in the form of deities worthy of worship and adorable in various forms.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Saariva – Anantmool. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
In western countries, the practice of manufacturing blood purifying, healing medicines from sarsa root is going on since ancient times. And it is sent everywhere from the island of Jamaica in Central America. Every year these roots of Sarsaparella worth 40 thousand rupees come to India.
On all the disorders on which the said herb is used, Anantmool () also works very well on those disorders. And that is why it is called Desi Sarsaparella. It is a matter of great regret and surprise that it is being imported from abroad in such a large quantity, even though it is not of lesser quality than the above-mentioned exotic Sarsaparella. The reason for this is only ignorance of our society. In reality .
After fully examining the properties of Anantmool, in 1864, European doctors recognized it and gave it a prominent place in the British Pharmacopoeia. And Colonel Chopra says that it has been known from every test of Anantmool that its curative ability is not less than Bilyati Sarsaparella in any part.
Due to the pods of Anantamul being like the beak of a crow, they are called Kaglio Kundhare in Gujarati towards Porbandar. Because of the confusion of the shape of its pods, some call it Meshashringi and some call it Kakamachi. Meshashringi and Kakamachi are completely different herbs. Some mistakenly consider the ultimate root to be the eternal root. The root is called wild Pikvan or Khadki Rasna.
There is another fragment of the same shape and size as the eternal root, which is found here and there almost everywhere without any reason. It bears bell-shaped four-budded flowers of light purple color, milk also comes out of it. And some fragrance comes in the root just like the real Anantmool. Just 4 or 5 years ago, rubber plants were collected from all around by the Government of India. It was also cultivated by the government in many districts like Mathura etc. its milk. There was a plan to prepare rubber by coagulation by chemical process, but it probably did not succeed.
Keep in mind that the said herb is not the real eternal root. Rather, it is a type of gar poisoned vine. Its use makes a lot of nausea, nervousness. Some people start having diarrhea like cholera and the condition becomes dangerous. As long as its poison remains in the body, the patient remains restless. It is not an antidote, but gradually the poison gets digested and automatically becomes peaceful. Is. At some places, due to confusion, it is called infinite root and suffers loss by using it. Its leaves are just like the original letters, but they do not have white lines. There are differences in flowers too.
White and Krishna of infinite origin are considered to be two such differences in Arya medicine. White Saariva is special aromatic and beneficial, and it is called Hemidesmus indicus in Latin. Krishna Saariva or Bengali Saariva is called Ichnocarpus frutiscens in Latin and not Cryptolepis buchnani (the Latin word is actually a derivative of ‘milkweed’) as believed by many scholars.
| White Saariva | Black Saariva | |
| Sanskrit | Anantmool, Sharda, Gopaballi, Svetlata, Gopakanya, Asphota, Kashtha Saariva. | Krishna Saariva, black root, kalapeshi sandalwood, Saariva, kalaghantika, subhadra shyamalatha. |
| Hindi | Gaurisar, Anantmool, Dudhaud, Chudhaud, Hind Salsa, Gauraiya. | Kalisar, Kali Dudhi, Shyamalata, Bengali, Saariva. |
| Marathi | Uparsal, Lahan Kawdi, Uparsari, Dudhmuli. | Mothikavadi, Kalikavadi, Upalsari. |
| Gujarati | Dhuribel, Kagdio Kunder, Kapoorimadhuri, Usvon, Dholi Upalsari. | Black Upalsari, Dhuribel. |
| Bengali | Infinite root, Saariva. | Blackness, milky, bell. |
| Punjabi | Infinite root! | Anantamal. |
| English | Indian Sarasaparilla. | Indian Sarsparilla. |
| Latin | ‘Hemidesmus indicus. | Ichnocarpus frtissans. |
Many people also call white Saariva camphor madhuri and gorakh ganja. But in reality, camphor madhuri or camphor herb and gorakh ganja are completely different herbs.
There are many types of roots available in the markets under the name of infinite root. It is accompanied by a mixture of coconut roots, camphor madhuri, gorakh ganja etc. roots. We should test by fragrance and take the real Saariva.
It occurs abundantly in the Punjab and northern Hindustan from Banda to Awadh and Sikkim and in the south from Bombay, Konkan, Kathiawar and Travancore to Ceylon on stony, sandy, red clay hilly soil in muddy soil.
Kali Saariva is found mainly in the Himalayas, Bengal, Bihar and South Konkan.
This is a plant of Lata caste. There is only one very long crooked root in a vine. The root of Kali Saariva is longer and blacker than the original white one. The root of white Saariva smells like camphor kachari or sandalwood, very less or not in black. The upper bark of the root is somewhat reddish in colour. Charpari with some sweetness in taste is not as much Krishna Saariva as it is Saariva Mool. By breaking the fresh root, milk comes out in white. The root bark of both is visible with torn lines on drying. The lower part of the bark is woody, slightly yellowish, very strong. As long as the root of white sorghum remains fresh, only then it has fragrance, when it becomes old, the fragrance does not remain. This fragrance is present only in the upper part of the root. It does not occur in the inner woody part. That’s why its fine roots or bark of knotted roots are taken for medicinal purposes. The reason is that due to the combination of the aromatic oil in it, the specific medicinal action is proved.
From the stem or branches, twine to small finger like bushy, rough, gray and black colored branches come out spreading all around. On these there are fine soft roy of white or brown color. These branches (vines) are very strong. Rural men often tie bundles of grass etc. with this. It does not break quickly after breaking and when it breaks to some extent, white, shiny, thin lines are visible inside it, in which milk comes out. Milk usually does not come out of the branches of Krishna Saariva like this. These branches are from 5 to 15 feet in length. The bark of Krishna Saariva vine gets uprooted every year. And when old it shines like a lotus.
The whole creeper of Krishna Saariva and the root or root bark of White Saariva are mostly used as medicine.
Leaf – The length and width of the leaves varies. However, the leaves of Shvet Saariva are somewhat like Jamun and Meshshrungi leaves, 2 or 3 inches long and ½ to 1½ inches wide. The leaves of Krishna Saariva are like Kaner leaves but are thinner, wider and sharper than them. Leaves are 5 to 6 inches long and 1 to 3/4 inch wide. The letter which is longer is usually thin and long pointed. The leaves of White Saariva are smaller than those of Krishna. There are white lines on the leaves of both the mustard. These letters often appear in front of the vine. The leaf stalk of white is very short, the stalk of Krishna is 1 inch long. Many vines of both have long, round, pointed leaves and many have leaves without points. Milk comes out by plucking the leaves, but very little in Krishna. The smell of the leaves is pungent and the taste is acidic astringent.
Flowers – In white Saariva, small clove-shaped flowers with 5 petals of blue tinged purple hues come in autumn, and in Krishna Saariva, usually in spring, especially in spring, slightly larger (slightly larger than the above flower) with clove-shaped flowers. Flowers arrive. In some places, even in the summer season, they are seen in white Saariva and their fragrance is like sandalwood. The flower stalk is 4 to 6 inches long and emerges near the petiole. There are hairs of almond color on its front and the flower leaves with pointed diseases look bunched one above the other. These flowers usually develop in the afternoon. The flowers wither as soon as they are plucked. The flower outer sheath is of five small petals. These petals are covered with purple hairs. The lower part of the petals in the anther is somewhat circular, with a shade of purple from inside and blueish from outside. It has 5 stamens and 1 pistil. ,
Legumes – Legumes in Shvet Saariva are small and usually planted in Kartik Margshirsh and on drying in Falgun or Chaitra month, crackle and burst and the seeds inside get scattered.
In Krishna Saariva, 2-2 large pods emerge only near the leaves which are facing each other. These usually come out in Vaishakh Jyeshtha, ripen till Bhadrapada and when they burst after drying, they fly in the air with different cotton balls along with the seeds. These beans are bent like the horns of a ram. Due to this confusion it is called Medhasingi by some. The upper surface of the pod is flat and has a vertical line on it and there are white hairs on top. These pods are 3 to 5 inches long and 1 to 1. inches wide. In the first raw condition, green color and on ripening deep purple color, like the horns of ram, are bent inside. Inside the pod, there is a red colored line in the middle part, from which side many white, sticky flat seeds are covered with a kind of cotton. After ripening and bursting in this way, the same cotton is seen flying here and there along with the seeds. In the raw condition, the smell of both the pods of Saariva is strong and the taste is astringent.
Seeds – Its seeds are 4 inch to 5/16 inch long and flattened on one side. In condition of white color, on ripening, they become brown or black edged. Let it slope to one side. (Utdar) and on the other side are uplifted. On the side where they are raised, a vertical raised vein and a pit is visible in the first part of that side. The useful parts of this plant are root, leaves and milk.
White Saariva – Soft, sweet, thankful, heavy, aliphatic, bitter, fragrant, Varnya (radiant), Kanthya (voice purifier), Breast – Shodhani, Dahprashamni, Balya, Shothaghna and Tridoshamak and leprosy, condu, fever, body odor, Mandagni, Breath, Kaas, Aruchi, Blood disorder, Diarrhea (Pittaj), Trisha Daha, Raktpitta, Pradar, Vatarakt, Updanshaj Vatdosh, Sandhivat etc., mango, poison and pardvikar are killers.
Krishna Saariva – Vata, Pitta, Blood disorder, Aruchi, Vamana, Antipyretic and Coolant, Semen enhancer, Thickening of feces, Antiphlegmatic etc. and the rest of the properties are similar to that of White Saariva. It is sweet and slightly bitter in juice, cold and bitter in semen, astringent and shukra by effect, that is, the main elements of earth and water are found in it.
Its different functions in the body – Due to the development of blood vessels under the skin, blood circulation starts in the best way. Thereafter the stool is thrown out. Due to which the color of the body starts improving and due to this its work is better and sedative in small leprosy. Using it with sulfur chemical works very well.
It is especially useful in syphilitic skin diseases. Its and Chopchini’s work on various syphilitic nuisances is creditable. In fact, if no anti-syphilis element is found in it, even then it is successful in this work with chopchini, manjishtha, barberry etc. in its effect. Its effect is especially in the second stage of syphilis, when the patient is given Ashtamurti of Parad Kalpa, Vyadhiharana etc. medicines, which usually destroy the poison of syphilis. But the distorted heat persists. It brings the increased perverted heat in the blood to the same condition without cooling it completely like asparagus etc. / The work of blood cell formation and improvement in the body is done by its yoga. Therefore, it also works well in panduroga caused by pitta, rakta dosha or subdanshadi disorders. In such condition, it is used along with iron, silver, shilajit etc. From this point of view, it is very beneficial for small children and women.
Anti-inflammatory action – Quenching inflammation or bile is one of its main functions, and from this point of view, it is used almost everywhere in medicine. Saarivadigan (Vagbhat Sutra 15-11), Drakshadimanth (Vagbhat Ch.), Mahatiktakaghrit (Bagbhat) and Chandan Bala Lakshadi Tail (Yogarlakar) etc. in Siddha experiments, the causative action of Saariva seems clear. It especially suppresses blood inflammation. Due to this, peace of burns like eye irritation, skin irritation etc. is achieved quickly by its use. If there is a burning sensation in the hands, feet and eyes etc. in case of fever, then a decoction is prepared by mixing poppy seeds, licorice, white sandalwood and red sandalwood with it, which is beneficial quickly.
Fever every action – Although it is not actually fever, but due to improvement in cutaneous blood circulation by its combination, sweat glands get strength and exchange process of sweat and skin improves. It is indirectly used in fever and febrile inflammation due to the removal of internal defects through sweating. In the same way, due to the expulsion of urethral defects, there is peace in the fever. It is said from this that its best action in blood fever, it suppresses acute blood disorders. In almost all fevers, using this along with anti-inflammatory experiments gives benefits. Sushrut has included infinite root in each yoga useful for all three doshas in the treatment of fever.
It has been seen in typhoid that the symptoms which often occur like unconsciousness, delirium etc. do not occur, if it is used in its treatment from the very beginning. Similarly, if other heterogeneous fevers are blood-metallic, then it is of best use. In such a condition, it purifies the blood by digesting the raktastha ama dosha and suppressing the poison. Due to which the symptoms of delirium, unconsciousness, strong thirst, confusion etc. do not occur and the fever gradually improves. That’s why it is a main substance in Patoladi Kwath. Similarly, it has a very beneficial effect in explosive fevers as well.
The anti- Cholesterol properties in it are not of the excellent form like Adusa, but of a mild nature. In case of fever or obstruction of urine in any condition, by its effect (due to predominance of earth and water elements in it) it removes heat-related disorders and purifies excreta.
Varnya and kanthya functions – By improving the discolored color of the skin due to cold semen, it nourishes it well and creates blood in it. Therefore, it is one of the main medicines among the complexion-correcting medicines. And this use of it is done only by internal consumption. If throat deformity is caused due to pitta dosha, then consuming proven kwath mixed with licorice, dry grapes, kateri, sugar candy etc. is beneficial.
Stomach- Strengthening action- If the digestion process is not good due to the weakness of the stomach, there is no appetite and indigestion etc., then it improves it with its sweet, bitter and strong properties, increases the power of the stomach. Being heavy, it stays in the stomach for a long time and helps in proper secretion of digestive juices from the bile producing bodies. Its action is not in a stimulating and pungent form like Trikatu or Ajwain, but in a mild manner by providing strength to the bile-producing (digestive rasotpadak) bodies.
It also works well in the above way in the case of agnimandya and biliary dyspepsia. Due to this, not only the stomach but also the opposite pancreas also gets strength. There is proper extraction of bile. By destroying the intestinal defect or disharmony, there is an increase in appetite, loss of appetite and the best remedy for diet. And by this, there is better chemical work in the form of improvement in digestion, absorption and nutrition activities.
It nullifies the pungency and acidity of increased pitta. Therefore, it has a good effect in bile-borne vomiting.
Carminative function – This blood destroys metallic vatadushi, due to which it works best on disorders like arthritis, rheumatism, blood pressure (blood pressure) etc. In such a condition, it is consumed with Shilajit. Due to this quality, it has been included in proven experiments like Saarivasav, Arvindasav, Balatail etc.
In Sandhivat, due to the accumulation and circulation of Puya (Radha) in any place inside the body, the pain becomes intense. In such a condition, it stops the puya construction work and benefits in sandhivat. Similarly, in rheumatism, it benefits by taking out common poison from the urethra. Therefore, due to these properties, it is very useful in common toxic disorders like Vatarakta, Aadhyabat, Urustambha, Shirshashaal etc. There are very few other drugs that can match it on syphilitic vata disorders.
It is necessary to consume it for some time on the above disorders. Then its benefits are seen.
Diarrheal and urinary function – Ayurveda has not told its direct use in the treatment of urinary tract or urinary retention. But modern doctors greatly appreciate its diuretic properties. In fact, raining urine is not a special function of Anantmool, its special function is to remove inflammation caused by blood disorders. Therefore, it removes the research that is created due to blood deformity in the urine bodies (kidneys); And at the same time urine purifies the pitta dosha, due to which the urine becomes clear and the internal disorders come out with urine. More than this, it does not do any other work in relation to urine. Keep in mind that in the case of nephritis, the pain in the kidneys gets intensified by the use of other alkaline medicines. But by using it the work gets done easily. In such a condition, its use along with Punarnava is very beneficial. Not only inflammation of the pelvis, but also inflammation of the whole body. By using it with Punarnava, the disorders of tajjanya urine, urine deficiency etc. are removed. If the urine is bloody, it is given along with bunions. And if there is research containing inflammation in the urethra, then giving its font with Giloy, cumin and sugar candy is beneficial.
On the disorders of Raktpitta, Raktapradar, Raktatisar, Raktamitra etc., it stops the outflow of blood by offering blood with its properties and giving strength to the blood vessels.
It is also included in the 10 important medicines that Charkacharya ji has enumerated, which are important for the treatment of defects in women’s milk. It purifies milk by removing the root causes of spoilage, heat, intensity of bile, irritation of the rasvahinis etc., and increases it with its mild, sweet, strong etc. properties. If a milk-drinking child develops bilious disease due to the said milk disorder, then it is beneficial to use it in mother’s medicine and as a paste on the breast.
Leucorrhoea and vaginal curative action This is an excellent working medicine in women’s leucorrhoea. Severe leucorrhoea as a result of syphilis or gonorrhea, delivery before full term, death of the infant at birth, or death of the infant at birth due to boils, rashes, burns, ulcer like ulcers etc. In case of diseases etc., preparing and drinking decoction or font mixed with both Saariva with rasna, padyakashtha and licorice is beneficial. Or prepare a font of only Saariva and mix milk and sugar candy in it and consume it regularly. It is necessary to give this Kwath or Font to the woman in advance, or it should be given from the time of pregnancy till the time of delivery, only then there is complete benefit and the child becomes healthy.
Anti-toxic action- It easily calms the poisonous inflammation with its sweet, bitter, cold etc. properties. That’s why Anantapool is also used along with other substances in Ayurvedic ‘Agad’, which is prepared on the bites of poisonous creatures like scorpions, wasps etc. It is also put in the causative plasters of bites.
Consuming the powder of Saarivamool with honey in Arthritis or by rubbing it with water inside the pitcher and heating the pitcher a little, and consuming this curd, sweet or sour, in diarrhea, the aloe made by it is beneficial. In case of rat poison, after drinking it mixed with water, on all kinds of poisons, by instilling decoction made from it in the eyes or by instilling honey mixed in this decoction, in eye diseases, mixing bividang with it, grinding it and applying it to the eyes. Drinking a decoction of these two cures goiter, indigestion etc. In pain, making decoction mixed with it and mixing sugar candy when it cools down, drinking it in gall fever, drinking it after filtering it with adusa leaf, in vertigo,By tying a red cloth with the root of Semal and getting it worn in the Skanda Pramar of the children, by making a decoction of it, in the saliva or Kafnav; And with this, making a decoction of jasmine and kaner leaves, washing the ulcers or grinding it with water only and applying it is beneficial in the purification of ulcers.
Grinding the leaves of equal part of the cardamom with its leaves and keeping it under the teeth, dental disorders like toothache, dental worm etc. are destroyed and the teeth become strong. Saariwadi Vati (Bhaisjya Ratnavali) is best for ear diseases.
Note – For medicinal work, the root or bark of the root should be taken within one year and the leaves should be taken fresh.
It is hot and dry in the second grade. Its root is beneficial in diarrhoea, antipyretic, diuretic and migraine, joint pain, syphilis and leprosy. Its leaves are beneficial in vomiting, cold, wounds and white leprosy. Its fresh wooden toothache is beneficial on toothache.
It is beneficial to ascites and semen enhancer. It is beneficial in vaginal diseases, vaginal wounds which are caused due to excessive bleeding and uterine disorders, gonorrhea, paralysis, cough and breathing. It is also beneficial in diseases of the brain and liver.
It is diuretic, diaphoretic, appetizer, stimulant; Khagdoshhar and blood purifier. Its urine purification religion is very clear and perfect. Its font (root powder mix 1 pint in 2 ounces of hot water and filter it after 2 hours, quantity – 5 tola, give every one hour. Drink all fonts in a day) increases the amount of urine three times, quadruples. ; Urine bodies don’t even feel any pain. Its sweating religion is simple, yet appropriate. In this, the stimulatory religion of life exchange action is very superior, the appetizing religion is of the middle category. Their religion increases with the combination of Gudich and aromatic substances.
Its font is excellent in preventing kidney inflammation and compressing them. Its action is also very good on the skin. By giving this paste in fever, sweat and urine come out properly, due to which the heat of the body decreases, digestion process increases. In fever, it is necessary to mix propellant with it, because it itself does not have antipyretic properties. This is the best beneficial in blood-defective Pandu. It is very beneficial in pediatric diseases. If the child is dying due to rickets, giving it along with bividang gives a lot of improvement. For the health of the body, it should be sprinkled with warm milk and sugar for years. If there is conjunctivitis, there is inflammation in the eyes, there is cobweb inside, then by applying its fresh milk, a lot of water comes out in the beginning and then after cooling down, the inflammation goes away.
Modern research has revealed that Anantmool has a direct effect on the blood. And from the point of view of blood purification and metal modification, it is more useful than American Sarsaparella. It is useful in loss of nutritional power and also on syphilis, rheumatism, snakebite and scorpion bite. It has a good effect on the stomach, bladder and nervous system.
Doctors and Vaidyas of Tamil Nadu give its powder with cow’s milk up to 4 ounces in urine and stone disease.
Iodine of potassium is mixed in its decoction on syphilis disease, it gives quick benefits.
In the absence of white and black sariya, sugarcane is taken.
Saariwadi Kwath – 3 tolas of Saariva root, jokut and cook in one seer of water. Blood disorders like itching, nausea, leprosy, etc. are cured by consuming sugar mixed with sugar candy when the eighth part is left.
Cook the thick powder of both types of Saariva mool, Indrayanamool and Patol with 32 tolas of water for 6 mashes. Sieve after remaining a quarter (4 tola), consume 4 tola in the morning and 4 tola in the evening mixed with a little pure Google and Peepal powder. This decoction is the best blood purifier, diuretic and sweat.
See Yogaratnakar etc. for the formulations of Saariwadi Kwath on Visarp, Ba Rog, Kafjwar etc.
Saarivadyavleh – Grind 5 seers of Saria root and cook it in 32 seers of water. Sieve when 8 seer of water remains. Then cook that water and thicken it, when it becomes thick, then mix 2-2 tola powder of Giloy, Satavar, Vidarikand, Jeevak, Nisot, Mundi, Triphala, small cardamom and chopchini and take it down. On cooling down Keep the honey you got safe.
Quantity – Consuming 1 tola with milk cures syphilis, gonorrhea, urinary tract, pramehpidika, other blood-defective disorders and all mercury disorders. Strength, character and fire increase.
Saarwadi Ghrita – Take 4-4 tolas of both Saariva root, Kamal, Lodhra, and Neelofar and grind them all with betel leaves. Mix yak kalk and 8 seer milk in two seers ghee and cook it on Mandagni. Sieve it when only ghee is left. By giving its nasya, blood bile is destroyed. It is also useful in arthritis, leucorrhoea, burning sensation of hands and feet and body.
There is a use of ‘Saarivadi Ghrita’ in Vagbhat, massaging which removes all planetary disorders.
Saarwadi oil – Saarivamool, licorice, resin and wax 4-4 tolas castor oil 2 seers and cow urine 8 seers mix together and cook. Filter it when only oil remains. Its massaging removes gout.
See the use of other ‘Saarivadi oil’ in the Gardangraha book.
Saarivadi Churna – White Saariva root 10 tola, Rasna, Satavari Chopchini 5-5 tola, Mulathi, Giloysat, Hard 2-2 tola, Vayvidang and Kuth (Kushtha) 2-2 tola, Clove and Nagarmotha 6-6 Mashe, Make fine powder of all these.
Quantity- 2 or 3 mashes, taken with milk in the morning and evening, is beneficial in gonorrhea, chronic fever, weakness, lethargy, blood disorders and constipation.
Saariva sorbet – After boiling 11 seers of water, mix 10 tolas of grated Saariva root in it, keep it covered for four hours, then filter it and mix two and a half seers of sugar in the water, cook it on a low flame. When the sherbet syrup comes, fill it in the bottle and keep it.
Quantity – Half tola to 2 tola mixed water, consuming in the morning and evening is beneficial for all types of blood disorders.
Boil half a seer of sorghum root in 5 seers of water, filter it when half is left and mix bottle extract of Bedmush and 1 seer of sugar candy to make a perfect sugar syrup.
Quantity – Taking up to 3 tolas with fresh and hot cow’s milk at both times is beneficial on blood disorders like syphilis.
Grind 10-10 tolas of Saarivamul and Vaybidang and cook in 1 seer of water. When about 1 tola of water is left, filter it and mix 1 seer of sugar candy or sugar in it, cook it on a low flame. When the sugar syrup of one wire comes, take it down, put 6-6 mashes of ‘hypophosphate soda’ and ‘hypophosphate calcium’ in it, mix it well and fill it in the bottle. This is ‘Balamrit Sharbat’. If given to children 3 or 4 times a day for 2 to 6 months according to their condition, digestion power increases, juice gets purified and rickets is cured.
saarasaaparela – anantamool aur manjishthaadi kvaath ka choorn 20-20 tole lekar 4 ser. jal mila pakaaven, 1 ser rahane par chhaan len . pun: use ubaalen jab aadh ser rah jaay tab usamen ekstraikt saarsaaparila likvid aur rektiphaid spirit 5-5 tole tatha potaash aayodaid 5 maashe mila botal mein bhar rakkhen . maatra – 3 se 6 maashe tak, duguna jal mila din mein 3 baar sevan karane se khaaj, khujalee aadi rakt vikaar aur upadansh ke vikaar door hote hain. Sarsaparella – Anantmool and Manjishthadi Kwath’s powder by taking 20-20 tolas 4 ser. Cook with water, filter when 1 seer remains. Boil it again when it remains half a seer, then add 5-5 tolas of extract sarsaparilla liquid and rectified spirit and 5 mashes of potash iodide and fill it in a bottle.
Quantity – 3 to 6 Mashes, mixed with double water, consuming it 3 times a day cures itching, itching etc. blood disorders and syphilis disorders.
Saarivadyark- Saariva half a seer, and Murndi, Majith, Satyanashi’s almanac, Bad’s Jata, Peepal’s Jata, Patha, Jawasa root, Coriander, Fennel, Red Sandalwood, Cedar, Unnao and Gavjawan 20 – 20 tolas, cut all into two parts Mix 10 tola jaggery and 32 seer water in one part and keep it soaked for two days. Then, by straining the extract, mix the remaining second part and 10 tola jaggery in that extract, after soaking it for two days, again draw the extract up to 8 seers and keep it safe in bottles.
Quantity- Mix 1 tola honey in 2 tola extracts and drink. Appetite is good, blood is purified, and the body remains healthy and perfect.
Saariva Tincture and Aaswarishta – After grinding the root of good ripe and fresh Anantamul, mixed with quadruple alcohol (40 or 60 percent), put it in sugar or glass paper and keep it for 7 days. Shake it in between, so that the infinite essence gets mixed properly. If it is winter or rainy season, then it is necessary to give some heat to the vessel. After the period, filter this infusion with a bannat or flannel sieve and fill it in a bottle.
Dose – By mixing water for 4 to 8 months to the elders and consuming it, all types of blood disorders and religious diseases go away. It is also beneficial for cough, bronchitis and laryngitis and syphilitic gonorrhea. See the use of its infusion and Arishta in the texts.
Sariya Sattva – This Sattva is extracted in the same way as Giloy’s Sattva. It has all the properties of Saariva. Quantity – 2 to 6 ratti.
Saariva Tea – Take the powder of fresh bark of Anantmool and put it in a cup of 10 tola floured water for 6 months, cover it. Filtered after 15 minutes, mixed with milk and sugar as required, and consuming it regularly in the morning removes the accumulated defects in the blood and gives health. Or – Anantmool powder 10 tola, fennel powder 5 tola and cinnamon powder 10 mashes together and fill it in a bottle. Make tea according to the above method and drink it.
Grind equal parts of Anantamul, Kaunch Beej, Madjith and Gokhru, roast them with a little ghee and fill them in cans and make tea in the above way and consume it, along with the above benefits, the body becomes healthy and strong. In the case of anulom decay, giving a quantity of oral ashes along with this tea gives special benefits.
Burn the metals made of Saariva Yoga – Gold, Bang or Yashad by throat-throating and extinguishing them in the swaras of Anantmool (Pt. Bhagirath Swami who says to extinguish two hundred times.) Better than 8 or 10 times putting Gets ready. Which removes disorders related to blood, abdomen, stomach, bladder, bladder.
Put 1 tola of pure copper sheet or copper filings in the pulp of both Anantmool Panchang 2 parts and Kateri Panchang 1 part, do 7 kaprautis in Sarao Sanpur, give Gajpur twice, the best copper ash is prepared, which is free from cough, breath. Beneficial on colic, dysentery, chronic fever
On blood disorder – Take 5 tola of Anantmool and soak it in half a head of boiling water for two hours and filter the squeeze; Consuming 5 tola quantity 4 or 5 times a day cures blood disorders and skin disorders caused by Firang, Atshak etc. quickly. See other uses Saariva Sarsa Parila, Saarivadyarishta, Asav, Tea etc.
Urinary disorders – By crushing the small soft root of Saariva, in the banana leaf. Wrap it, put it in the ground of fire. When the top leaf gets burnt, take out the pulp inside and eat it with roasted cumin seeds and powdered sugar. Urine and semen related disorders go away by taking it in the morning and evening.
Its root 2 tola, Giloy fresh 1 tola and cumin roasted and manjith 6-6 months, put 10 tola of their jokut powder in boiling water and keep it covered for an hour. Then filter this font and drink it. In this way, by making a font and consuming it thrice a day, the urine becomes clear and all the related disorders go away. Or – Saarivasav, Ark, Kwath, Avleh etc. should be consumed.
Fever- It is mixed with root, khas sonth, nagarmotha and kutki, after proving Ashtamansh Kwath, drinking it cures all types of fever. The diarrhea gets cleared and the appetite increases.
In Pitnar, a decoction made of its root with lotus seeds is given mixed with sugar candy.
In acute feve – Take the powder of its original bark and eat it by keeping two pieces in a betel leaf. Only lime and katha should be applied.
Leucorrhoea etc disorders of pregnancy – After wrapping 10 tolas of fresh Anantamul bark in a banana leaf and cooking putpak vibhi, adding 2 tolas of white cumin, 10 tolas of fried onions and 20 tolas of sugar, grind them finely and get Goughrit in equal parts of all, daily. Consume 3 tola in the morning and evening for 7 days. After that make it again in the above way for 7 days. Consuming it in such a way for 41 days makes the body radiant by removing the heat absorbed in the body and purifying the metal and blood. Abortion, miscarriage etc. disorders do not happen.
The above benefits are also given by the consumption of only its astringent or font. See above its different functions in the body.
Syphilis disorders, scrofula, boils, etc – Give 2.5 tola cold decoction of its root or ice in the morning and evening. See above for specific usage.
Kamla – Its root bark, two mashes and 11 pieces of black pepper, grinding both with two and a half tola water and drinking it for 7 days, the yellowness of the eyes and the body goes away, and the nausea and fever caused by Kamla disease also ends. goes.
Vomiting – After evaporating its fresh root by potpak method, mixing a little bit of asafetida in it, grinding it fine and mixing it with good ghee, it is beneficial.
Burns or distorted heat – Roast Anantmool powder in ghee, consuming this powder with sugar for about 4 ratti to 1 masa for a few days removes the heat absorbed in the body. This experiment is best to remove the heat that gets accumulated in the body at the end of smallpox, typhoid etc.
Eye diseases – Rubbing its root in stale water or rubbing the ash of its leaves with honey after rubbing it with a cloth reduces eye puffiness.
The milk that comes out after plucking its fresh soft leaves, applying it to the eyes removes swelling and cobwebs.
The use of scripture ‘Saarivadi Varti’ (see Yogaratnakar, Bangsen and other texts) is beneficial in gallstone disease.
On leprosy (corruption) – two parts of its root, giloy, pittapapada, berries bark, kuda, bark, chirayata and dhawda mango, Adusa, Arjuna, bamboo, guava and lemon leaves 1-1 parts, collect all of them and give them a decoction. , And giving the steam of this decoction in the whole body is beneficial.
Snakebite – Grinding its root and feeding it with rice wash and rubbing it in the eye provides relief in snakebite.
Scorpion bite – Taking the root of Krishna Saariva in the hand and pulling it in the opposite direction (towards the bite site) from where the poison has entered is beneficial. If the root is dry, then rubbing it in water and rubbing it on the hands should be moved from top to bottom.
For hair growth – A man’s head and beard had lost hair in many places, and thin white hair used to grow in those places. He was given its original powder with water for 6 months daily. Within a month the disease was cured and natural hair started growing and growing. Dosage – 2-2 Mashe, was given 3 times a day.
Send us whatsapp / email for any purchase, medicine preparation, dosage intake, disease related queries of Adarak – Ginger. Its our absolutely free 24*7 medical helpline services)
In Sanskrit, adra means from wet to moist (ginger), this word has been coined for dry ginger, the same when it becomes dry or dry (shunthati) when it is called shunthi (sonth). Due to the formation of a type of volatile oil in dry condition, it becomes especially hot and receptive.
In ancient Arsha texts, its mention is found on the post. Not only this, almost every medicine powder, decoction, gutika, avaleh etc. has been used since ancient times. Still some see it as an object of some tropical region outside Asia (Hindustan), and say that from there it was brought to India. It is regrettable that despite it being produced in India in abundance, like many other substances, many of its preparations like tincture, ginger, essence ginger, pulp ginger etc. are being prepared in Europe and America from the ginger grown in Cueva, Jamaica etc. West Indies. We come here to treat people. From here too, ginger or dry ginger is sent in abundance to countries like Europe every year and many of its preparations, even ginger sherbet and marmalade, are made here. The wild ginger grown in the forest is different.
Sanskrit – Ardraka, Shrangber, Katubhadra, Katuskat etc. Hindi – Ginger. Marathi – Aalen Gujarati – Aadu, Ardu. Bengali – Ada. English – Ginger Ruth Latin – Zingiver officinalis.
It is mostly found in watery and flowing land of tropical regions. Generally found everywhere in India but especially in abundance in Madras, Cochin, Travancore, Bengal, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. It is widely practiced in many villages of Bombay province, Surat and Ahmedabad districts. It can be produced almost in all these places where potato, radish, sweet potato etc are grown.
It does not have any seed. Its tubers are buried in small pieces like potatoes. With the help of fertilizer, water and sunlight, plants emerge and gradually grow one or two feet. The knotted branches in the roots are called ginger. Its leaves are like bamboo leaves but somewhat smaller in size. Flowers rarely come on it. If it is not dug in Ashwin or Kartik, then sometimes small flowers of blue color or some berry-like color come, but very few which are seen only occasionally.
It is cultivated in the month of Chaitra and Baisakh, and it is dug and selected in Ashwin and Kartik. If it is not dug at that time, its leaves remain green till the month of Magha. As soon as the month of Magh begins, the leaves wither and start drying up. At that time, farmers dig it all out from the fields. At the time of digging, fiber and non-fiber ginger are separated. The de-fibered ginger is tender and tastes great.
It is cool, sweet, pungent, beneficial to the heart and throat, piercing (document), fire-lamp, dry, appetizing, seminal, digestive and swelling, anorexia, tax vat, cough, breathing, afra, fecal matter, van It is the destroyer of colic, throat, head and chest diseases. It is also beneficial for heartburn, arthritis and ascites.
It is always healthy to eat pieces of rock salt sprinkled on it before meals. This eliminates loss of appetite, clears the tongue and throat and increases appetite. This is why it is said that – ‘Bhojanagre sada patham lavanardrak bhakshanam.’
It increases the digestive juice in the stomach, hence its consumption helps in ripening of food in a better way. Even though it is a substance that expels air and feces, it definitely has some receptors. Digests and thickens the stool by closing unripe and thin stools. That is why it is also beneficial in diseases like diarrhea, flow etc.
If it is consumed in proper quantity, then the signs of old age which come in most of the people in young age, can never come. And the food is digested well, due to which the juices, blood etc. metals start increasing gradually, due to which the body becomes healthy and beautiful. That is why Ayurveda has called it long-lasting, It gives strength to the pancreas, liver and all the digestive institutions. It is given in proportion to other medicines to reduce wind and phlegm.
Consuming honey mixed in its swaras causes problems in breathing, cough, phlegm disorder, dyspepsia, pratishya and also in vataj andavaridhi; Mixing lemon juice in intestinal dyspepsia and indigestion; Mixing sugar and drinking it after heating, drinking old jaggery in cold and cough, in all-round inflammation and cholelithiasis; Tulsi juice in new phlegm and pratishyaya by mixing misro and honey, Mixing honey and peacock feather ash and giving it in vomiting; Got rid of head pain due to giving nasya; Grinding carom seeds and rubbing it on the body causes pain; Consuming Triphala and jaggery helps in treating jaundice and mixing Trikatu and Saindhava salt helps in typhus; There is special benefit when there is phlegm in the throat of the patient.
Dropping only two or three drops of its juice in the eyes provides relief in eye pain, taking Nasya in feverish unconsciousness, humming something and putting it in the ears helps in ear pain, and taking appropriate quantity of betel leaf provides relief in reed pain.
Always keep ginger in the mouth on the nuisance of vermilion poison, eat it mixed with bread or eat it little by little with salt for 7 days, it is beneficial.
By applying finely ground ginger, the split ends of the hands and feet completely disappear; using kanji and rock salt along with it is beneficial in rheumatism. Prohibition of consuming ginger – in leprosy, pandu, urinary tract, biliousness, fever, burning and ulcer disease and those with bile or hot nature, should not consume it without any need in summer and autumn, because in such condition and time it causes bile There is a possibility of harm to the body due to outbreak of cough and destruction of cough.
But Ayurveda also says that consuming ginger with jambhiri lemon and rock salt purifies the mouth and cures dysentery, biliousness, ulcers, urinary diseases, asthenia, fever, burning sensation and bile in autumn and summer. Is. Its remaining parts are similar in properties to dry ginger.
It is aromatic, stimulating, illuminating, appetizing, reddening and digestive. With external use it is a nerve stimulant and neuro-expander.
Ginger relieves stomach upset and stimulates the bowels. That is why it has received so much importance in Indian medical sciences. Many medicines are made from its mixture in Indian and British pharmacology. This chamber penetrates the air and comes out.
In a place called Payanur in Malabar, its fresh juice is considered beneficial in dropsy and diuretic. About 3 such cases have been seen in which giving it medicinally has been beneficial. By giving this, there is also benefit in the swelling of the stomach. But it was not useful in heart disease and kidney disease (Bright’s disease), rather its use worsened the patient’s condition. (Col. Kirtikar and Major Basu).
In English dispensaries, its syrup and tincture are used for digestion, digestion and gas relief.
Some scholars say that the essence of ginger destroys the power of glass (lead). Jugglers soften glass by quenching it in its juice. And then chew it in the mouth, but do not let it go into the stomach. Many people first eat ginger and then chew the glass with their teeth.
Quantity – Its juice should be given from half tola to 15 tola and powder should be given from 5 ratti to 15 ratti.
Ardrakavaleh – (a) Take 1 seer of ginger juice, add 1 pav of old jaggery in it, make thin syrup on low flame. Then mix 6-6 pieces of fine powder of Taj, Patraj, Nagkeshar, Choti, Cardamom, Clove, Dry ginger, Black pepper and Peepal in it. Quantity – 1 Masha to 1 Tola. Consuming it relieves shortness of breath, cough, heartburn and loss of appetite.
(b) Equal parts jaggery in 2 seer juice of ginger and fine powder of coriander, caraway, iron ash, cumin (black), cinnamon, bay leaf, cardamom and motha. Cook the mixture on low heat till it is mixed and keep stirring it with a ladle. Take it off when it becomes like an awl. Consuming it in proper quantity is beneficial in cough, piles, fever, pinus, vigola and rajayakshma.
(c) Mix ginger juice 1 seer, jaggery 32 tola and bijora lemon juice 16 tola and cook on low flame. Once the syrup is thin, add cinnamon, bay leaf, cardamom, dry ginger, chilli, popal, triphala, dhamasa, chitrak, piplamool, coriander and both cumin seeds, 1 tola of each great powder and take it down and keep it aside. Its use provides relief in loss of appetite, caries, jaundice, jaundice, swelling, cough, shortness of breath, dyspepsia, stomach diseases, gout, spleen and colic.
(d) Ginger Mix equal parts ghee and jaggery in pav kalk (first fry ginger kalk in ghee, when it turns red then add jaggery syrup to it) prepare avaleh. Consuming up to 1 tola quantity cures anorexia, indigestion, flatulence, mango growth and phlegm growth. This Avaleh can be made with sugar in place of jaggery, but for pregnant women, it is better with jaggery only.
Humid section – Grind 1 seer of ginger and fry it in 32 tolas of ghee. Then mix 1 seer of sugar in 2 seer of cow milk and cook. When the thick sugar syrup rises, add 4-4 tolas of the above-ground roasted kalk and 4-4 tolas of fine powder of Peepal, Piplamul, Chilli, Dry ginger, Chitrak, Byvidang, Montha, Nagkeshar, Cinnamon, Cardamom, Patraj and Kachoor. Consuming 1 to 4 tola daily in the morning is beneficial in diseases like cold, udard, rajayakshma, raktapitta, kaas, breath, anorexia, vagola, udavart, swelling, worm, Kandu etc. Gastric fire and semen etc increase.
Adrak Pak – Peel the ginger and grind it on a stone (do not grind it very finely), then fry it with Goughrit in a strong vessel of iron or clay. After that add jaggery in equal quantity to ginger and cook on low flame, keep stirring with a ladle. After it becomes pure and cools down, add powder of dry ginger, cumin, chilli, Nagkeshar, mace, cardamom, cinnamon, leaves, peepal, coriander, black cumin, peepal root and vayabidang. Consuming it daily in the quantity of 2 tola helps in getting rid of asthma. It is beneficial in memory loss, vocal disorders etc. See special recipe in ‘Brihat Paksangraha’.
Wet Ghee – Cook ginger paste and fresh Ghee both in ginger juice. Once the ghee is ready, filter it and keep it aside. This ghee cures flatulence, heartburn and all types of stomach diseases.
Murabba Moisturizer – Peel 1 seer ginger and crush it thoroughly with a sharp stick. Then dissolve slaked lime in water and put ginger in it. After two days, take it out and wash it with clean water. Divide 5 tola blackberry leaves along with ginger and boil in 2 liters of water till it boils. Then wash the bottom 5 or 6 times with cold water. Put 1 seer of sugar candy in sugar syrup and keep rolling. When it becomes somewhat thick, take it off and mix it between two tolas of rose water and two tolas of small cardamom and keep it in a clean vessel. Beneficial in cough, breathing, indigestion and cold related diseases.
Or peel the ginger (remove the top bark) and cut it into small pieces and soak them in water. When it becomes half buff, then three times sugar syrup is made in it, put the said ginger in it. If you want to add saffron and cardamom, you can add it. Consuming quantity 1 tola regularly destroys anorexia by removing fire. Very beneficial for heart related diseases.
Sherbet Adarak – Mix half water and equal part of sugar in the juice of Andrakh and cook. When all the water evaporates and turns into a fine syrup, add the powder of saffron, cardamom, nutmeg, mace and cloves in small quantities and keep it in a bottle. Quantity up to 211 tola. Beneficial in bile, biliousness, breathlessness, cough, dyspepsia and loss of appetite.
Once the string becomes syrup, grind 2 pieces of saffron and mix it in the juice and take it off. Quantity from 1 or 2 mache to 2 tola. If taken in the morning and evening, it is digestive, interesting and appetizing. It is good for cold related disorders like cough etc.
Ginger syrup is very beneficial in children’s cough, cough, indigestion, pouring milk from the mouth etc.
Ginger Tea – Take 6 to 12 pieces of ginger, cut it into small pieces and cook it in a cup of water. When the remaining half pav of water remains, filter it, add cow milk and sugar and drink it slowly with a spoon like tea. It relieves phlegm, cough, cold, headache, back, rib and chest pain and opens the body’s sources by inducing sweating. It is also very tasty to drink.
Ginger vegetable or chutney – peel ginger into small pieces with a knife, add raisins, coriander, cumin, cardamom, rock salt, mint and black pepper, put them in a vessel filled with water, take them in the cold on fire and put them in a ceramic or glass vessel. Put the cooked lemon juice in it and fill it till the top. It can also be called ginger pickle. It is very tasty, appetizing, digestive, appetizing and gastric lamp. Consume it regularly with food.
Many people make pickle by adding things like mustard, red chilli, asafoetida, salt etc., which is very digestive, but not that tasty. Many people put ginger in vinegar to make pickle or chutney, which is delicious, but is extremely irritating and increases bile.
Ardrakadi Kaval Graha – Mix some rock salt and fine powder of Trikatu (dry ginger, chilli, peepal) in ginger juice and do Kavalgrahaan and keep spitting again and again. By doing this, the phlegm that is stuck in the heart, mouth, gills, carotid, sides and throat etc. gets released and the feeling becomes lighter and dysentery, fever, unconsciousness, sleep, breathing, throat, mouth, eyes, diseases, disinterest, gravity, inertia etc. go away. There are This should be done 2 or 4 times after considering its strength. It is especially beneficial for typhus.
Mix some jaggery in this essence and make pills. It is very beneficial in cold. These tablets are also given in pneumonia. It is a digestive enhancer. Quantity 1 to 3 tablets.
Cough, breath and catarrh- If cough is due to common cold or phlegm, then lick 10 or 20 drops of its juice mixed with the same amount of honey. In this way, give 4 or 6 times in the day and night. And drink some black salt mixed in its juice.
Burning ginger with salt and consuming it with honey helps in removing phlegm and helps in bad breath.
Consume the above mentioned ginger sherbet.
On breathing – Peel ginger and cut it into small pieces and put it in a pot of ghee and grind a quarter of rock salt from ginger and mix it, and add ginger juice to the same amount (fourth part) and mix it well in a handi. Close it and bury it in the amount of grains. Remove after one month.
Consuming quantity- 1 to 3 months in the morning and evening, it is beneficial in breathing and cough by removing phlegm. It is refreshing and energizing.
Ginger juice mixed with 1 tola juice of Sehund’s bark should be given to respiratory diseases in the morning. Give it only once a day during severe attack of the disease. Due to this, vomiting, purgation cures the disease. If there is no peace after using it once. Consume one quantity again after the month. After the end of vomiting, give rice paste, and follow a complete diet. Its use is prohibited for pregnant women, children and weak men. The patient who is not very weak, should be given a diet of Yavastva, Santhi rice, arrowroot etc. one day before consuming this experiment, and on the second day, after vomiting, purgation again; Give them diet.
If there is normal breathing, mix 30 to 40 drops of ginger juice with 1 tablespoon of ghee and a pinch of sugar and lick it 6 times a day and night.
Pratishyaya – 3 pieces of ginger, 5 pieces of black pepper, 6 pieces of sugar candy, boil 3 teaspoons of these in water, drink when one-fourth is left.
In fever –Mucoid fever or influenza, which often occurs due to getting wet in rain water at the time of change of season, excessive consumption of cold things, being in contact with the patient, etc. If there are symptoms like pain in the body, heaviness in the eyes and head, then use 6 mashes of ginger juice mixed with equal parts honey 3 or 4 times a day. There is benefit.
In areas where there is an outbreak of influenza fever, consuming a small amount of ginger in the morning and evening reduces the risk of getting it. Along with the above experiment, keep gargling with ginger juice to the patient suffering from this fever. See the above experiment ‘Ardakadikaval Graha’. There is a special benefit from this.
In case of typhus – when the patient is suffering due to accumulation of phlegm in the throat, then giving Adrak Swaras along with Trikuta and Sendhav Churna helps in expelling the phlegm and gives special relief to the patient.
In case of bronchial fever – or pneumonia, mixing 1 or 2 years old Ghee Camphor in Ginger Swaras, heating it and applying it on the chest gives immediate relief.
Indigestion, Mandagni, Aruchi and Acidity – Indigestion, only ginger juice should be given for a few days for 6 months.
In Mandagni and Aruchi, take ginger juice 5 pieces, lemon juice 3 pieces, cumin (roasted) and rock salt 1-1 piece, dry grapes 5 pieces and small cardamom seeds 8 or 10 pieces (this is total 1 quantity) and make a sauce. (See rest of the uses for ginger chutney, pickle, marmalade, etc.)
Acidity – ginger juice should be consumed mixed with equal parts pomegranate juice in 6 mashes.
Along with indigestion, if there are stomach disorders like acidity, colic, flatulence, gout etc., then consumption of ginger with Rasayana Kalpa method is very beneficial – On the first day, ginger with equal parts jaggery, on the second day with two pieces of jaggery, on the third day with 4 pieces of ginger and four pieces of jaggery, on the fourth day both 8-8 pieces, on the fifth day both 2-2 tolas and on the 10th day both 4- Taking 4 tolas on the 11th day, both 2-2 tolas were removed in the same order on the 20th day. Come to Ratti. If there is no benefit in 20 days, then in the same order, 20 days would have been consumed again. Consume only milk and rice in the diet. Drink only milk when you are thirsty.
Avoidance of navel and diarrhea – Fill ginger juice in the navel of the patient. First, grind the dried gooseberries on a wheel and make a strong circle around the navel and fill ginger juice inside it. The patient should remain lying down for about 2 hours. By doing this twice a day, severe diarrhea subsides and the navel comes on track.
A cloth should be soaked in ginger juice and placed on the navel. Keep changing the cloth after every 15 minutes.
Add a little warming substance to the above-mentioned ginger-sattva, soak a cotton swab in it and place it over the navel and tie castor or mahua leaves on top. This remedy is more beneficial for children.
In the above condition, the patient should not be given anything else to eat except milk or sago. Drink ginger juice in appropriate quantity 1 or 2 times a day in between, you will get quick relief.
Arthritis, head pain etc. – Mixing 1 seer of ginger juice with half a seer of sesame oil and massaging with it relieves joint pain.
Mix rock salt or asafoetida in ginger and massage.
If there is pain and inertia in the head, then there is a quick benefit from mardan its juice. If there is pain in half vial, collect ginger juice, honey and water in equal parts and make the patient lie on the bed in such a way that his head hangs down, drip this mixture 2-3 drops from the nostril of the painful side. . If the medicine does not reach the brain, it comes out through the mouth, then put it again at the same time. Similarly, reaching it to the head 3 or 4 times gives quick benefits.
Ear pain: Warming its juice a little and putting it in the ear provides instant relief from pain.
Chest pain: Consume 40 drops of its juice mixed with 1 masha of sugar candy.
Dental pain – pressing a piece of it between the teeth.
Swelling and ascites – Mix 2 tolas of old jaggery in 1 tola of ginger juice, consuming it in the morning and evening destroys edema, but only goat’s milk should be there in the patient’s diet. On ascites – On the first day, grind 5 tolas of fresh ginger and give mixed sugar mixed in its juice in the morning. On the second day, take out the juice of weighed ginger and give it to drink along with sugar candy. In the same way, gradually increasing the juice of 2 tolas of ginger per day, when it reaches 25 tolas, then reducing it to 2 tolas per day, the quantity reaches 5 tolas and suspend the experiment. If the swelling does not go away completely, then start again in the above way. The patient is required to live only on milk.
In case of indigenous water disorders (water from abroad) – Take 1 tola juice of ginger mixed with 1 quantity of jawakhar. Those who keep consuming it in proper quantity do not have disorders arising from changing water.
Bahumutra – Consuming it in the morning and evening after mixing sugar candy in its juice is beneficial.
On vomiting – Mixing onion juice in 1 tola of its juice is beneficial.
On Cholera – Tablets are made by grinding Arkamool and black pepper in its juice which are famous among the physicians.
Body Shaitya – When the body becomes cold in Sannipataka condition, then mix some garlic juice in its juice and massage it. If there is life left then the body will become warm again.
Ovarian growth (Vatajanya) – Consume it mixed with honey for 2 to 6 months daily in the morning for one month.
On hoarseness – make a hole in ginger, add a pinch of asafoetida in it, wrap it in a cloth and keep it in the earth. When the ginger is roasted and the smell starts coming out, take out the ginger, grind it and make a pill and eat it slowly.
Eye disease – burning ginger, grinding its ashes finely and applying it on the eyes is very beneficial for the cobwebs and discharge.
Intoxication of cannabis- intake of ginger removes flatulence and intoxication subsides soon goes.
Eliminating impurities, reducing symptoms, increasing resistance to disease, reducing worry, and increasing harmony in life

Discover Integrative Cancer Management at Nakra Ayurveda Hospitals and Herbals Pvt Ltd. Our holistic approach combines Ayurveda, Western Herbology, Aromatherapy, Nutrition, Yoga, and more with conventional cancer treatments. Dr. Nakra, a global Ayurveda advocate since 2001, has consulted patients in 120+ countries. Consult us for comprehensive ayurveda treatment care and overall well-being.
Nakra Ayurveda Hospitals and Herbals Pvt Ltd
ITI Road, Street #1 (Towards Sector 9), Sadanand Colony, Near HP Petrol Pump, Karnal, Haryana – 132001 (Bharat)
Email: dramit.nakra@gmail.com
Website: www.nakraayurveda.com
Medicinal Herbs of Ayurveda – Nakra Ayurveda deals in such diverse range of Medicinal Herbs of ayurveda and provides customized extracts to patients in form of oil, powder, tablets, kwatha etc.
©2023. Nakra Ayurveda Hospitals and Herbals Pvt Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Appointment on WhatsApp